This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
- 1: Getting started
- 2: Concepts
- 2.1: AWS Connector
- 2.2: Container management
- 2.3: Software update
- 2.4: Update manager
- 2.5: Suite connector
- 2.6: Local digital twins
- 2.7: File upload
- 3: How-to guides
- 3.1: Update software
- 3.2: Upload files
- 3.3: Back up and restore files
- 3.4: Create and update the containers `Desired State`
- 3.5: Monitor system metrics
- 3.6: Verify signed container images
- 3.7: Offline explore edge device
- 3.8: Build Yocto Image for Raspberry Pi
- 4: References
- 4.1: Remote connectivity configuration
- 4.1.1: AWS Connector configuration
- 4.1.2: Azure Connector configuration
- 4.1.3: Suite connector configuration
- 4.1.4: Local digital twins configuration
- 4.2: Container management configuration
- 4.2.1: Manager configuration
- 4.2.2: Container configuration
- 4.2.3: API Reference
- 4.2.3.1: Container Factory API
- 4.2.3.2: Container API
- 4.2.3.3: Metrics API
- 4.2.3.4: Software Updatable API
- 4.2.4: Container configuration as Desired State component
- 4.3: Software Updatable
- 4.3.1: Software update configuration
- 4.3.2: Software Updatable API
- 4.4: File Upload
- 4.4.1: File upload configuration
- 4.4.2: File Upload API
- 4.5: File Backup
- 4.5.1: File backup configuration
- 4.5.2: File Backup API
- 4.6: System Metrics
- 4.6.1: System metrics configuration
- 4.6.2: System Metrics API
- 4.7: Update Manager
- 4.7.1: Update Manager API
- 4.7.2: Update manager configuration
1 - Getting started
1.1 - Install Eclipse Kanto
Before you begin
The containerd Debian package is required. You can install it manually or run:
curl -fsSL https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/kanto/raw/main/quickstart/install_ctrd.sh | sh
Install Eclipse Kanto
Choose the Eclipse Kanto Debian package for your target device architecture from the ones available at the project’s GitHub Releases page. Download and install it via executing the following (adjusted to your package name):
wget https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/kanto/releases/download/v1.0.0/kanto_1.0.0_linux_x86_64.deb && \
sudo apt install ./kanto_1.0.0_linux_x86_64.deb
Verify
It’s important to check if all the services provided by the Eclipse Kanto package are up and running successfully. You can quickly do that via executing:
systemctl status \
suite-connector.service \
container-management.service \
software-update.service \
file-upload.service \
file-backup.service \
system-metrics.service \
kanto-update-manager.service
All listed services must be in an active running state.
What’s next
1.2 - Explore via Eclipse Hono
By following the steps below you will connect your first device to a publicly available Eclipse Hono sandbox using Eclipse Kanto. A couple of simple Eclipse Hono northbound business applications written in Python are provided to explore the capabilities for remotely managing and monitoring your edge device.
Before you begin
The location where the Python applications and utility shell scripts will run does not have to be your edge device as they communicate remotely with Eclipse Hono only. To run them, you need:
The quickstart applications and provisioning scripts
You can execute the script below to download them automatically:
mkdir quickstart && cd quickstart && \ wget https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/kanto/raw/main/quickstart/hono_commands.py && \ wget https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/kanto/raw/main/quickstart/hono_events.py && \ wget https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/kanto/raw/main/quickstart/requirements.txt && \ wget https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/kanto/raw/main/quickstart/hono_provisioning.shOpenSSL and the following SSL and SASL related libraries:
pkg-config,swig,libsasl2-dev,libsasl2-2libsasl2-modules-gssapi-mitandlibssl-dev, e.g.:sudo apt install openssl pkg-config swig libsasl2-dev libsasl2-2 libsasl2-modules-gssapi-mit libssl-devRequired Python dependencies to run the scripts
You can install them by using the downloaded
requirements.txtfile via executing:pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Provision the Eclipse Hono tenant and device
In order to be able to connect your device to Eclipse Hono, you need to have a dedicated tenant and a device instance
provisioned for it. Fill in the required empty environmental variables definitions in the hono_provisioning.sh, e.g.:
# The Hono tenant to be created
export TENANT=demo
# The identifier of the device on the tenant
# Note! It's important for the ID to follow the convention namespace:name (e.g. demo:device)
export DEVICE_ID=demo:device
# The authentication identifier of the device
export AUTH_ID=demo_device
# A password for the device to authenticate with
export PWD=secret
Run the provisioning script and you will have your Eclipse Hono tenant and device ready to be connected:
./hono_provisioning.sh
Configure Eclipse Kanto
Eclipse Kanto uses the /etc/suite-connector/config.json to acquire all the remote communication, identification and
authentication data to establish the remote connection. Update it with the following:
{
"caCert": "/etc/suite-connector/iothub.crt",
"logFile": "/var/log/suite-connector/suite-connector.log",
"address": "mqtts://hono.eclipseprojects.io:8883",
"tenantId": "demo",
"deviceId": "demo:device",
"authId": "demo_device",
"password": "secret"
}
Restart the Suite Connector service for the changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart suite-connector.service
Verify
To explore remote containerized applications management, we will use the two Python scripts to run, monitor and remove a simple InfluxDB container using its public container image available at Docker Hub.
First, start the monitoring application that requires the configured Eclipse Hono tenant (-t) and will print all
received events triggered by the device:
python3 hono_events.py -t demo
In another terminal, we are ready to spin up an InfluxDB container instance at the edge via executing the second application
that requires the command to execute (run), the Eclipse Hono tenant (-t), device identifier (-d) and
the full container image reference to use (--img):
python3 hono_commands.py run -t demo -d demo:device --img docker.io/library/influxdb:1.8.4
After the script exits with success, you can check out the new container running on your edge device via executing:
sudo kanto-cm list
Looking at the terminal where the monitoring application is running, you will be able to see all the events triggered by the operation.
To remove the newly created container, execute the same application script
only this time with the rm command and the identifier of the container to remove (--id), e.g.:
python3 hono_commands.py rm -t demo -d demo:device --id e6f7fbea-0e95-433c-acc7-16ef21b9c033
2 - Concepts
2.1 - AWS Connector
AWS Connector enables the remote connectivity to an AWS IoT cloud ecosystem. It provides the following use cases:
- Enriched remote connection
- Optimized - to pass the messages via a single underlying connection
- Secured - to protect the edge identity and data via TLS with basic and certificate-based authentication
- Maintained - with a reconnect exponential backoff algorithm
- Synchronized - on a connectivity recovering via a message buffering
- Application protection - AWS Connector is the only one component with a remote connectivity i.e. all local applications are protected from exposure to the public network
- Offline mode - local applications don’t need to care about the status of the remote connection, they can stay fully operable in offline mode
- Device Shadow - messages sent to the Twin Channel are converted to messages more suitable for AWS Device Shadow service and sent to it.
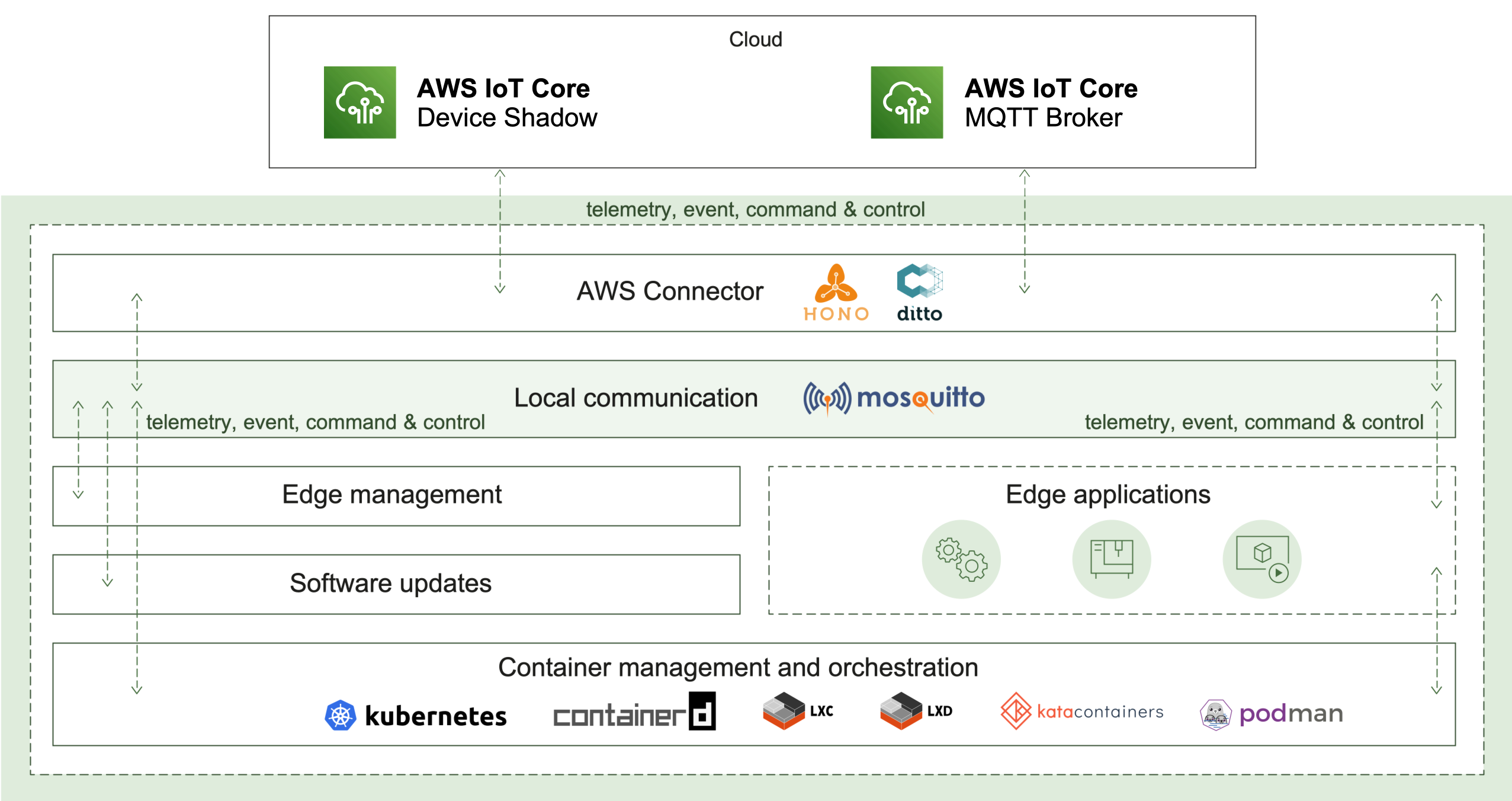
How it works
The AWS Connector plays a key role in two communication aspects - local and remote.
Cloud connectivity
To initiate its connection, the edge has to be manually or automatically provisioned. The result of this operation is different parameters and identifiers. Currently, AWS Connector supports MQTT transport as a connection-oriented and requiring less resources in comparison to AMQP. Once established, the connection is used as a channel to pass the edge telemetry and event messages. The IoT cloud can control the edge via commands and responses.
In case of a connection interruption, the AWS Connector will switch to offline mode. The message buffer mechanism will be activated to ensure that there is no data loss. Reconnect exponential backoff algorithm will be started to guarantee that no excessive load will be generated to the IoT cloud. All local applications are not affected and can continue to operate as normal. Once the remote connection is restored, all buffered messages will be sent and the edge will be fully restored to online mode.
Local communication
Ensuring that local applications are loosely coupled, Eclipse Hono™ MQTT definitions are in use. The event-driven local messages exchange is done via a MQTT message broker - Eclipse Mosquitto™. The AWS Connector takes the responsibility to forward these messages to the IoT cloud and vice versa.
Monitoring of the remote connection status is also enabled locally as well, along with details like the last known state of the connection, timestamp and a predefined connect/disconnect reason.
2.2 - Container management
Container management enables a lightweight standard runtime which is capable to run containerized applications with all advantages of the technology: isolation, portability and efficiency. The deployment and management are available both locally and remotely via an IoT cloud ecosystem of choice. The following use cases are provided:
- Standardized approach - with OCI (Open Container Initiative) compliant container images and runtime
- Lightweight runtime - with a default integration of
containerdand a possibility for another container technology of choice like podman, LXC and more - Isolation - with a default isolation from other containerized applications and the host system
- Portability - with an option to run one and the same containerized application on different platforms
- Pluggable architecture - with extension points on different levels
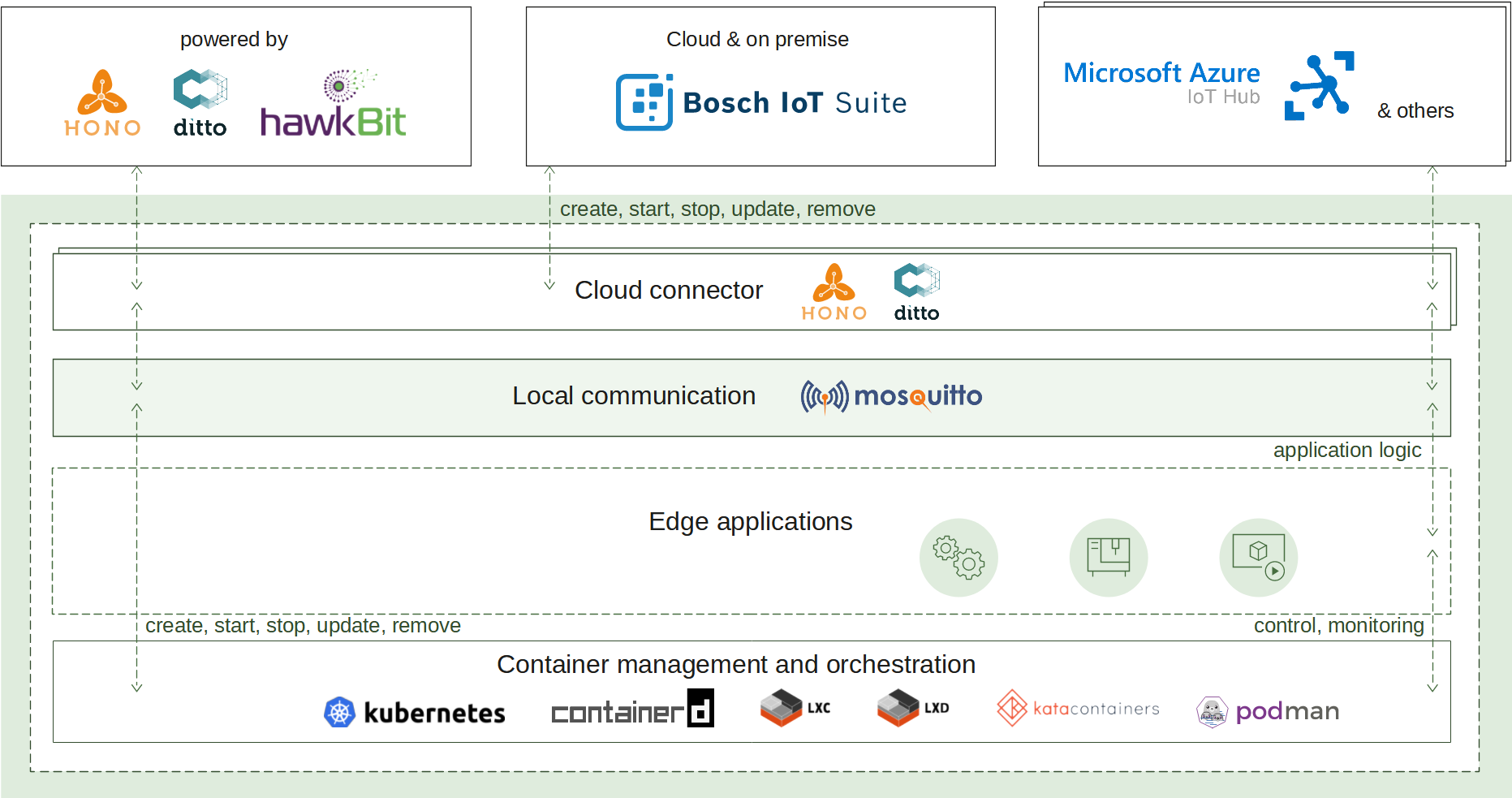
How it works
A container image packs the application executable along with all its needed dependencies into a single artifact that can be built by a tooling of choice. The built image is made available for usage by being pushed to a container image registry where the runtime can refer it to.
To create a new container instance, the container management uses such an image reference and a configuration for it to produce a fully functional container.
The container lifecycle (start, update, stop, remove) and environment (memory constraints, restart policy, etc.) are also handled by the runtime.
The container management continuously ensures the applications availability via state awareness and restart policies, provides monitoring via flexible logging and fine-grained resources management.
All of that is achieved on top of an underlying runtime of choice (containerd by default) that takes care of the low-level isolation mechanisms.
2.3 - Software update
Software update enables the deployment and management of various software artifacts, both locally and remotely via an IoT cloud ecosystem of choice. It provides the following use cases:
- Robust download - with a retry and resume mechanism when the network connection is interrupted
- Artifact validation - with an integrity validation of every downloaded artifact
- Universal installation - with customizable install scripts to handle any kind of software
- Operation monitoring - with a status reporting of the download and install operations
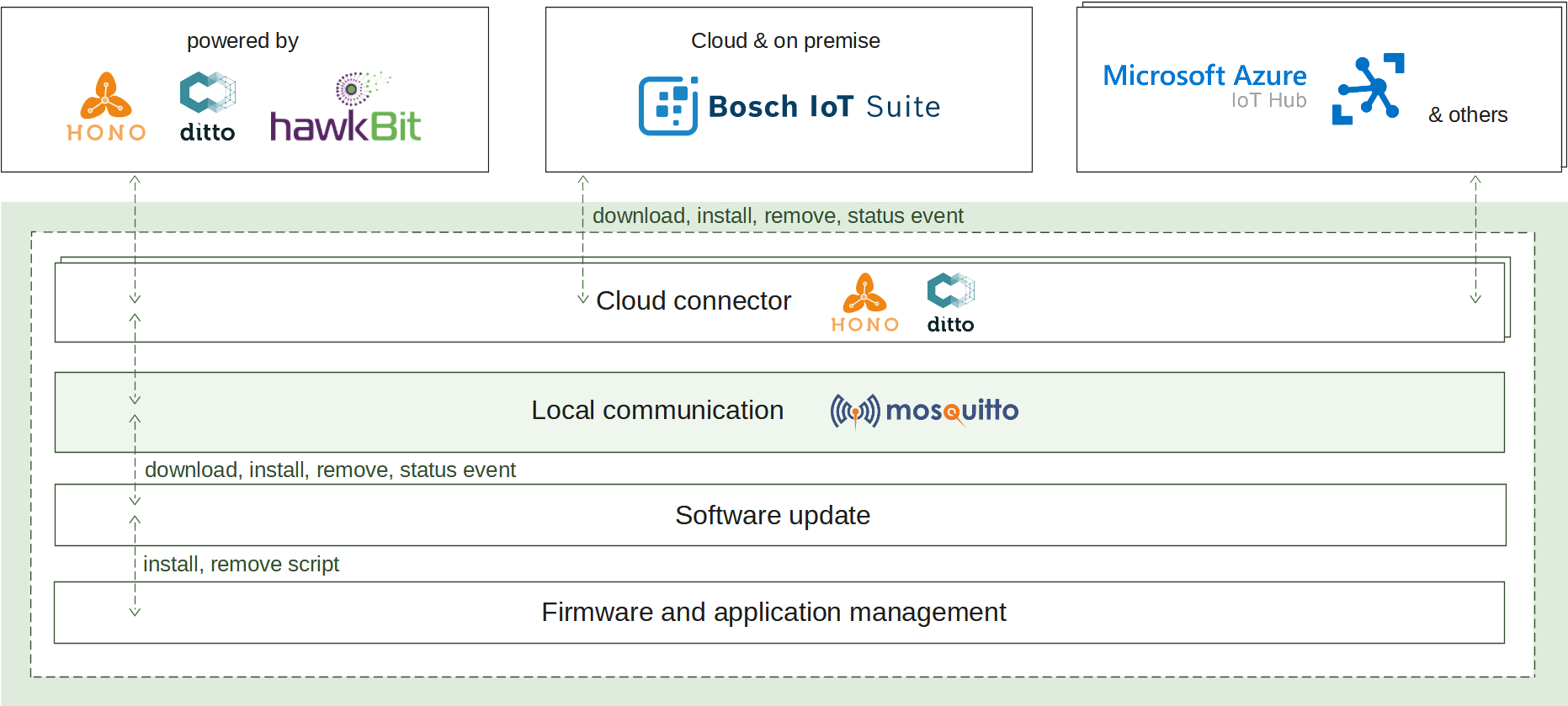
How it works
When the install operation is received at the edge, the download process is initiated. Retrieving the artifacts will continue until they are stored at the edge or their size threshold is reached. If successful, the artifacts are validated for integrity and further processed by the configured script. It is responsible to apply the new software and finish the operation. A status report is announced on each step of the process enabling its transparent monitoring.
On start up, if there have been any ongoing operations, they will be automatically resumed as the operation state is persistently stored.
What’s next
2.4 - Update manager
Update manager enables a lightweight core component which is capable to easily perform complex OTA update scenarios on a target device. The following capabilities are provided:
- Lightweight - consists of a single core component which orchestrates the update process
- Flexible deployment - supports different deployment models - natively, as an executable or container
- Unified API - all domain agents utilize a unified Update Agent API for interacting with the Update Manager
- MQTT Connectivity - the connectivity and communication between the Update Manager and domain agent is MQTT-based
- Multi-domain integration - easily integrates, scales and performs complex update operations across multiple domains
- Default update agents - integrates with the Kanto provided out-of-the box domain update agent implementation for deployment of container into the Kanto container management
- Pluggable architecture - provides an extensible model for plug-in custom orchestration logic
- Asynchronous updates - asynchronous and independent update process across the different domains
- Multi-staged updates - the update process is organized into different stages
- Configurable - offers a variety of configuration options for connectivity, supported domains, message reporting and etc
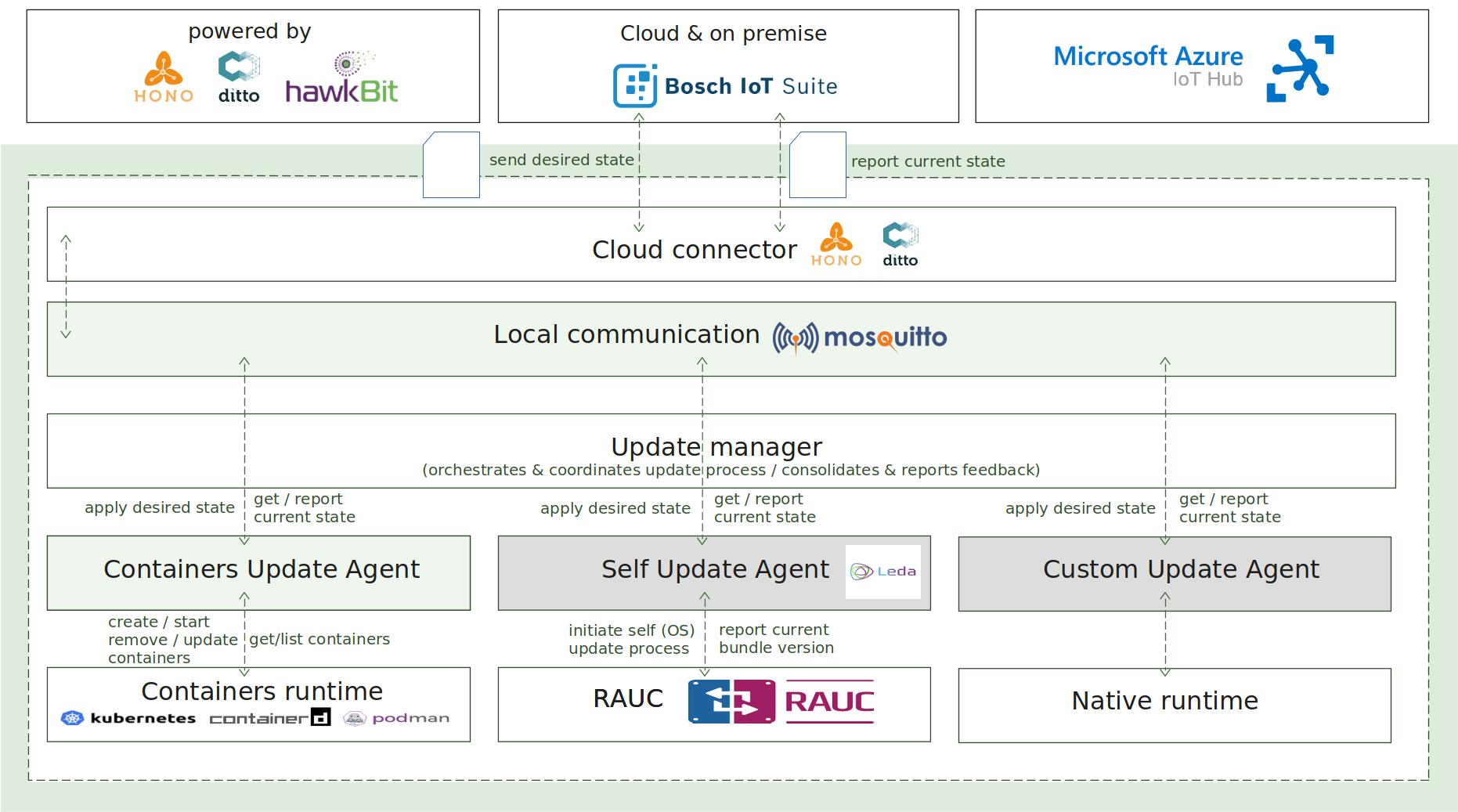
How it works
The update process is initiated by sending the desired state specification as an MQTT message towards the device, which is handled by the Update Manager component.
The desired state specification in the scope of the Update Manager is a JSON-based document, which consists of multiple component definitions per domain, representing the desired state to be applied on the target device. A component in the same context means a single, atomic and updatable unit, for example, OCI-compliant container, software application or firmware image.
Each domain agent is a separate and independent software component, which implements the Update Agent API for interaction with the Update Manager and manages the update logic for concrete domain. For example - container management.
The Update Manager, operating as a coordinator, is responsible for processing the desired state specification, distributing the split specification across the different domain agents, orchestrating the update process via MQTT-based commands, collecting and consolidating the feedback responses from the domain update agents, and reporting the final result of the update campaign to the backend.
As extra features and capabilities, the Update Manager enables reboot of the host after the update process is completed and reporting of the current state of the system to the backend.
2.5 - Suite connector
Suite connector enables the remote connectivity to an IoT cloud ecosystem of choice, powered by Eclipse Hono™ (e.g. Eclipse Cloud2Edge and Bosch IoT Suite). It provides the following use cases:
- Enriched remote connection
- Optimized - to pass the messages via a single underlying connection
- Secured - to protect the edge identity and data via TLS with basic and certificate-based authentication
- Maintained - with a reconnect exponential backoff algorithm
- Synchronized - on a connectivity recovering via a message buffering
- Application protection - suite connector is the only one component with a remote connectivity i.e. all local applications are protected from exposure to the public network
- Offline mode - local applications don’t need to care about the status of the remote connection, they can stay fully operable in offline mode
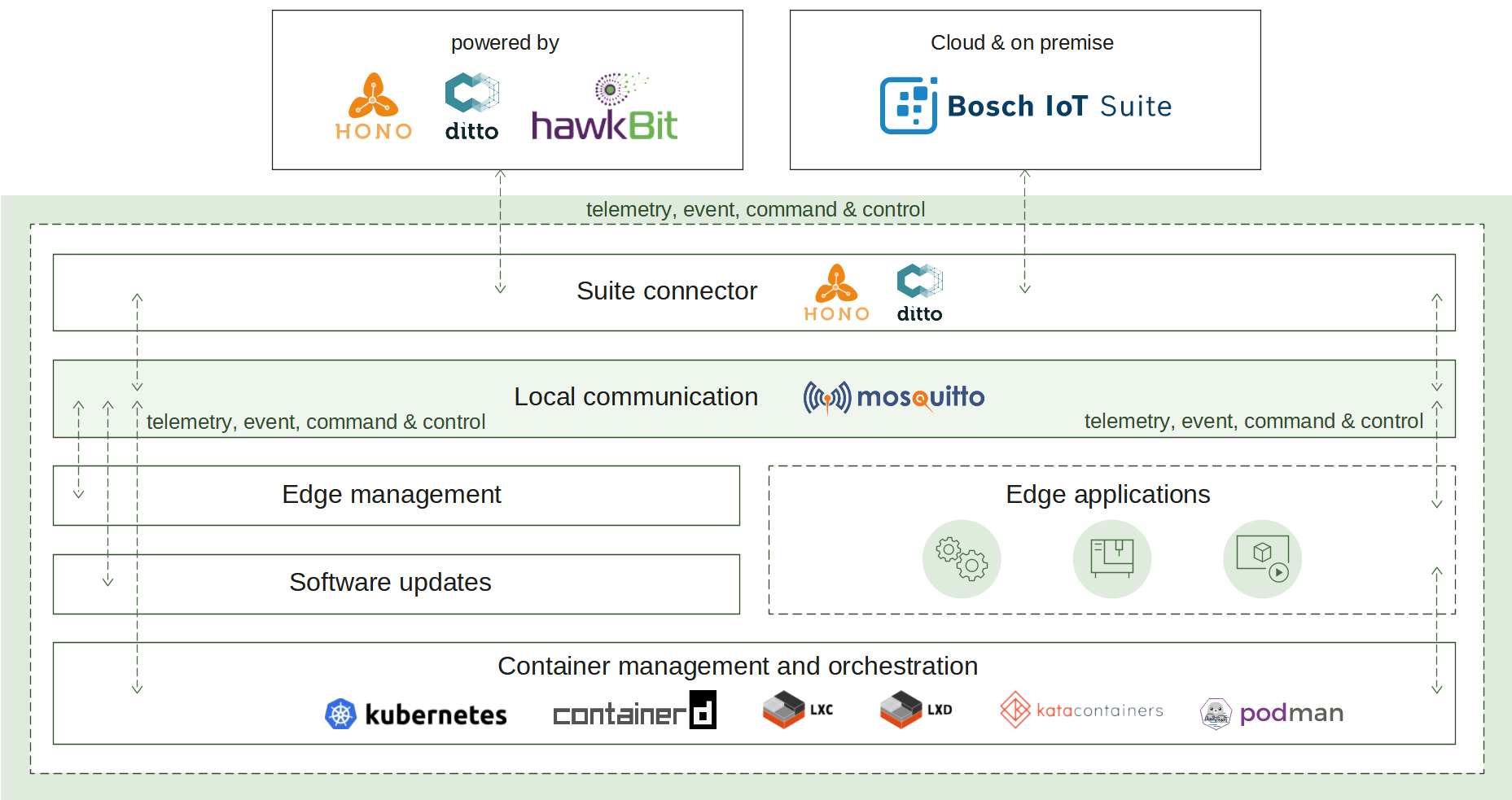
How it works
The suite connector plays a key role in two communication aspects - local and remote.
Cloud connectivity
To initiate its connection, the edge has to be manually or automatically provisioned. The result of this operation is different parameters and identifiers. Currently, suite connector supports MQTT transport as a connection-oriented and requiring less resources in comparison to AMQP. Once established, the connection is used as a channel to pass the edge telemetry and event messages. The IoT cloud can control the edge via commands and responses.
In case of a connection interruption, the suite connector will switch to offline mode. The message buffer mechanism will be activated to ensure that there is no data loss. Reconnect exponential backoff algorithm will be started to guarantee that no excessive load will be generated to the IoT cloud. All local applications are not affected and can continue to operate as normal. Once the remote connection is restored, all buffered messages will be sent and the edge will be fully restored to online mode.
Local communication
Ensuring that local applications are loosely coupled, Eclipse Hono™ MQTT definitions are in use. The event-driven local messages exchange is done via a MQTT message broker - Eclipse Mosquitto™. The suite connector takes the responsibility to forward these messages to the IoT cloud and vice versa.
The provisioning information used to establish the remote communication is available locally both on request via a predefined message and on update populated via an announcement. Applications that would like to extend the edge functionality can further use it in Eclipse Hono™ and Eclipse Ditto™ definitions.
Monitoring of the remote connection status is also enabled locally as well, along with details like the last known state of the connection, timestamp and a predefined connect/disconnect reason.
2.6 - Local digital twins
Local digital twins enables the digital twin state on a local level even in offline scenarios. It provides the following use cases:
- Mirrors the applications
- Persistency - digital twins are stored locally
- Cloud connectivity - provide connectivity to the cloud (similar to Suite connector)
- Offline scenarios - local applications stay fully operable as if the connection with the cloud is not interrupted Synchronization - when connection to the cloud is established the last known digital twin state is synchronized
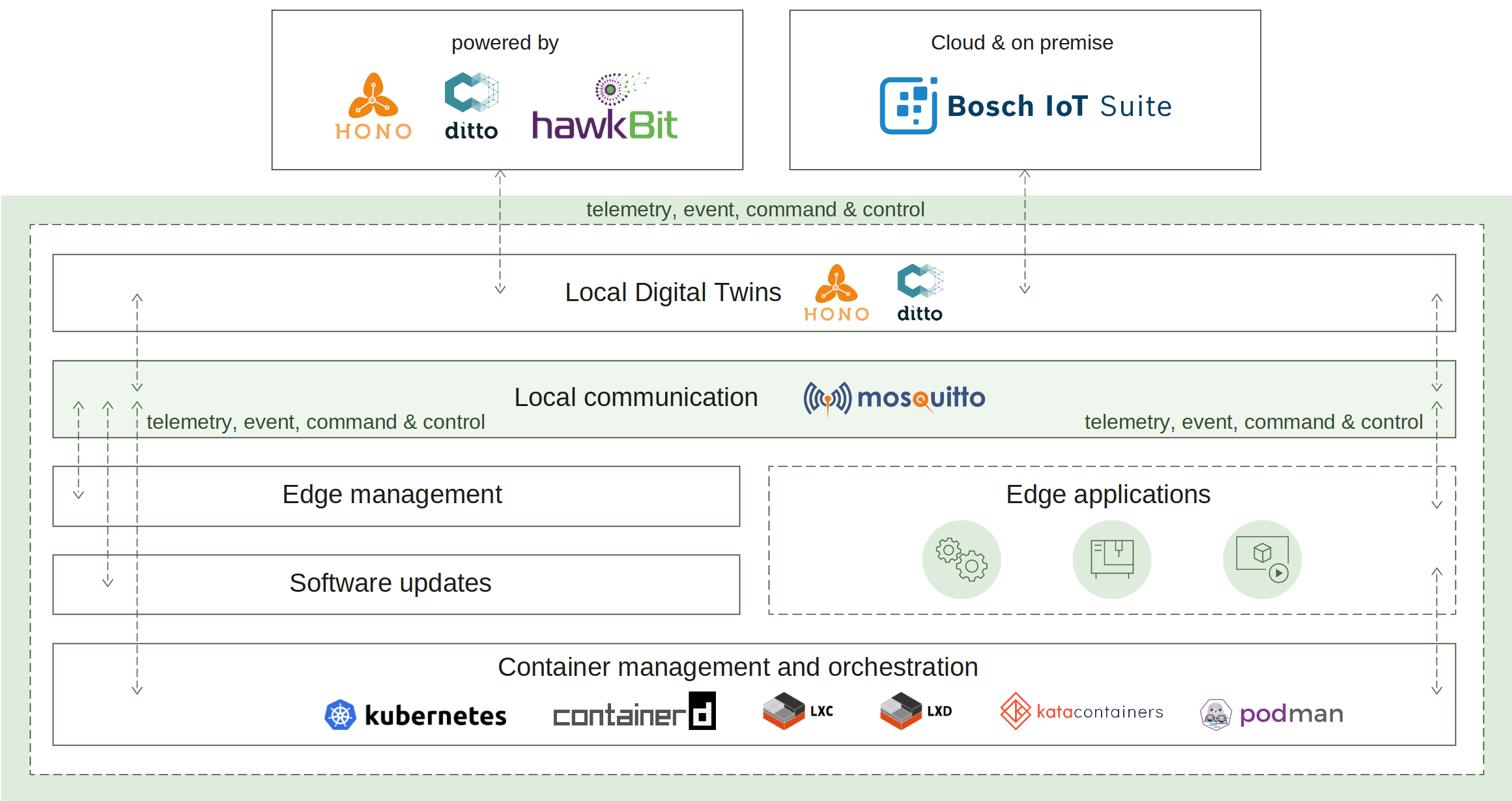
How it works
Similar to the Suite connector service the local digital twins service needs to establish a connection to the cloud. To do this this the edge has to be manually or automatically provisioned. This connection is then used as a channel to pass the edge telemetry and event messages. Once a connection is established the device can be operated via commands.
To ensure that the digital twin state is available on a local level even in offline mode (no matter of the connection state) the local digital twins service persist all changes locally. Such capabilities were implemented to support offline scenarios and advanced edge computing involving synchronization with the cloud after disruptions or outages. The synchronization mechanisms were also designed in a way to significantly reduce data traffic, and efficiently prevent data loss due to long-lasting disruptions.
Upon reconnection, the local digital twins will notify the cloud of any changes during the offline mode and synchronize the digital twins state.
The synchronization works in both directions:
- Cloud -> Local digital twins - desired properties are updated if such changes are requested from the cloud.
- Local digital twins -> Cloud - local digital twins state is sent to the cloud (e.g. all current features, their reported properties values, and any removed features while there was no connection).
What’s next
2.7 - File upload
File upload enables sending of files to a backend storage of choice. It can be used both locally and remotely via a desired IoT cloud ecosystem. The following use cases are provided:
- Storage diversity - with ready to use integrations with Azure Blob Storage, Amazon S3 and standard HTTP upload
- Automatic uploads - with periodically triggered uploads at a specified interval in a given time frame
- Data integrity - with an option to calculate and send the integrity check required information
- Operation monitoring - with a status reporting of the upload operation

How it works
It’s not always possible to inline all the data into exchanged messages. For example, large log files or large diagnostic files cannot be sent as a telemetry message. In such scenarios, file upload can assist enabling massive amount of data to be stored to the backend storage.
There are different triggers which can initiate the upload operation: periodic or explicit. Once initiated, the request will be sent to the IoT cloud for confirmation or cancellation transferred back to the edge. If starting is confirmed, the files to upload will be selected according to the specified configuration, their integrity check information can be calculated and the transfer of the binary content will begin. A status report is announced on each step of the upload process enabling its transparent monitoring.
What’s next
3 - How-to guides
3.1 - Update software
By following the steps below you will install ahello
Debian package via a publicly available Eclipse Hono sandbox using Eclipse Kanto.
A couple of simple Eclipse Hono northbound business applications written in Python are provided to explore
the capabilities for remotely installing and monitoring.
On the edge side, a basic
install_hello.sh
script will be downloaded and executed.
Before you begin
To ensure that your edge device is capable to execute the steps in this guide, you need:
Debian-based linux distribution and the
aptcommand line toolIf you don’t have an installed and running Eclipse Kanto, follow Install Eclipse Kanto
If you don’t have a connected Eclipse Kanto to Eclipse Hono sandbox, follow Explore via Eclipse Hono
The software update application
Navigate to the
quickstartfolder where the resources from the Explore via Eclipse Hono guide are located and execute the following script:wget https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/kanto/raw/main/quickstart/hono_commands_su.pyExecuting
helloin the terminal will return that the command is not found
Install Debian package
To explore the software management, we will use two Python scripts to install and monitor the hello Debian package.
The location where the Python applications will run does not have to be your edge device as they communicate remotely
with Eclipse Hono only.
First, start the monitoring application that requires the configured Eclipse Hono tenant (-t) and will print all
received events triggered by the device:
python3 hono_events.py -t demo
In another terminal, we are ready to spin up a hello Debian package at the edge via executing the second application
that requires the Eclipse Hono tenant (-t) and the device identifier (-d):
python3 hono_commands_su.py -t demo -d demo:device
Verify
You can check out that the new package is installed on your edge device via executing:
hello
The command now displays: Hello, world!
Clean up
The installed hello Debian package can be removed via executing:
sudo apt remove hello
3.2 - Upload files
By following the steps below you will upload an example log file to your HTTP file server via a publicly available Eclipse Hono sandbox using Eclipse Kanto. A simple Eclipse Hono northbound business application written in Python is provided to explore the capabilities for remotely uploading and monitoring.
Before you begin
To ensure that all steps in this guide can be executed, you need:
servefileinstalledThis is a small Python HTTP server used in the example to serve the uploads. It does not have to be running on your edge device but it has to be accessible from there. You can install it by executing:
pip3 install servefileIf you don’t have an installed and running Eclipse Kanto on your edge device, follow Install Eclipse Kanto
If you don’t have a connected Eclipse Kanto to Eclipse Hono sandbox, follow Explore via Eclipse Hono
Navigate to the
quickstartfolder where the resources from the Explore via Eclipse Hono guide are located and execute the following script:wget https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/kanto/raw/main/quickstart/hono_commands_fu.py
Upload log file
By default, all files in /var/tmp/file-upload/ directory can be uploaded.
For example, grab the suite connector log file and place it in the directory via executing:
mkdir -p /var/tmp/file-upload/ && sudo cp /var/log/suite-connector/suite-connector.log /var/tmp/file-upload/
Choose a directory where the log file will be uploaded, open a new terminal there and run servefile:
servefile -u .
To explore the file upload, we will use a Python script to request and monitor the operation. The location where the Python application will run does not have to be your edge device as it communicates remotely with Eclipse Hono only.
Now we are ready to request the log file upload from the edge via executing the application
that requires the Eclipse Hono tenant (-t) and the device identifier (-d):
python3 hono_commands_fu.py -t demo -d demo:device
Verify
You can check out that the log file is on your HTTP file server by listing the content of servefile working directory.
Clean up
Stop servefile and clean up its working directory.
3.3 - Back up and restore files
By following the steps below you will back up a simple text file to an HTTP file server and then restore it back via a publicly available Eclipse Hono sandbox using Eclipse Kanto. A simple Eclipse Hono northbound business application written in Python is provided to explore the capabilities for remotely backing up and restoring files.
Before you begin
To ensure that all steps in this guide can be executed, you need:
servefileinstalledThis is a small Python HTTP server used in the example to serve the uploads and downloads. It does not have to be running on your edge device, but it has to be accessible from there. You can install it by executing:
pip3 install servefileIf you don’t have an installed and running Eclipse Kanto on your edge device, follow Install Eclipse Kanto
If you don’t have a connected Eclipse Kanto to Eclipse Hono sandbox, follow Explore via Eclipse Hono
The file backup and restore application
Navigate to the
quickstartfolder where the resources from the Explore via Eclipse Hono guide are located and execute the following script:wget https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/kanto/raw/main/quickstart/hono_commands_fb.py
Back up
By default, all directories in /var/tmp/file-backup/ or the directory itself can be backed up.
For this example, create a file data.txt which will be later backed up:
sudo mkdir -p /var/tmp/file-backup && sudo echo "This is the first line in the file!" >> /var/tmp/file-backup/data.txt
You can verify that the file was successfully created by executing the following command:
cat /var/tmp/file-backup/data.txt
This should produce This is the first line in the file! as an output.
Choose a directory where the text file will be uploaded, open a new terminal there and run servefile
with the flag -u to enable a file upload:
servefile -u .
To explore the file backup, we will use a Python script to request and monitor the operation. The location where the Python application will run does not have to be your edge device as it communicates remotely with Eclipse Hono only.
Now we are ready to request the text file backup from the edge via executing the application that requires the command
to execute (backup), Eclipse Hono tenant (-t), the device identifier (-d) and the host where the backup will
be uploaded to:
python3 hono_commands_fb.py backup -t demo -d demo:device -h localhost
You can check out that the backup file data.zip is on your HTTP file server by
listing the content of the servefile working directory.
Restore
To explore the restore capabilities you will first modify the data.txt file, and then you will restore it to
the version before the changes by using the backup, that was created earlier.
You can modify the data.txt file with the following command:
sudo echo "This is the second line in the file!" >> /var/tmp/file-backup/data.txt
You can verify that the file was successfully updated by executing the following command:
cat /var/tmp/file-backup/data.txt
This output should be:
This is the first line in the file!
This is the second line in the file!
Navigate to the terminal where servefile was started and terminate it.
Start it again with the flag -l to enable a file download:
servefile -l .
To explore the file restore, we will use a Python script to request and monitor the operation. The location where the Python application will run does not have to be your edge device as it communicates remotely with Eclipse Hono only.
Now we are ready to request the text file restore from the edge via executing the application that requires the command
to execute (restore), Eclipse Hono tenant (-t), the device identifier (-d) and the host where the backup file
will be downloaded from:
python3 hono_commands_fb.py restore -t demo -d demo:device -h localhost
Verify
You can check out that the original file is restored by executing the following command:
cat /var/tmp/file-backup/data.txt
This should produce This is the first line in the file! as an output.
Clean up
Stop servefile and clean up its working directory.
Remove the data.txt file from the /var/tmp/file-backup directory.
3.4 - Create and update the containers `Desired State`
Desired State using the update-manageBy following the steps below you will publish a simple Desired State specification via a publicly available Eclipse Hono sandbox and then the specification will be handled by the Eclipse Kanto Update Manager, which will trigger an OTA update on
the edge device.
A simple monitoring application will track the progress and the status of the update process.
Before you begin
To ensure that all steps in this guide can be executed, you need:
Debian-based linux distribution and the
aptcommand line toolIf you don’t have an installed and running Eclipse Kanto, follow Install Eclipse Kanto
If you don’t have a connected Eclipse Kanto to Eclipse Hono sandbox, follow Explore via Eclipse Hono
The update manager application
Navigate to the
quickstartfolder where the resources from the Explore via Eclipse Hono guide are located and execute the following script:wget https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/kanto/raw/main/quickstart/hono_commands_um.pyEnable the
containers update agentservice of theContainer Managementby adding the"update_agent": {"enable": true}property to thecontainer-managementservice configuration (by default located at/etc/container-management/config.json) and restart the service:systemctl restart container-management
Publish the Desired State specification
First, start the monitoring application that requires the configured Eclipse Hono tenant (-t) and an optional filter parameter (-f). It will print all
received feedback events triggered by the device:
python3 hono_events.py -t demo -f demo/device/things/live/messages/feedback
The starting point of the OTA update process is to publish the example Desired State specification:
python3 hono_commands_um.py -t demo -d demo:device -o apply
The Desired State specification in this case consists of single domain section definition for the containers domain and a three container components - influxdb, hello-world and alpine image.
Apply Desired State specification
The Update Manager receives the published Desired State to the local Mosquitto broker, splits the specification (in this case into single domain) and then
distributes the processed specification to the domain agents which initiates the actual update process logic on the domain agents side.
The update process is organized into multiple phases, which are triggered by sending specific Desired State commands (DOWNLOAD/UPDATE/ACTIVATE).
In the example scenario, the three images for the three container components will be pulled (if not available in the cache locally), created as containers during the UPDATING phase and
started in the ACTIVATING phase.
Monitor OTA update progress
During the OTA update, the progress can be tracked in the monitoring application fot the Desired State feedback messages, started in the prerequisite section above.
The Update Manager reports at a time interval of a second the status of the active update process. For example:
{
"activityId":"e5c858cc-2057-41b0-bd5f-83aee0aad22e",
"timestamp":1693201088401,
"desiredStateFeedback":{
"status":"RUNNING",
"actions":[
{
"component":{
"id":"containers:alpine",
"version":"latest"
},
"status":"UPDATE_SUCCESS",
"message":"New container instance is started."
},
{
"component":{
"id":"containers:hello-world",
"version":"latest"
},
"status":"UPDATE_SUCCESS",
"message":"New container instance is started."
},
{
"component":{
"id":"containers:influxdb",
"version":"2.7.1"
},
"status":"UPDATING",
"message":"New container created."
}
]
}
}
List containers
After the update process is completed, list the installed containers by executing the command kanto-cm list to verify if the Desired State is applied correctly.
The output of the command should display the info about the three containers, described in the Desired State specification. The influxdb is expected to be in RUNNING state and
the other containers in status EXITED. For example :
ID |Name |Image |Status |Finished At |Exit Code
|-------------------------------------|-------------|------------------------------------|----------------------|---------
7fe6b689-eb76-476d-a730-c2f422d6e8ea |influxdb |docker.io/library/influxdb:1.8.4 |Running | |0
c36523d7-8d17-4255-ae0c-37f11003f658 |hello-world |docker.io/library/hello-world:latest|Exited | |0
9b99978b-2593-4736-bb52-7a07be4a7ed1 |alpine |docker.io/library/alpine:latest |Exited | |0
Update Desired State specification
To update the existing Desired State run the command below. The update changes affect two containers - alpine and influxdb. Being not present in the updated Desired State specification, the alpine container will be removed from the system. The influxdb will be updated to version 1.8.5. The last container - hello-world is not affected and any events will be not reported from the container update agent for this particular container.
python3 hono_commands_um.py -t demo -d demo:device -o update
List updated containers
After the update process of the existing Desired State is completed, list again the available containers to the verify the Desired State is updated correctly.
The output of the command should display the info about the two containers, described in the Desired State specification. The influxdb is expected to be updated with the version 1.8.5 and in RUNNING state and hello-world container to be status EXITED with version unchanged. The alpine container must be removed and not displayed.
ID |Name |Image |Status |Finished At |Exit Code
|-------------------------------------|-------------|------------------------------------|----------------------|---------
7fe6b689-eb76-476d-a730-c2f422d6e8ea |influxdb |docker.io/library/influxdb:1.8.5 |Running | |0
c36523d7-8d17-4255-ae0c-37f11003f658 |hello-world |docker.io/library/hello-world:latest|Exited | |0
Remove all containers
To remove all containers, publish an empty Desired State specification (with empty components section):
python3 hono_commands_um.py -t demo -d demo:device -o clean
As a final step, execute the command kanto-cm list to verify that the containers are actually removed from the Kanto container management.
The expected output is No found containers..
3.5 - Monitor system metrics
By following the steps below you will be able to monitor the system metrics from your edge device via a publicly available Eclipse Hono sandbox using Eclipse Kanto. A simple Eclipse Hono northbound business application written in Python is provided to explore the capabilities for remotely monitoring the CPU and memory utilization.
Before you begin
To ensure that all steps in this guide can be executed, you need:
Plotlyis an open-source plotting library andDashis a framework for building data application in Python. They are used in this example to run a simple HTTP server and visualize the incoming system metrics data in real time, and they do not have to be running on your edge device. You can install them by executing:pip3 install plotly dashIf you don’t have an installed and running Eclipse Kanto on your edge device, follow Install Eclipse Kanto
If you don’t have a connected Eclipse Kanto to Eclipse Hono sandbox, follow Explore via Eclipse Hono
The system metrics application
Navigate to the
quickstartfolder where the resources from the Explore via Eclipse Hono guide are located and execute the following script:wget https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/kanto/raw/main/quickstart/hono_commands_sm.py
Monitor system metrics
To explore the system metrics, we will use a Python script to request and monitor the CPU and memory utilization. The location where the Python application will run does not have to be your edge device as it communicates remotely with Eclipse Hono only.
Now we are ready to request the system metrics from the edge via executing the application
that requires the Eclipse Hono tenant (-t) and the device identifier (-d):
python3 hono_commands_sm.py -t demo -d demo:device
Verify
You can check out that the CPU and memory utilization metrics are properly received and displayed by checking out the application dashboard (by default - http://127.0.0.1:8050).
3.6 - Verify signed container images
By following the steps below, you will sign a container image and push it to a local registry using anotation. Then a notation trust policy and the Kanto Container Management service will be configured in a way that running containers from the signed image via kanto-cm CLI will be successful, while running containers from unsigned images will fail.
Before you begin
To ensure that your edge device is capable to execute the steps in this guide, you need:
- If you don’t have an installed and running Eclipse Kanto, follow Install Eclipse Kanto
- Installed Notation CLI
- Installed and running Docker
Create an image and push it to a local registry using docker and than sign it with notation
Create and run a local container registry:
sudo kanto-cm create --ports 5000:5000 --e REGISTRY_STORAGE_DELETE_ENABLED=true --name registry docker.io/library/registry:latest
sudo kanto-cm start -n registry
Build a dummy hello world image and push it to the registry:
cat <<EOF | sudo docker build -t localhost:5000/dummy-hello:signed -
FROM busybox:latest
CMD [ "echo", "Hello World" ]
EOF
sudo docker push localhost:5000/dummy-hello:signed
export IMAGE=$(sudo docker inspect --format='{{index .RepoDigests 0}}' localhost:5000/dummy-hello:signed)
echo $IMAGE
Generate a key-pair with notation and add it as the default signing key:
notation cert generate-test --default "kanto"
Sign the image and store the signature in the registry:
notation sign $IMAGE
Configure notation truspolicy and container management verifier
Get the notation config directory and assign it to an environment variable to be used in the next steps of the guide:
export NOTATION_CONFIG=${XDG_CONFIG_HOME:-$HOME/.config}/notation
echo $NOTATION_CONFIG
Create a simple notation trustpolicy as a trustpolicy.json file in the notation config directory:
cat <<EOF | tee $NOTATION_CONFIG/trustpolicy.json
{
"version": "1.0",
"trustPolicies": [
{
"name": "kanto-images",
"registryScopes": [ "*" ],
"signatureVerification": {
"level" : "strict"
},
"trustStores": [ "ca:kanto" ],
"trustedIdentities": [ "*" ]
}
]
}
EOF
Create a backup of the initial Kanto Container Management configuration that is found in /etc/container-management/config.json(the backup will be restored at the end of the guide):
sudo cp /etc/container-management/config.json /etc/container-management/config-backup.json
Configure the use of notation verifier, set its config directory, mark the local registry as an insecure one, and set the image expiry time to zero seconds, so the local cache of the images used in the how-to will be deleted upon container removal:
cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/container-management/config.json
{
"log": {
"log_file": "/var/log/container-management/container-management.log"
},
"containers": {
"image_verifier_type": "notation",
"image_verifier_config": {
"configDir": "$NOTATION_CONFIG"
},
"insecure_registries": [ "localhost:5000" ],
"image_expiry": "0s"
}
}
EOF
Restart the Container Management service for the changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart container-management.service
Verify
Create and run a container from the signed image. The container prints Hello world to the console:
sudo kanto-cm create --name dummy-hello --rp no --t $IMAGE
sudo kanto-cm start --name dummy-hello --a
Make sure that a docker hub hello-world image is not cached locally, by removing any containers with this image, and verify that creating containers from it fails, as the image is not signed, and the signature verification fails:
sudo kanto-cm remove -f $(sudo kanto-cm list --quiet --filter image=docker.io/library/hello-world:latest)
sudo kanto-cm create --name dockerhub-hello --rp no --t docker.io/library/hello-world:latest
Clean up
Remove the created containers from the Kanto Container Management:
sudo kanto-cm remove -n dummy-hello
sudo kanto-cm remove -n registry -f
Restore the initial Kanto Container Management configuration and restart the service:
sudo mv -f /etc/container-management/config-backup.json /etc/container-management/config.json
sudo systemctl restart container-management.service
Remove the localy cached images from Docker:
sudo docker image rm localhost:5000/dummy-hello:signed registry:latest
Reset the notation configuration by removing the directory:
rm -r $NOTATION_CONFIG
Unset exported environment variables:
unset IMAGE NOTATION_CONFIG
3.7 - Offline explore edge device
By following the steps below, you will get the structure of the edge digital twins with all its features and properties using Eclipse Kanto. A simple Eclipse Hono northbound business application written in Python is provided to display the things’ and their features’ structure.
Before you begin
To ensure that your edge device is capable to execute the steps in this guide, you need:
If you don’t have an installed and running Eclipse Kanto on your edge device, follow Install Eclipse Kanto
If you don’t have a connected Eclipse Kanto to Eclipse Hono sandbox, follow Explore via Eclipse Hono
Stop
suite-connector.service. The local digital twins service is a replacement for the suite connector service, that is why either one of the services must be running.sudo systemctl stop suite-connector.serviceThe offline explore application
Navigate to the
quickstartfolder where the resources from the Explore via Eclipse Hono guide are located and execute the following script:wget https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/kanto/raw/main/quickstart/hono_commands_ldt.py
Configure Local digital twins
Open file /etc/suite-connector/config.json, copy tenantId, deviceId, authId and password.
{
...
"tenantId": "demo",
"deviceId": "demo:device",
"authId": "demo_device",
"password": "secret"
...
}
The local digital twins service uses the /etc/local-digital-twins/config.json to acquire all the remote communication, identification and
authentication data to establish the remote connection. Update the configuration as shown below and
replace tenantId, deviceId, authId and password with the settings that you copied in the previous step.
{
"logFile": "/var/log/local-digital-twins/local-digital-twins.log",
"caCert": "/etc/local-digital-twins/iothub.crt",
"thingsDb": "/var/lib/local-digital-twins/thing.db",
"tenantId": "demo",
"deviceId": "demo:device",
"authId": "demo_device",
"password": "secret"
}
Save the configuration and start the local digital twins service using the following command:
sudo systemctl start local-digital-twins.service
Receive the structure of the edge device
Now we are ready to request the structure of the edge digital twins via executing the offline explore application that requires the local digital twins tenant (-t) and the device identifier (-d):
python3 hono_commands_ldt.py -t demo -d demo:device
Verify
On the shell there will be output of the structure of the edge digital twins with all its features and properties. Things with the following identifiers will be presented:
- demo:device
- demo:device:edge:containers
Clean up
Stop the local digital twins service and start suite connector service by executing:
sudo systemctl stop local-digital-twins.service && \
sudo systemctl restart suite-connector.service
3.8 - Build Yocto Image for Raspberry Pi
Building a Yocto Image for a Raspberry Pi involves several steps, including setting up the environment, download the necessary layers, configuring the build and compiling the image.
Before you begin
- Install the required packages required for the build on a Ubuntu/Debian system
sudo apt-get update sudo apt install -y gawk wget git-core diffstat unzip texinfo gcc-multilib \ build-essential chrpath socat cpio python3 python3-pip python3-pexpect \ xz-utils debianutils iputils-ping libsdl1.2-dev xterm zstd liblz4-tool \
Clone the Yocto/Poky Repository
Verify the Yocto Version of Kanto availabe in meta-kanto layer, https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/meta-kanto, this example provides information for kirkstone branch.
Create a Source folder
mkdir sources cd sourcesIf it is kirkstone branch then, clone poky for kirkstone version in source directory
git clone https://github.com/yoctoproject/poky.git cd poky git checkout kirkstoneNote : Change branch based on meta-kanto layer.
Add Meta Layers to the source directory
Based on the yocto version, clone the meta layers in the source directory
meta-raspberrypimeta-openembeddedmeta-virtualizationmeta-lts-mixinsClone meta-raspberry pi layer to sources directory
cd .. git clone git://git.yoctoproject.org/meta-raspberrypi cd meta-raspberrypi git checkout kirkstoneClone meta-openembedded layer to sources directory
cd .. git clone https://github.com/openembedded/meta-openembedded.git cd meta-openembedded git checkout kirkstoneClone meta-virtualization layer to sources directory
cd .. git clone https://git.yoctoproject.org/git/meta-virtualization cd meta-virtualization git checkout kirkstoneClone meta-lts-mixins layers to source directory
cd .. git clone https://git.yoctoproject.org/git/meta-lts-mixins cd meta-lts-mixins git checkout kirkstone/goNote : The above layer is required to get the updated go version to be added in the yocto build, since kanto requires go version 1.19 and above.
Add meta-kanto layer to the sources directory
Clone meta-kanto layer to the sources directory
cd .. git clone https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/meta-kanto.git cd meta-kanto git checkout kirkstoneNote : Make sure all the layers cloned are of same yocto version ( kirkstone in this case)
Create Build Directory
After cloning all the required meta layers, move out of source directory to create build directory
cd ../.. source sources/poky/oe-init-build-envRun the below command to view the layers present in
bblayers.conffilebitbake-layers show-layersNote : Resolve any dependendencies if occured while running bitbake command.
Configure bblayer.conf file
By Default in the bblayer.conf file some of the layers will be added
Add all the layers to the bblayers.conf file with below command
bitbake-layers add-layer /home/path/to/meta/layer/directoryThe following layers should be added in the bblayer.conf file
meta-raspberrypi meta-openembedded meta-virtualization meta-lts-mixins meta-openembedded/meta-oe meta-openembedded/meta-python meta-opemembedded/meta-networking meta-openembedded/meta-filesystems meta-kantoExample to add layers to bblayers.conf file
while adding layers bitbake might have dependencies, add the dependent layers first. Example,
To add meta-kanto layer to bblayer.conf file which is kept at
/home/yocto/sources/meta-kantobitbake-layers add-layers /home/yocto/sources/meta-kantoAfter adding all the required layers in bblayer.conf file, verify again by running the below command
bitbake-layers show-layers
Configure local.conf file
Open local.conf file which is placed at the below location in build directory
vi conf/local.confChange the machine variable in local.conf file to raspberry pi machine
MACHINE ??= "raspberrypi4"Note: Check the sources/meta-raspberrypi/conf/machine for the availabe machines for raspberry pi.
Add required variables in local.conf file as shown and provided in the link below,
https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/meta-kanto# Add the required DISTRO_FEATURES DISTRO_FEATURES:append = " virtualization systemd" # Configure the kernel modules required to be included MACHINE_ESSENTIAL_EXTRA_RRECOMMENDS += "kernel-modules" # System initialization manager setup VIRTUAL-RUNTIME_init_manager = "systemd" DISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED = "sysvinit" VIRTUAL-RUNTIME_initscripts = "systemd-compat-units" # Add the Eclipse Kanto components IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " mosquitto" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " suite-connector" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " aws-connector" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " azure-connector" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " software-updates" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " file-upload" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " file-backup" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " update-manager" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " container-management" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " local-digital-twins"Run bitbake `target-name’ availabe as shown below,
Common targets are: core-image-minimal core-image-full-cmdline core-image-sato core-image-weston meta-toolchain meta-ide-supportNote : If any build issues comes up, resolve the issue and run the bitbake `target-name’ command again for the build.
Final Build Image Repository Location
After the successful build, the image will be availabe at the below location.
build/tmp/deploy/images/`machine_name`/
Run & Test the image with QEMU (Quick Emulator)
If RaspberryPi device is not availabe, the image can be run and tested on QEMU. Make the below changes to run on QEMU.
In `build/conf/local.conf’ file
Change the machine variable name to relevant qemu arch as shown below by changing the
MACHINEvarilabe from raspberrypi4 to ‘qemux86_64`# You need to select a specific machine to target the build with. There are a selection # of emulated machines available which can boot and run in the QEMU emulator: # #MACHINE ?= "qemuarm" #MACHINE ?= "qemuarm64" #MACHINE ?= "qemux86" #MACHINE ?= "qemux86-64" # This sets the default machine to be qemux86-64 if no other machine is selected: MACHINE ??= "qemuarm64"Run bitbake
target-namecommand by sourcing theoe-init-build-envscriptIn the same build directory run the below command to run qemu
runqemu qemuarm64
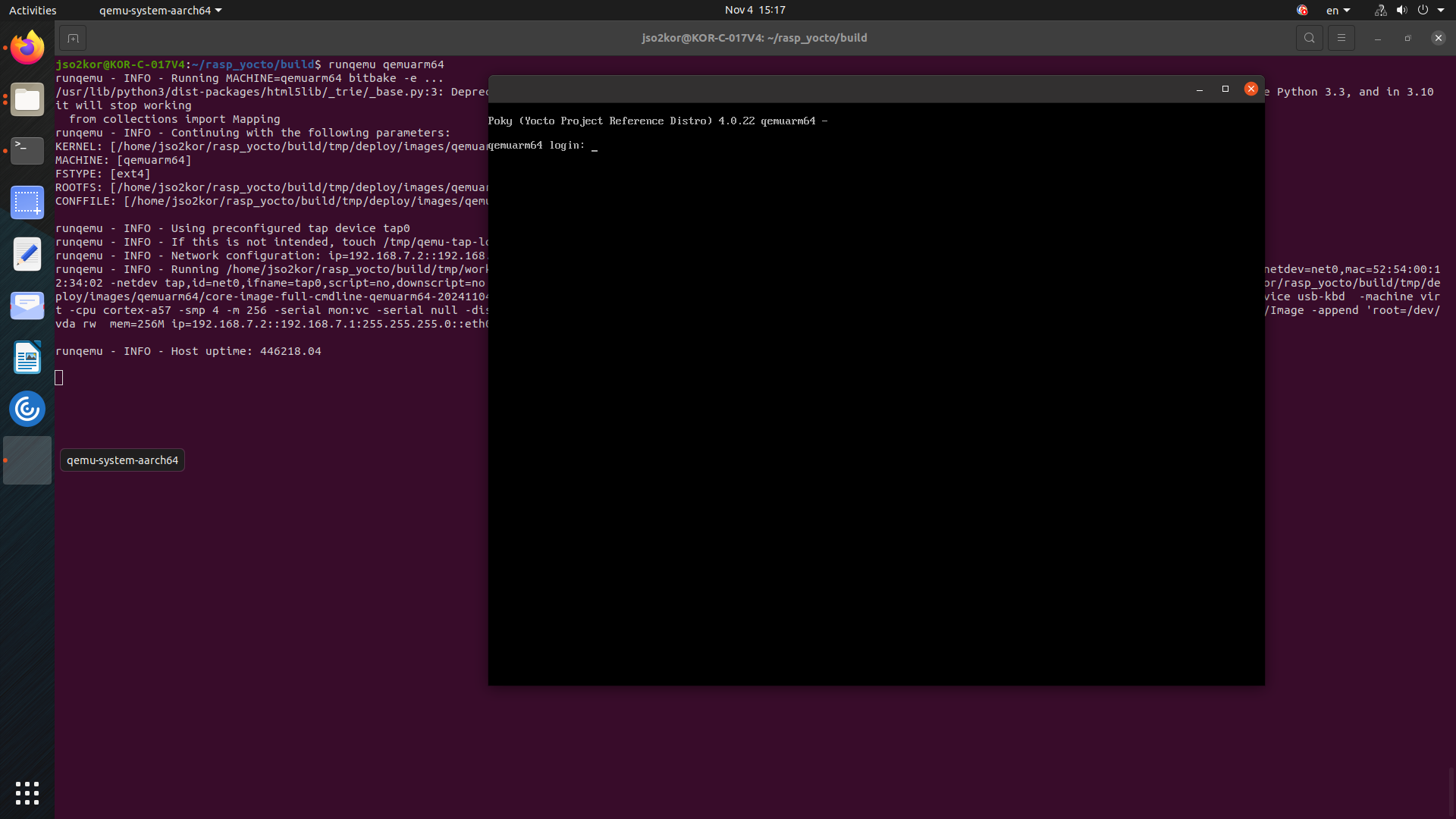
The above command will open a window which boots as “YOCTO PROJECT” and it enters to command line window. Enter login as `root’, and check for kanto components with the below commands.
systemctl status \ suite-connector.service \ container-management.service \ software-update.service \ file-upload.service \ file-backup.service \ system-metrics.service \ kanto-update-manager.serviceAll listed services must be in an active running state.
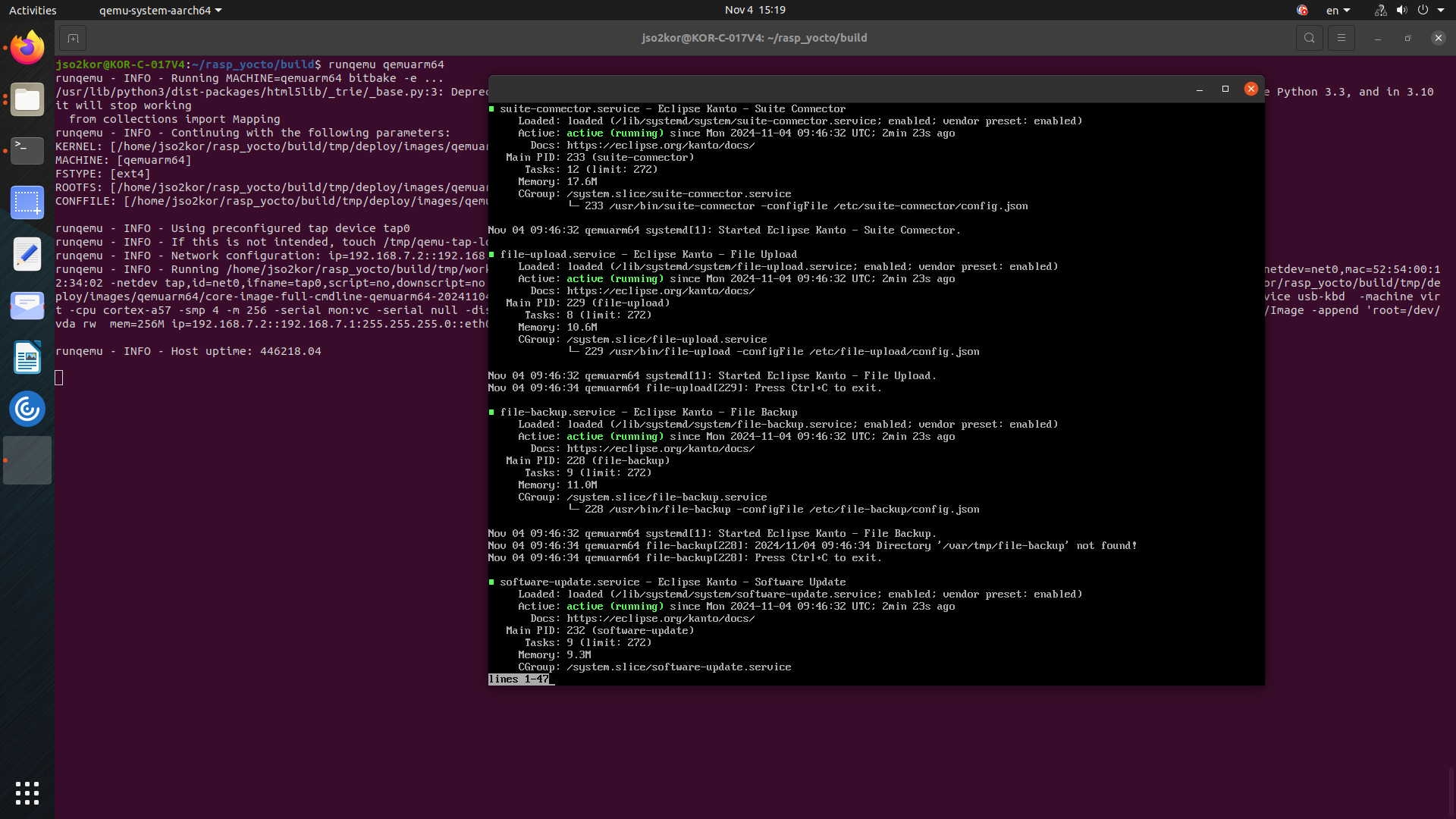
Flash the image on Raspberry Pi
The build image will be availabe at
build/tmp/deploy/images/raspberrypi4/Identify the SD Card Device with the below command to find the device name of your SD card
lsblkFlash the image to sd card
sudo dd if=/path/to/image.wic of=/dev/sdX bs=4M status=progressBoot the Raspberry Pi,
Insert the SD card into your Raspberry Pi and power it on. The Pi should boot from the Yocto image.Login to your device and run the below command to verify the kanto components.
systemctl status \ suite-connector.service \ container-management.service \ software-update.service \ file-upload.service \ file-backup.service \ system-metrics.service \ kanto-update-manager.service
4 - References
4.1 - Remote connectivity configuration
4.1.1 - AWS Connector configuration
Properties
To control all aspects of the aws connector behavior.
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| topicFilter | string | Regex filter used to block incoming messages by their topic | |
| payloadFilters | string | Regex filters used to exclude parts of the incoming messages payload | |
| Remote connectivity | |||
| address | string | Address of the MQTT endpoint that the connector will connect for the remote communication, the format is: scheme://host:port | |
| tenantId | string | default-tenant-id | Tenant unique identifier that the device belongs to |
| clientId | string | MQTT client unique identifier | |
| Remote connectivity - TLS | |||
| alpn | string[] | TLS application layer protocol negotiation options space separated for cloud access | |
| caCert | string | aws.crt | PEM encoded CA certificates file |
| cert | string | PEM encoded certificate file to authenticate to the MQTT endpoint | |
| key | string | PEM encoded unencrypted private key file to authenticate to the MQTT endpoint | |
| Remote connectivity - TLS over TPM | |||
| tpmDevice | string | Path to the device file or the unix socket to access the TPM 2.0 | |
| tpmHandle | int | TPM 2.0 storage root key handle, the type is unsigned 64-bit integer | |
| tpmKeyPub | string | File path to the public part of the TPM 2.0 key | |
| tpmKey | string | File path to the private part of the TPM 2.0 key | |
| Local connectivity | |||
| localAddress | string | tcp://localhost:1883 | Address of the MQTT server/broker that the aws connector will connect for the local communication, the format is: scheme://host:port |
| localUsername | string | Username that is a part of the credentials | |
| localPassword | string | Password that is a part of the credentials | |
| Local connectivity - TLS | |||
| localCACert | string | PEM encoded CA certificates file | |
| localCert | string | PEM encoded certificate file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| localKey | string | PEM encoded unencrypted private key file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| Logging | |||
| logFile | string | logs/aws-connector.log | Path to the file where log messages are written |
| logLevel | string | INFO | All log messages at this or a higher level will be logged, the log levels in descending order are: ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG and TRACE |
| logFileCount | int | 5 | Log file maximum rotations count |
| logFileMaxAge | int | 28 | Log file rotations maximum age in days, use 0 to not remove old log files |
| logFileSize | int | 2 | Log file size in MB before it gets rotated |
Example
The minimal required configuration to connect.
{
"address": "tls://<AWS-endpoint-address>:8883",
"caCert": "AmazonRootCA1.pem",
"cert": "example-device.crt",
"key": "example-device.key",
"clientId": "org.eclipse.kanto:exampleDevice",
"logFile": "/var/log/aws-connector/aws-connector.log"
}
Template
The configuration can be further adjusted according to the use case. The following template illustrates all possible properties with their default values.
{
"topicFilter": "",
"payloadFilters": [],
"address": "",
"tenantId": "default-tenant-id",
"clientId": "",
"alpn" : [],
"caCert": "aws.crt",
"cert": "",
"key": "",
"tpmDevice": "",
"tpmHandle": 0,
"tpmKeyPub": "",
"tpmKey": "",
"localAddress": "tcp://localhost:1883",
"localUsername": "",
"localPassword": "",
"localCACert": "",
"localCert": "",
"localKey": "",
"logFile": "logs/aws-connector.log",
"logLevel": "INFO",
"logFileCount": 5,
"logFileMaxAge": 28,
"logFileSize": 2
}
4.1.2 - Azure Connector configuration
Properties
To control all aspects of the azure connector behavior.
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| tenantId | string | defaultTenant | Tenant unique identifier that the device belongs to |
| connectionString | string | The connection string for connectivity to Azure IoT Hub, the format is: "HostName=newHostName.azure-devices.net;DeviceId=deviceId;SharedAccessKey=accessKey" | |
| sasTokenValidity | string | 1h | The validity period for the generated SAS token for device authentication. Positive integer number followed by a unit suffix, such as ‘300m’, ‘1h’, etc., time units are: m, h, d |
| idScope | string | ID scope for Azure Device Provisioning service | |
| Remote connectivity - TLS | |||
| alpn | string[] | TLS application layer protocol negotiation options space separated for cloud access | |
| caCert | string | iothub.crt | PEM encoded CA certificates file |
| cert | string | PEM encoded certificate file to authenticate to the MQTT endpoint | |
| key | string | PEM encoded unencrypted private key file to authenticate to the MQTT endpoint | |
| Remote connectivity - TLS over TPM | |||
| tpmDevice | string | Path to the device file or the unix socket to access the TPM 2.0 | |
| tpmHandle | int | TPM 2.0 storage root key handle, the type is unsigned 64-bit integer | |
| tpmKeyPub | string | File path to the public part of the TPM 2.0 key | |
| tpmKey | string | File path to the private part of the TPM 2.0 key | |
| Local connectivity | |||
| localAddress | string | tcp://localhost:1883 | Address of the MQTT server/broker that the azure connector will connect for the local communication, the format is: scheme://host:port |
| localUsername | string | Username that is a part of the credentials | |
| localPassword | string | Password that is a part of the credentials | |
| Local connectivity - TLS | |||
| localCACert | string | PEM encoded CA certificates file | |
| localCert | string | PEM encoded certificate file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| localKey | string | PEM encoded unencrypted private key file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| Logging | |||
| logFile | string | logs/azure-connector.log | Path to the file where log messages are written |
| logLevel | string | INFO | All log messages at this or a higher level will be logged, the log levels in descending order are: ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG and TRACE |
| logFileCount | int | 5 | Log file maximum rotations count |
| logFileMaxAge | int | 28 | Log file rotations maximum age in days, use 0 to not remove old log files |
| logFileSize | int | 2 | Log file size in MB before it gets rotated |
Example
The minimal required configuration to connect.
{
"connectionString": "HostName=hostName.azure-devices.net;DeviceId=deviceId;SharedAccessKey=cGFzc3AvcKQ=",
"caCert": "/etc/azure-connector/iothub.crt",
"logFile": "/var/log/azure-connector/azure-connector.log"
}
Template
The configuration can be further adjusted according to the use case. The following template illustrates all possible properties with their default values.
{
"tenantId": "defaultTenant",
"connectionString": "",
"sasTokenValidity": "1h",
"idScope": "",
"alpn" : [],
"caCert": "iothub.crt",
"cert": "",
"key": "",
"tpmDevice": "",
"tpmHandle": 0,
"tpmKeyPub": "",
"tpmKey": "",
"localAddress": "tcp://localhost:1883",
"localUsername": "",
"localPassword": "",
"localCACert": "",
"localCert": "",
"localKey": "",
"logFile": "logs/azure-connector.log",
"logLevel": "INFO",
"logFileCount": 5,
"logFileMaxAge": 28,
"logFileSize": 2
}
4.1.3 - Suite connector configuration
Properties
To control all aspects of the suite connector behavior.
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote connectivity | |||
| address | string | mqtts://mqtt.bosch-iot-hub.com:8883 | Address of the MQTT endpoint that the suite connector will connect for the remote communication, the format is: scheme://host:port |
| deviceId | string | Device unique identifier | |
| authId | string | Authentication unique identifier that is a part of the credentials | |
| tenantId | string | Tenant unique identifier that the device belongs to | |
| username | string | MQTT username that is a part of the credentials. This parameter takes precedence over authId and tenantId | |
| password | string | Password that is a part of the credentials | |
| clientId | string | MQTT client unique identifier | |
| policyId | string | Policy unique identifier of the digital twin | |
| generic | bool | Force use of modified topics for cloud access | |
| Remote connectivity - TLS | |||
| alpn | string[] | TLS application layer protocol negotiation options space separated for cloud access | |
| caCert | string | iothub.crt | PEM encoded CA certificates file |
| cert | string | PEM encoded certificate file to authenticate to the MQTT endpoint | |
| key | string | PEM encoded unencrypted private key file to authenticate to the MQTT endpoint | |
| deviceIdPattern | string | Pattern to generate the device identifier, {{subject-dn}} and {{subject-cn}} placeholders can be part of it | |
| Remote connectivity - TLS over TPM | |||
| tpmDevice | string | Path to the device file or the unix socket to access the TPM 2.0 | |
| tpmHandle | int | TPM 2.0 storage root key handle, the type is unsigned 64-bit integer | |
| tpmKeyPub | string | File path to the public part of the TPM 2.0 key | |
| tpmKey | string | File path to the private part of the TPM 2.0 key | |
| Local connectivity | |||
| localAddress | string | tcp://localhost:1883 | Address of the MQTT server/broker that the suite connector will connect for the local communication, the format is: scheme://host:port |
| localUsername | string | Username that is a part of the credentials | |
| localPassword | string | Password that is a part of the credentials | |
| Local connectivity - TLS | |||
| localCACert | string | PEM encoded CA certificates file | |
| localCert | string | PEM encoded certificate file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| localKey | string | PEM encoded unencrypted private key file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| Logging | |||
| logFile | string | log/suite-connector.log | Path to the file where log messages are written |
| logLevel | string | INFO | All log messages at this or a higher level will be logged, the log levels in descending order are: ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG and TRACE |
| logFileCount | int | 5 | Log file maximum rotations count |
| logFileMaxAge | int | 28 | Log file rotations maximum age in days, use 0 to not remove old log files |
| logFileSize | int | 2 | Log file size in MB before it gets rotated |
Example
The minimal required configuration to connect the publicly available Eclipse Hono sandbox.
{
"address": "hono.eclipseprojects.io:1883",
"caCert": "/etc/suite-connector/iothub.crt",
"tenantId": "org.eclipse.kanto",
"deviceId": "org.eclipse.kanto:exampleDevice",
"authId": "org.eclipse.kanto_example",
"password": "secret",
"logFile": "/var/log/suite-connector/suite-connector.log"
}
Template
The configuration can be further adjusted according to the use case. The following template illustrates all possible properties with their default values.
{
"address": "mqtts://mqtt.bosch-iot-hub.com:8883",
"deviceId": "",
"authId": "",
"tenantId": "",
"username": "",
"password": "",
"clientId": "",
"policyId": "",
"generic": false,
"alpn" : [],
"caCert": "iothub.crt",
"cert": "",
"key": "",
"deviceIdPattern": "",
"tpmDevice": "",
"tpmHandle": 0,
"tpmKeyPub": "",
"tpmKey": "",
"localAddress": "tcp://localhost:1883",
"localUsername": "",
"localPassword": "",
"localCACert": "",
"localCert": "",
"localKey": "",
"logFile": "log/suite-connector.log",
"logLevel": "INFO",
"logFileCount": 5,
"logFileMaxAge": 28,
"logFileSize": 2
}
4.1.4 - Local digital twins configuration
Properties
To control all aspects of the local digital twins behavior.
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| thingsDb | string | things.db | Path to the file where digital twins will be stored |
| Remote connectivity | |||
| address | string | mqtts://mqtt.bosch-iot-hub.com:8883 | Address of the MQTT endpoint that the local digital twins will connect for the remote communication, the format is: scheme://host:port |
| deviceId | string | Device unique identifier | |
| authId | string | Authentication unique identifier that is a part of the credentials | |
| tenantId | string | Tenant unique identifier that the device belongs to | |
| password | string | Password that is a part of the credentials | |
| clientId | string | MQTT client unique identifier | |
| policyId | string | Policy unique identifier of the digital twin | |
| Remote connectivity - TLS | |||
| caCert | string | iothub.crt | PEM encoded CA certificates file |
| cert | string | PEM encoded certificate file to authenticate to the MQTT endpoint | |
| key | string | PEM encoded unencrypted private key file to authenticate to the MQTT endpoint | |
| deviceIdPattern | string | Pattern to generate the device identifier, {{subject-dn}} and {{subject-cn}} placeholders can be part of it | |
| Remote connectivity - TLS over TPM | |||
| tpmDevice | string | Path to the device file or the unix socket to access the TPM 2.0 | |
| tpmHandle | int | TPM 2.0 storage root key handle, the type is unsigned 64-bit integer | |
| tpmKeyPub | string | File path to the public part of the TPM 2.0 key | |
| tpmKey | string | File path to the private part of the TPM 2.0 key | |
| Local connectivity | |||
| localAddress | string | tcp://localhost:1883 | Address of the MQTT server/broker that the local digital twins will connect for the local communication, the format is: scheme://host:port |
| localUsername | string | Username that is a part of the credentials | |
| localPassword | string | Password that is a part of the credentials | |
| Local connectivity - TLS | |||
| localCACert | string | PEM encoded CA certificates file | |
| localCert | string | PEM encoded certificate file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| localKey | string | PEM encoded unencrypted private key file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| Logging | |||
| logFile | string | log/local-digital-twins.log | Path to the file where log messages are written |
| logLevel | string | INFO | All log messages at this or a higher level will be logged, the log levels in descending order are: ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG and TRACE |
| logFileCount | int | 5 | Log file maximum rotations count |
| logFileMaxAge | int | 28 | Log file rotations maximum age in days, use 0 to not remove old log files |
| logFileSize | int | 2 | Log file size in MB before it gets rotated |
Example
The minimal required configuration to enable the local digital twins and their synchronization with the publicly available Eclipse Hono sandbox.
{
"address": "hono.eclipseprojects.io:1883",
"caCert": "/etc/local-digital-twins/iothub.crt",
"tenantId": "org.eclipse.kanto",
"deviceId": "org.eclipse.kanto:exampleDevice",
"authId": "org.eclipse.kanto_example",
"password": "secret",
"thingsDb": "/var/lib/local-digital-twins/thing.db",
"logFile": "/var/log/local-digital-twins/local-digital-twins.log"
}
Template
The configuration can be further adjusted according to the use case. The following template illustrates all possible properties with their default values.
{
"thingsDb": "things.db",
"address": "mqtts://mqtt.bosch-iot-hub.com:8883",
"deviceId": "",
"authId": "",
"tenantId": "",
"password": "",
"clientId": "",
"policyId": "",
"caCert": "iothub.crt",
"cert": "",
"key": "",
"deviceIdPattern": "",
"tpmDevice": "",
"tpmHandle": 0,
"tpmKeyPub": "",
"tpmKey": "",
"localAddress": "tcp://localhost:1883",
"localUsername": "",
"localPassword": "",
"localCACert": "",
"localCert": "",
"localKey": "",
"logFile": "log/local-digital-twins.log",
"logLevel": "INFO",
"logFileCount": 5,
"logFileMaxAge": 28,
"logFileSize": 2
}
4.2 - Container management configuration
4.2.1 - Manager configuration
Properties
To control all aspects of the container manager behavior.
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| home_dir | string | /var/lib/container-management | Home directory for the container manager data |
| exec_root_dir | string | /var/run/container-management | Root directory for the container manager’s executable artifacts |
| container_client_sid | string | container-management.service.local.v1.service-containerd-client | Unique identifier that is used for an interaction with the runtime |
| network_manager_sid | string | container-management.service.local.v1.service-libnetwork-manager | Unique identifier that is used for networking |
| default_ctrs_stop_timeout | string | 30s | Timeout for a container to stop gracefully in duration string format (e.g. 1h2m3s5ms), otherwise its root process will be forcefully stopped |
| Runtime | |||
| default_ns | string | kanto-cm | Namespace that is used by the runtime for isolation |
| address_path | string | /run/containerd/containerd.sock | Path to the runtime’s communication endpoint |
| home_dir | string | /var/lib/container-management | Home directory for the runtime data |
| exec_root_dir | string | /var/run/container-management | Root directory for the runtime’s executable artifacts |
| image_dec_keys | string[] | Private keys (GPG private key ring, JWE or PKCS7) used for decrypting container images, the format is: filepath_private_key[:password] | |
| image_dec_recipients | string[] | Recipients (only for PKCS7 and must be an x509) used for decrypting container images, the format is: pkcs7:filepath_x509_certificate | |
| runc_runtime | string | io.containerd.runc.v2 | Runc communication mode, the possible values are: io.containerd.runtime.v1.linux, io.containerd.runc.v1 and io.containerd.runc.v2 |
| image_expiry | string | 744h | Time period for the cached images and content to be kept in the form of e.g. 72h3m0.5s |
| image_expiry_disable | bool | false | Disable expiry management of cached images and content, must be used with caution as it may lead to large memory volumes being persistently allocated |
| lease_id | string | kanto-cm.lease | Lease identifier to be used for container resources persistence |
| image_verifier_type | string | none | The image verifier type - possible values are none and notation, when set to none image signatures wil not be verified |
| image_verifier_config | map[string]string | The configuration of the image verifier, as a string map - possible keys for notation verifier are configDir and libexecDir, for more info check notation documentation | |
| Registry access - secure | |||
| user_id | string | User unique identifier to authenticate to the image registry | |
| password | string | Password to authenticate to the image registry | |
| root_ca | string | PEM encoded CA certificates file | |
| client_cert | string | PEM encoded certificate file to authenticate to the image registry | |
| client_key | string | PEM encoded unencrypted private key file to authenticate to the image registry | |
| Registry access - insecure | |||
| insecure_registries | string[] | localhost | Image registries that do not use valid certificates or do not require a HTTPS connection, the format is: host[:port] |
| Networking | |||
| home_dir | string | /var/lib/container-management | Home directory for the network manager data |
| exec_root_dir | string | /var/run/container-management | Root directory for the network manager’s executable artifacts |
| Networking - bridge | |||
| name | string | kanto-cm0 | Bridge name |
| ip4 | string | Bridge IPv4 address | |
| fcidr4 | string | IPv4 address range for the bridge, using the standard CIDR notation | |
| gwip4 | string | Bridge gateway IPv4 address | |
| enable_ip6 | bool | false | Permit the bridge IPv6 support |
| mtu | int | 1500 | Bridge maximum transmission unit in bytes |
| icc | bool | true | Permit the inter-container communication |
| ip_tables | bool | true | Permit the IP tables rules |
| ip_forward | bool | true | Permit the IP forwarding |
| ip_masq | bool | true | Permit the IP masquerading |
| userland_proxy | bool | false | Forbid the userland proxy for the loopback traffic |
| Local communication | |||
| protocol | string | unix | Communication protocol used for accessing the gRPC server, the possible values are: tcp, tcp4, tcp6, unix or unixpacket |
| address_path | string | /run/container-management/container-management.sock | Path to the gRPC server’s communication endpoint |
| Digital twin | |||
| enable | bool | true | Permit the container manager digital twin representation |
| home_dir | string | /var/lib/container-management | Home directory for the digital twin data |
| features | string[] | ContainerFactory, SoftwareUpdatable, Metrics | Features that will be registered for the container manager digital twin, the possible values are: ContainerFactory, SoftwareUpdatable and Metrics |
| Update Agent | |||
| enable | bool | true | Permit the containers update agent service |
| domain | string | containers | The domain of the update agent, used as a prefix in MQTT topic handled by the update agent implementation |
| containers | string[] | List of system (core) containers that shall not be updated/destroyed by the containers update agent | |
| verbose_inventory_report | bool | false | Includes extensive, verbose key-value properties in containers software nodes for the current state report. If not set, only valuable and non-default key-value parameters are reported |
| Local connectivity | |||
| broker_url | string | tcp://localhost:1883 | Address of the MQTT server/broker that the container manager will connect for the local communication, the format is: scheme://host:port |
| keep_alive | string | 20s | Keep alive duration for the MQTT requests, duration string format, e.g. 1h2m3s5ms |
| disconnect_timeout | string | 250ms | Disconnect timeout for the MQTT server/broker, duration string format, e.g. 1h2m3s5ms |
| client_username | string | Username that is a part of the credentials | |
| client_password | string | Password that is a part of the credentials | |
| connect_timeout | string | 30s | Connect timeout for the MQTT server/broker, duration string format, e.g. 1h2m3s5ms |
| acknowledge_timeout | string | 15s | Acknowledge timeout for the MQTT requests, duration string format, e.g. 1h2m3s5ms |
| subscribe_timeout | string | 15s | Subscribe timeout for the MQTT requests, duration string format, e.g. 1h2m3s5ms |
| unsubscribe_timeout | string | 5s | Unsubscribe timeout for the MQTT requests, duration string format, e.g. 1h2m3s5ms |
| Local connectivity - TLS | |||
| root_ca | string | PEM encoded CA certificates file | |
| client_cert | string | PEM encoded certificate file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| client_key | string | PEM encoded unencrypted private key file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| Logging | |||
| log_file | string | log/container-management.log | Path to the file where the container manager’s log messages are written |
| log_level | string | INFO | All log messages at this or a higher level will be logged, the log levels in descending order are: ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG and TRACE |
| log_file_count | int | 5 | Log file maximum rotations count |
| log_file_max_age | int | 28 | Log file rotations maximum age in days, use 0 to not remove old log files |
| log_file_size | int | 2 | Log file size in MB before it gets rotated |
| syslog | bool | false | Route logs to the local syslog |
| Deployment | |||
| enable | bool | true | Permit the deployment manager service providing installation/update of containers via the container descriptor files |
| mode | string | update | Deployment manager mode, the possible values are: init (container descriptors are processed only on first start, new containers are deployed and started), update (container descriptors are processed on each restart, new containers can be deployed and started, existing containers may be updated, no container removals) |
| home_dir | string | /var/lib/container-management | Home directory for the deployment manager data |
| ctr_dir | string | /etc/container-management/containers | Directory containing descriptors of containers that will be automatically deployed on first start or updated on restart |
Example
The minimal required configuration that sets a timeout period of 5 seconds for the managed containers to stop gracefully.
{
"manager": {
"default_ctrs_stop_timeout": 5
},
"log": {
"log_file": "/var/log/container-management/container-management.log"
}
}
Template
The configuration can be further adjusted according to the use case. The following template illustrates all possible properties with their default values.
{
"manager": {
"home_dir": "/var/lib/container-management",
"exec_root_dir": "/var/run/container-management",
"container_client_sid": "container-management.service.local.v1.service-containerd-client",
"network_manager_sid": "container-management.service.local.v1.service-libnetwork-manager",
"default_ctrs_stop_timeout": 30
},
"containers": {
"default_ns": "kanto-cm",
"address_path": "/run/containerd/containerd.sock",
"exec_root_dir": "/var/run/container-management",
"home_dir": "/var/lib/container-management",
"image_dec_keys": [],
"image_dec_recipients": [],
"runc_runtime": "io.containerd.runc.v2",
"image_expiry": "744h",
"image_expiry_disable": false,
"image_verifier_type": "notation",
"image_verifier_config": {
"configDir": "/home/user/.config/notation"
},
"lease_id": "kanto-cm.lease",
"registry_configurations": {
"": {
"credentials": {
"user_id": "",
"password": ""
},
"transport": {
"root_ca": "",
"client_cert": "",
"client_key": ""
}
}
},
"insecure_registries": [
"localhost"
]
},
"network": {
"home_dir": "/var/lib/container-management",
"exec_root_dir": "/var/run/container-management",
"default_bridge": {
"name": "kanto-cm0",
"ip4": "",
"fcidr4": "",
"enable_ip6": false,
"mtu": 1500,
"icc": true,
"ip_tables": true,
"ip_forward": true,
"ip_masq": true,
"userland_proxy": false
}
},
"grpc_server": {
"protocol": "unix",
"address_path": "/run/container-management/container-management.sock"
},
"things": {
"enable": true,
"home_dir": "/var/lib/container-management",
"features": [
"ContainerFactory",
"SoftwareUpdatable",
"Metrics"
],
"update_agent": {
"enable": true,
"domain": "containers",
"system_containers": [
"my-core-container-that-is-auto-deployed-and-updatable-only-through-firmware-update"
],
"verbose_inventory_report": false,
},
"connection": {
"broker_url": "tcp://localhost:1883",
"keep_alive": "20s",
"disconnect_timeout": "250ms",
"client_username": "",
"client_password": "",
"connect_timeout": "30s",
"acknowledge_timeout": "15s",
"subscribe_timeout": "15s",
"unsubscribe_timeout": "5s",
"transport": {
"root_ca": "",
"client_cert": "",
"client_key": ""
}
},
"log": {
"log_file": "log/container-management.log",
"log_level": "INFO",
"log_file_count": 5,
"log_file_size": 2,
"log_file_max_age": 28,
"syslog": false
},
"deployment": {
"enable": true,
"mode": "update",
"home_dir": "/var/lib/container-management",
"ctr_dir": "/etc/container-management/containers"
}
}
4.2.2 - Container configuration
Properties
To control all aspects of the container instance behavior.
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| container_name | string | <container_id> | User-defined name for the container, if omitted the internally auto-generated container ID will be set |
| Image | |||
| name | string | Fully qualified image reference, that follows the OCI Image Specification, the format is: host[:port]/[namespace/]name:tag | |
| Image - decryption | |||
| keys | string[] | Private keys (GPG private key ring, JWE or PKCS7) used for decrypting the container’s image, the format is: filepath_private_key[:password] | |
| recipients | string[] | Recipients (only for PKCS7 and must be an x509) used for decrypting the container’s image, the format is: pkcs7:filepath_x509_certificate | |
| Networking | |||
| domain_name | string | <container_name>-domain | Domain name inside the container, if omitted the container_name with suffix -domain will be set |
| host_name | string | <container_name>-host | Host name for the container, if omitted the container_name with suffix -host will be set |
| network_mode | string | bridge | The container’s networking capabilities type based on the desired communication mode, the possible options are: bridge or host |
| extra_hosts | string[] | Extra host name to IP address mappings added to the container network configuration, the format is: hostname:ip. If the IP of the host machine is to be added to the container’s hosts file the reserved host_ip[_<network-interface>] must be provided. If only host_ip (the network-interface part is skipped) is used, by default it will be resolved to the host’s IP on the default bridge network interface for containerm (the default configuration is kanto-cm0) and add it to the container’s hosts file. If the IP of a container in the same bridge network is to be added to the hosts file the reserved container_<container-host_name> must be provided. | |
| Networking - port mappings | |||
| proto | string | tcp | Protocol used for the port mapping from the container to the host, the possible options are: tcp and udp |
| container_port | int | Port number on the container that is mapped to the host port | |
| host_ip | string | 0.0.0.0 | Host IP address |
| host_port | int | Beginning of the host ports range | |
| host_port_end | int | <host_port> | Ending of the host ports range |
| Host resources - devices | |||
| path_on_host | string | Path to the device on the host | |
| path_in_container | string | Path to the device in the container | |
| cgroup_permissions | string | rwm | Cgroup permissions for the device access, possible options are: r(read), w(write), m(mknod) and all combinations are possible |
| privileged | bool | false | Grant root capabilities to all devices on the host system |
| extra_capabilities | string[] | Add additional Linux capabilities to the container | |
| Host resources - mount points | |||
| source | string | Path to the file or directory on the host that is referred from within the container | |
| destination | string | Path to the file or directory that is mounted inside the container | |
| propagation_mode | string | rprivate | Bind propagation for the mount, supported are: rprivate, private, rshared, shared, rslave or slave |
| Process | |||
| env | string[] | Environment variables that are set into the container | |
| cmd | string[] | Command with arguments that is executed upon the container’s start | |
| I/O | |||
| open_stdin | bool | Open the terminal’s standard input for an interaction with the current container | |
| tty | bool | Attach standard streams to a TTY | |
| Resource management | |||
| memory | string | Hard memory limitation of the container as a number with a unit suffix of B, K, M and G, the minimum allowed value is 3M | |
| memory_reservation | string | Soft memory limitation of the container as a number with a unit suffix of B, K, M and G, if memory is specified, the memory_reservation must be smaller than it | |
| memory_swap | string | Total amount of memory and swap that the container can use as a number with a unit suffix of B, K, M and G, use -1 to allow the container to use unlimited swap | |
| Lifecycle | |||
| type | string | unless-stopped | The container’s restart policy, the supported types are: always, no, on-failure and unless-stopped |
| maximum_retry_count | int | Maximum number of retries that are made to restart the container on exit with fail, if the type is on-failure | |
| retry_timeout | int | Timeout period in seconds for each retry that is made to restart the container on exit with fail, if the type is on-failure | |
| Logging | |||
| type | string | json-file | Type in which the logs are produced, the possible options are: json-file or none |
| max_files | int | 2 | Maximum log files before getting rotated |
| max_size | string | 100M | Maximum log file size before getting rotated as a number with a unit suffix of B, K, M and G |
| root_dir | string | <meta_path>/containers/<container_id> | Root directory where the container’s log messages are stored |
| mode | string | blocking | Messaging delivery mode from the container to the log driver, the supported modes are: blocking and non-blocking |
| max_buffer_size | string | 1M | Maximum size of the buffered container’s log messages in a non-blocking mode as a number with a unit suffix of B, K, M and G |
Example
The minimal required configuration to spin up an InfluxDB container instance.
{
"image": {
"name": "docker.io/library/influxdb:1.8.4"
}
}
Template
The configuration can be further adjusted according to the use case. The following template illustrates all possible properties with their default values.
{
"container_name": "",
"image": {
"name": "",
"decrypt_config": {
"keys": [],
"recipients": []
}
},
"domain_name": "",
"host_name": "",
"mount_points": [
{
"destination": "",
"source": "",
"propagation_mode": "rprivate"
}
],
"config": {
"env": [],
"cmd": []
},
"io_config": {
"open_stdin": false,
"tty": false
},
"host_config": {
"devices": [
{
"path_on_host": "",
"path_in_container": "",
"cgroup_permissions": "rwm"
}
],
"network_mode": "bridge",
"privileged": false,
"extra_hosts": [],
"extra_capabilities": [],
"port_mappings": [
{
"proto": "tcp",
"container_port": 0,
"host_ip": "0.0.0.0",
"host_port": 0,
"host_port_end": 0
}
],
"resources": {
"memory": "",
"memory_reservation": "",
"memory_swap": ""
},
"restart_policy": {
"type": "unless-stopped",
"maximum_retry_count": 0,
"retry_timeout": 0
},
"log_config": {
"driver_config": {
"type": "json-file",
"max_files": 2,
"max_size": "100M",
"root_dir": ""
},
"mode_config": {
"mode": "blocking",
"max_buffer_size": "1M"
}
}
}
}
4.2.3 - API Reference
4.2.3.1 - Container Factory API
Create
Create a container from a single container image reference with an option to start it.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/req//create
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/createInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/ContainerFactory/inbox/messages/createA path to the ContainerFactoryFeature, it’s message channel, and commandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id container UUID The container UUID Value imageRef URL Fully qualified image reference, that follows the OCI Image Specification, the format is: host[:port]/[namespace/]name:tagstart true/false Start or only create the container
Example : Create and automatically start a new Hello World container.
Topic: command//edge:device:edge:containers/req//create
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/create",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/ContainerFactory/inbox/messages/create",
"value":{
"imageRef":"docker.io/library/hello-world:latest",
"start":true
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/res//create
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/createInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/ContainerFactory/outbox/messages/createA path to the Feature, it’s message channel, and command Headers Additional headers content-type application/json The content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the request message Value UUID of the created container
Example : Response of a create operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device:edge:containers/res//create``
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/create",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/ContainerFactory/outbox/messages/create",
"value":"<Container UUID>"
}
Create with config
Create a container with a specified container configuration.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/req//createWithConfig
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/createWithConfigInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/ContainerFactory/inbox/messages/createWithConfigA path to the ContainerFactoryFeature, it’s message channel, and commandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id container UUID The container UUID Value imageRef URL Fully qualified image reference, that follows the OCI Image Specification, the format is: host[:port]/[namespace/]name:tagstart true/false Force to start created container config json presentation of the configuration domainName Domain name inside the container, if omitted the container’s domain name will be set to a system-defined value hostName Host name for the container, if omitted the container’s hostname will be set to a system-defined value env An array of environment variables that are set into the container cmd An array of command with arguments that is executed upon the container’s start privileged false Grant root capabilities to all devices on the host system extraHosts An array of additional extra host names to IP address mappings added to the container network configuration, the format is: hostname:ip. If the IP of the host machine is to be added to the container’s hosts file the reserved host_ip[ ] must be provided. If only host_ip (the network-interface part is skipped) is used, by default it will be resolved to the host’s IP on the default bridge network interface for containerm (the default configuration is kanto-cm0) and add it to the container’s hosts file. If the IP of a container in the same bridge network is to be added to the hosts file the reserved container <container-host_name> must be provided.extraCapabilities An array of additional capabilities for a container networkMode The container’s networking capabilities type based on the desired communication mode. The possible options are: bridge or host openStdin true/false Open the terminal’s standard input for an interaction with the current container tty true/false Attach standard streams to a TTY mountPoints An array of the mount points source Path to the file or directory on the host that is referred from within the container destination Path to the file or directory that is mounted inside the container propagationMode Bind propagation for the mount, supported are: rprivate, private, rshared, shared, rslave or slave decryption keys A string array of private keys (GPG private key ring, JWE or PKCS7) used for decrypting the container’s image, the format is: filepath_private_key[:password]recipients A string array of recipients (only for PKCS7 and must be an x509) used for decrypting the container’s image, the format is: pkcs7:filepath_x509_certificatedevices An array of accessible devices from the host pathOnHost Path to the device on the host pathInContainer Path to the device in the container cgroupPermissions rwm Cgroup permissions for the device access, possible options are: r(read), w(write), m(mknod) and all combinations are possible restartPolicy The container restart policy type unless-stopped The container’s restart policy, the supported types are: always, no, on-failure and unless-stopped maxRetryCount Maximum number of retries that are made to restart the container on exit with fail, if the typeis on-failureretryTimeout Timeout period in seconds for each retry that is made to restart the container on exit with fail, if the typeis on-failureportMappings An array of port mappings from the host to a container proto tcp Protocol used for the port mapping from the container to the host, the possible options are: tcp and udp containerPort Port number on the container that is mapped to the host port hostIP 0.0.0.0 Host IP address hostPort Beginning of the host ports range hostPortEnd <host_port> Ending of the host ports range log type json-file Type in which the logs are produced, the possible options are: json-file or none maxFiles 2 Maximum log files before getting rotated maxSize 100M Maximum log file size before getting rotated as a number with a unit suffix of B, K, M and G rootDir <meta_path>/containers/<container_id> Root directory where the container’s log messages are stored mode blocking Messaging delivery mode from the container to the log driver, the supported modes are: blocking and non-blocking maxBufferSize 1M Maximum size of the buffered container’s log messages in a non-blocking mode as a number with a unit suffix of B, K, M and G resources memory Hard memory limitation of the container as a number with a unit suffix of B, K, M and G, the minimum allowed value is 3M memoryReservation Soft memory limitation of the container as a number with a unit suffix of B, K, M and G, if memoryis specified, thememoryReservationmust be smaller than itmemorySwap Total amount of memory and swap that the container can use as a number with a unit suffix of B, K, M and G, use -1 to allow the container to use unlimited swap
Example : Create and automatically start a new Hello World container.
Topic: command//edge:device:edge:containers/req//createWithConfig
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/createWithConfig",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/ContainerFactory/inbox/messages/createWithConfig",
"value":{
"imageRef":"docker.io/library/influxdb:1.8.4",
"start":true,
"config":{
"domainName": "",
"hostName": "",
"env": [],
"cmd": [],
"privileged": false,
"extraHosts": ["ctrhost:host_ip"],
"extraCapabilities": [],
"networkMode": "bridge",
"openStdin": false,
"tty": false,
"mountPoints": [
{
"source": "",
"destination": "",
"propagationMode": "rprivate"
}
],
"decryption": {
"keys": [],
"recipients": []
},
"devices": [
{
"pathOnHost": "",
"pathInContainer": "",
"cgroupPermissions": "rwm"
}
],
"restartPolicy": {
"type": "unless-stopped",
"maxRetryCount": 0,
"retryTimeout": 0
},
"portMappings":[
{
"proto": "tcp",
"containerPort": 80,
"hostIP": "0.0.0.0",
"hostPort": 5000,
"hostPortEnd": 5005,
}
],
"log": {
"type": "json-file",
"maxFiles": 2,
"maxSize": "100M",
"rootDir": "",
"mode": "blocking",
"maxBufferSize": "1M"
},
"resources": {
"memory": "",
"memoryReservation": "",
"memorySwap": ""
},
}
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/res//createWithConfig
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/createWithConfigInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/ContainerFactory/outbox/messages/createWithConfigA path to the ContainerFactoryFeature, it’s message channel, and commandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> Value UUID of the created container
Example : Response of a createWithConfig operation.
Topic: command//edge:device:edge:containers/res//createWithConfig
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/createWithConfig",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/ContainerFactory/outbox/messages/createWithConfig",
"value":"<Container UUID>"
}
4.2.3.2 - Container API
Start
Start an existing container.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/req//start
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/startInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Container:<UUID>/inbox/messages/startA path to the ContainerFeature, it’s message channel, andstartcommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id container UUID The container UUID Value
Example : Start an existing container.
Topic: command//edge:device:edge:containers/req//start
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/start",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Container:<UUID>/inbox/messages/start",
"value":{}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/res//start
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/startInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Container:<UUID>/outbox/messages/startA path to the ContainerFeature, it’s message channel, andstartcommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the request message Status Status of the operation start over the container
Example : Response of a successful start operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device:edge:containers/res//start``
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/start",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Container:<UUID>/outbox/messages/start",
"status": 204
}
Stop
Stop an existing and running container.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/req//stop
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/stopInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Container:<UUID>/inbox/messages/stopA path to the ContainerFeature, it’s message channel, andstopcommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id container UUID The container UUID Value
Example : Stop an existing and running container.
Topic: command//edge:device:edge:containers/req//stop
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/stop",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Container:<UUID>/inbox/messages/stop",
"value":{}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/res//stop
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/stopInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Container:<UUID>/outbox/messages/stopA path to the ContainerFeature, it’s message channel, andstopcommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the request message Status Status of the operation stop over the container
Example : Response of a successful stop operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device:edge:containers/res//stop``
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/stop",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Container:<UUID>/outbox/messages/stop",
"status":204
}
Stop with options
Stop an existing and running container with given options.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/req//stopWithOptions
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/stopWithOptionsInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Container:<UUID>/inbox/messages/stopWithOptionsA path to the ContainerFeature, it’s message channel, andstopWithOptionscommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id container UUID The container UUID Value signal SIGTERMStop a container using a specific signal. Signals could be specified by using their names or numbers, e.g. SIGINTor 2timeout -1 « 63 // -9223372036854775808 Sets the timeout period in seconds to gracefully stop the container. When timeout expires the container process would be forcibly killed force true/false Whether to send a SIGKILL signal to the container’s process if it does not finish within the timeout specified
Example : Stop an existing and running container with specified options.
Topic: command//edge:device:edge:containers/req//stopWithOptions
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/stopWithOptions",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Container:<UUID>/inbox/messages/stopWithOptions",
"value":{
"signal":"SIGINT",
"timeout": 30,
"force": true
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/res//stopWithOptions
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/stopWithOptionsInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Container:<UUID>/outbox/messages/stopWithOptionsA path to the ContainerFeature, it’s message channel, andstopWithOptionscommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the request message Status Status of the operation stop with options over the container
Example : Response of a successful the stopWithOptions operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device:edge:containers/res//stopWithOptions``
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/stopWithOptions",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Container:<UUID>/outbox/messages/stopWithOptions",
"status":204
}
Rename
Change the name of an existing container to the specified new name.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/req//rename
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/renameInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Container:<UUID>/inbox/messages/renameA path to the ContainerFeature, it’s message channel, andrenamecommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id container UUID The container UUID Value The new name of the container
Example : Change the name of an existing container to the specified new name.
Topic: command//edge:device:edge:containers/req//rename
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/rename",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Container:<UUID>/inbox/messages/rename",
"value":"new_container_name"
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/res//rename
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/renameInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Container:<UUID>/outbox/messages/renameA path to the ContainerFeature, it’s message channel, andrenamecommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the request message Status Status of the operation rename container
Example : The response of the rename operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device:edge:containers/res//rename``
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/rename",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Container:<UUID>/outbox/messages/rename",
"status":204
}
Update
Update an existing container without recreating it. The provided configurations will be merged with the current one.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/req//update
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/updateInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Container:<UUID>/inbox/messages/updateA path to the ContainerFeature, it’s message channel, andupdatecommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id container UUID The container UUID Value restartPolicy Updates the restart policy for the container. The policy will be applied when the container exits type no/always/unless-stopped/on-failure The container’s restart policy, the supported types are: always, no, on-failure and unless-stopped maxRetryCount -1 « 31 // -2147483648 Maximum number of retries that are made to restart the container on exit with fail, if the typeis on-failuretimeout -1 « 63 // -9223372036854775808 Timeout period in seconds for each retry that is made to restart the container on exit with fail, if the typeis on-failureresources memory Hard memory limitation of the container as a number with a unit suffix of B, K, M and G, the minimum allowed value is 3M memoryReservation Soft memory limitation of the container as a number with a unit suffix of B, K, M and G, if memoryis specified, thememoryReservationmust be smaller than itmemorySwap Total amount of memory and swap that the container can use as a number with a unit suffix of B, K, M and G, use -1 to allow the container to use unlimited swap
Example : Update an existing container resources and restart policy.
Topic: command//edge:device:edge:containers/req//update
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/update",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Container:<UUID>/inbox/messages/update",
"value":{
"restartPolicy":{
"type":"on-failure",
"maxRetryCount":3,
"timeout":10
},
"resources":{
"memory":"500M",
"memoryReservation":"300M",
"memorySwap":"1G",
}
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/res//update
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/updateInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Container:<UUID>/outbox/messages/updateA path to the ContainerFeature, it’s message channel, andupdatecommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the request message Status Status of the updateoperation over the container
Example : Successful response of an update operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device:edge:containers/res//update``
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/update",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Container:<UUID>/outbox/messages/update",
"status":204
}
Remove
Remove an existing container.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/req//remove
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/removeInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Container:<UUID>/inbox/messages/removeA path to the ContainerFeature, it’s message channel, andremovecommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id container UUID The container UUID Value true/false Force stopping before removing a container
Example : Remove an existing container.
Topic: command//edge:device:edge:containers/req//remove
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/remove",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Container:<UUID>/inbox/messages/remove",
"value":true
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/res//remove
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/removeInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Container:<UUID>/outbox/messages/removeA path to the ContainerFeature, it’s message channel, andremovecommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the request message Status Status of the operation remove container
Example : Successful response of an remove operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device:edge:containers/res//remove``
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/remove",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Container:<UUID>/outbox/messages/remove",
"status":204
}
4.2.3.3 - Metrics API
Request
Request to receive data from the container.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/req//request
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/requestInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Metrics/inbox/messages/requestA path to the MetricsFeature, it’s message channel, andrequestcommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id container UUID The container UUID Value frequency Time interval of how often the metrics data will be published as duration string (e.g. 5s) filter Filter defines the type of metric data to be reported id An array of identifiers whose metric data to be reported, supported are: cpu.utilization,memory.utilization,memory.total,memory.used,io.readBytes,io.writeBytes,net.readBytes,net.writeBytes,pidsoriginator Metrics data originator
Example : Request metrics data with a specified filter and frequency.
Topic: command//edge:device:edge:containers/req//request
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/request",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Metrics/inbox/messages/request",
"value":{
"filter":[
{
"id":null,
"originator":"SYSTEM"
}
],
"frequency":"2s"
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/res//request
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/requestInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Metrics/outbox/messages/requestA path to the MetricsFeature, it’s message channel, andrequestcommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the sent request message Status Status of the requestmetrics operation
Example : The response of the request metrics data operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device:edge:containers/res//request``
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/request",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Metrics/outbox/messages/request",
"status": 204
}
Data
Metrics data from a container based on the frequency specified in the request.
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/res//data
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/dataInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Metrics/outbox/messages/dataA path to the MetricsFeature and it’s message channel.Headers Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type Value The value of the received data from the container in json format timestamp The timestamp in ms when this measure data is published shapshot All the measurements collected per originator originator The originator for whose metric data to be reported measurements An array of measurements identifier and value for originator id The identifier whose metric data to be reported, supported are: cpu.utilization,memory.utilization,memory.total,memory.used,io.readBytes,io.writeBytes,net.readBytes,net.writeBytes,pidsvalue The measured value per metric ID
Example : Metrics data from a container.
Topic: `command//edge:device:edge:containers/res//data``
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/data",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
},
"path":"/features/Metrics/outbox/messages/data",
"value":{
"snapshot":[
{
"originator":"Container:test",
"measurements":[
{
"id":"memory.total",
"value":10371616768
},
{
"id":"memory.used",
"value":1396736
},
{
"id":"memory.utilization",
"value":0.01346690714903206
},
{
"id":"net.readBytes",
"value":180
},
{
"id":"net.writeBytes",
"value":0
},
{
"id":"pids",
"value":6
}
]
},
{
"originator":"Container:test2",
"measurements":[
{
"id":"cpu.utilization",
"value":8.751566666666667
},
{
"id":"memory.total",
"value":10371616768
},
{
"id":"memory.used",
"value":4759552
},
{
"id":"memory.utilization",
"value":0.04589016453717083
},
{
"id":"io.readBytes",
"value":0
},
{
"id":"io.writeBytes",
"value":4096
},
{
"id":"net.readBytes",
"value":610
},
{
"id":"net.writeBytes",
"value":202
},
{
"id":"pids",
"value":14
}
]
}
],
"timestamp":1234567890
}
}
4.2.3.4 - Software Updatable API
Install
You can install a specified list of containers (software modules).
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/req//install
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/installInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/SoftwareUpdatable/inbox/messages/installA path to the SoftwareUpdatableFeature, it’s message channel, andinstallcommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id container UUID The container UUID Value correlationId Unique identifier that is used to associate and track the series of messages weight The weight is the priority in case of multiple, parallel instructions metadata The metadata is any other information which should be passed to the device forced true/false Forced to install the software modules softwareModules An array of modules that will be installed metadata The metadata is any other information which should be passed to the device softwareModule An unique identifier for the software module name The name of the software module version The version of the software module artifacts An array of artifacts contained in the software module filename The file name of the artifact behind the provided URLs size The size of the file in bytes download A map with protocols and links for artifact download key HTTP/HTTPS/FTP/SFTP Available transport protocols url URL to download the artifact md5url MD5URL to download the MD5SUM file checksums A map with checksums to verify the proper download MD5 MD5 checksum of the downloaded file SHA1 SHA1 checksum of the downloaded file SHA256 SHA256 checksum of the downloaded file
Example : In this example, you can install the listed modules.
Topic: command//edge:device:edge:containers/req//install
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/install",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/SoftwareUpdatable/inbox/messages/install",
"value":{
"correlationId":"other_correlation_id",
"forced":true,
"softwareModules":[
{
"softwareModule":{
"name":"influxdb",
"version":"1.8.4"
},
"artifacts":[
{
"filename":"valid.json",
"download":{
"HTTPS":{
"url":"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/eclipse-kanto/container-management/main/containerm/pkg/testutil/config/container/valid.json",
"md5url":"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/eclipse-kanto/container-management/main/containerm/pkg/testutil/config/container/valid.json"
}
},
"checksums":{
"MD5":"8c5a0fa2c01e218262d672bf643652fd",
"SHA1":"7539b451d818d94bcd97d401a5467b3e1c0b8981",
"SHA256":"be8f5def8e6a61caab078be0995826ae65f5993b1a35c18ed6045c3db37c4a3a"
},
"size":100
}
]
}
]
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/res//install
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/installInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/SoftwareUpdatable/outbox/messages/installA path to the SoftwareUpdatableFeature, it’s message channel, andinstallcommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the sent request message Status Status of the installoperation`
Example : Response of a successful install of the software modules.
Topic: `command//edge:device:edge:containers/res//install``
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/install",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/SoftwareUpdatable/outbox/messages/install",
"status": 204
}
Remove
Remove of an installed software module.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/req//remove
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/removeInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/SoftwareUpdatable/inbox/messages/removeA path to the SoftwareUpdatableFeature, it’s message channel, andremovecommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id container UUID The container UUID Value Json presentation of the software module to be removed correlationId Unique identifier that is used to associate and track the series of messages weight The weight is the priority in case of multiple, parallel instructions metadata The metadata is any other information which should be passed to the device forced true/false Force remove the software modules software An array of software modules to be removed group An identifier which groups the dependency into a certain category name The dependency name version The dependency version type The “category” classifier of the dependency
Example : In this example, you can remove an existing software modules.
Topic: command//edge:device:edge:containers/req//remove
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/remove",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/SoftwareUpdatable/inbox/messages/remove",
"value": {
"correlationId":"other_correlation_id",
"forced":true,
"software":[
{
"name":"influxdb",
"version":""
}
]
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>:edge:containers/res//remove
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>:edge:containers/things/live/messages/removeInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/SoftwareUpdatable/outbox/messages/removeA path to the SoftwareUpdatableFeature, it’s message channel, andremovecommandHeaders Additional headers correlation-id container UUID The container UUID Status Status of the operation remove software modules from container
Example : The response of successful removal of software modules.
Topic: `command//edge:device:edge:containers/res//remove``
{
"topic":"edge/device:edge:containers/things/live/messages/remove",
"headers":{
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/SoftwareUpdatable/outbox/messages/remove",
"status":204
}
4.2.4 - Container configuration as Desired State component
Domain Identifier
The default domain identifier for the Containers Update Agent is containers.
This can be modified within the update agent section in the container management JSON config file.
Containers Update Agent Properties
To control the container update agent behavior through desired state specification. As defined in the Desired State Specification, all properties are of type string.
| Key | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| systemContainers | No | Comma-separated list of container names that shall not be processed by the update agent during the application of the given desired state. This configuration option can be used to temporarily override the general systemContainers setting from the update agent section in the container management JSON config file. The setting is valid only for the given desired state where it is present. |
Container Properties
To control all aspects of the container instance behavior. As defined in the Desired State Specification, all properties are of type string.
| Key | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| General config | |||
| image | Yes | Fully qualified image reference, that follows the OCI Image Specification, the format is: host[:port]/[namespace/]name:tag. | |
| env | No | Sets the provided environment variable in the root container’s process environment.Example: VAR1=2. If VAR1= is used, the environment variable would be set to empty. If VAR1 is used, the environment variable would be removed from the container environment inherited from the image. The property can be included multiple times, each one specifying another environment variable. | |
| cmd | No | Command with arguments that is executed upon the container’s start. The property can be included multiple times (order is important), each one specifying another command argument. | |
| Host config | |||
| device | No | Device to be made available in the container and optional cgroups permissions configuration. Both path on host and in container must be set. Possible cgroup permissions options are “r” (read), “w” (write), “m” (mknod) and all combinations of the three are possible. If not set, “rwm” is default device configuration. Example: /dev/ttyACM0:/dev/ttyUSB0[:rwm]. The property can be included multiple times, each one specifying a separate device. | |
| port | No | Port to be mapped from the host to the container instance. Format: [<host-ip>:]<host-port>:<container-port>[-<range>][/<proto>]. Most common use-case: 80:80. Mapping the container’s 80 port to a host port in the 5000-6000 range: 5000-6000:80/udp. Specifying port protocol (default is tcp): 80:80/udp. By default the port mapping will set on all network interfaces, but this is also manageable: 0.0.0.0:80-100:80/udp. The property can be included multiple times, each one specifying another port mapping. | |
| network | No | bridge | Sets the networking mode for the container. Possible options are: bridge - the container is connected to the default bridge network interface of the engine and is assigned an IP. host - the container shares the network stack of the host (use with caution as this breaks the network’s isolation!) |
| host | No | Extra host to be added in the current container’s /etc/hosts file. Example: hostname1:host_ip[_<network-interface>] must be provided. Example: local.host.machine.ip.custom.if:host_ip_myNetIf0 - this will automatically resolve the host’s IP on the myNetIf0 network interface and add it to the container’s hosts file. local.host.machine.ip.default.bridge:host_ip - this will automatically resolve the host’s IP on the default bridge network interface for container management and add it to the container’s hosts file if the container is configured to use it. The property can be included multiple times, each one specifying another extra host | |
| mount | No | Sets mount points so a source directory on the host can be accessed via a destination directory in the container. Format: source:destination[:propagation_mode]. If the propagation mode parameter is omitted, rprivate will be set by default. Available propagation modes are: rprivate, private, rshared, shared, rslave, slave. The property can be included multiple times, each one specifying another mount point. | |
| IO config | |||
| terminal | No | false | Boolean flag. Enables terminal for the current container, e.g. attach standard streams to a TTY. |
| interactive | No | false | Boolean flag. Enables interaction with the container, e.g. open the terminal’s standard input for an interaction with the container. |
| privileged | No | false | Boolean flag. Creates the container as privileged, grants root capabilities to all devices on the host system |
| Restart policy config | |||
| restartPolicy | string | unless-stopped | The container’s restart policy, the supported values are: always - an attempt to restart the container will be made made each time the container exits regardless of the exit code, no - no attempts to restart the container for any reason will be made, on-failure - restart attempts will be made if the container exits with an exit code != 0, unless-stopped - restart attempts will be made only if the container has not been stopped by the user. |
| restartMaxRetries | No | 1 | Integer value. Maximum number of retries that are made to restart the container on exit with fail, valid only if the restartPolicy is on-failure. |
| restartTimeout | No | 30 | Integer value. Timeout period in seconds for each retry that is made to restart the container on exit with fail, valid only if the restartPolicy is on-failure. |
| Logging config | |||
| logDriver | No | json-file | Sets the type of the log driver to be used for the container - json-file, none. |
| logMaxFiles | No | 2 | Integer value. Sets the max number of log files to be rotated - applicable for json-file log driver only. |
| logMaxSize | No | 100M | Sets the max size of the logs files for rotation in the form of 1, 1.2m, 1g, etc. - applicable for json-file log driver only. |
| logPath | No | Sets the path to the directory where the log files will be stored - applicable for json-file log driver only. | |
| logMode | No | blocking | Sets the mode of the logger - blocking, non-blocking. |
| logMaxBufferSize | No | 1M | Sets the max size of the logger buffer in the form of 1, 1.2m - applicable for non-blocking mode only. |
| Resources config | |||
| memory | No | Sets the max amount of memory the container can use in the form of 200m, 1.2g. The minimum allowed value is 3m. By default, a container has no memory constraints. | |
| memorySwap | No | Sets the total amount of memory + swap that the container can use in the form of 200m, 1.2g. If set must not be smaller than memory. If equal to memory, then the container will not have access to swap. If not set and memory is set, than the container can use as much swap as the memory setting. If set to -1, the container can use unlimited swap, up to the amount available on the host. | |
| memoryReservation | No | Sets a soft memory limitation in the form of 200m, 1.2g. Must be smaller than memory. When the system detects memory contention or low memory, control groups are pushed back to their soft limits. There is no guarantee that the container memory usage will not exceed the soft limit. |
Desired State Containers Domain Example
{
"domains": [
{
"id": "containers",
"config": [
{
"key": "systemContainers",
"value": "self-update-agent"
}
],
"components": [
{
"id": "hello-world",
"version": "latest",
"config": [
{
"key": "image",
"value": "docker.io/library/hello-world:latest"
},
{
"key": "env",
"value": "x=y"
},
{
"key": "env",
"value": "a=b"
},
{
"key": "cmd",
"value": "arg1"
},
{
"key": "cmd",
"value": "arg2"
},
{
"key": "device",
"value": "/dev/tty:/dev/tty:rw"
},
{
"key": "port",
"value": "80:80/tcp"
},
{
"key": "network",
"value": "host"
},
{
"key": "host",
"value": "host_name"
},
{
"key": "mount",
"value": "/data:/data:private"
},
{
"key": "terminal",
"value": "true"
},
{
"key": "interactive",
"value": "true"
},
{
"key": "privileged",
"value": "true"
},
{
"key": "restartPolicy",
"value": "always"
},
{
"key": "restartMaxRetries",
"value": "3"
},
{
"key": "restartTimeout",
"value": "1000"
},
{
"key": "logDriver",
"value": "json-file"
},
{
"key": "logMaxFiles",
"value": "3"
},
{
"key": "logMaxSize",
"value": "5M"
},
{
"key": "logPath",
"value": "/var/log"
},
{
"key": "logMode",
"value": "blocking"
},
{
"key": "logMaxBufferSize",
"value": "1M"
},
{
"key": "memory",
"value": "200M"
},
{
"key": "memorySwap",
"value": "300M"
},
{
"key": "memoryReservation",
"value": "100M"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
4.3 - Software Updatable
4.3.1 - Software update configuration
Properties
To control all aspects of the software update behavior.
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| featureId | string | SoftwareUpdatable | Feature unique identifier in the scope of the edge digital twin |
| moduleType | string | software | Type of the software that is managed by this feature |
| artifactType | string | archive | Type of the artifact that is to be processed: archive or plain |
| install | string[] | Absolute path to the install script/command and an optional sequence of additional flags/parameters | |
| storageLocation | string | ./ | Path to the storage directory where the working files are stored |
| installDirs | string[] | File system directories where the local artifacts are stored | |
| mode | string | strict | Restriction where the local artifacts can be stored on the file system, the supported modes are: strict, lax and scope |
| Download | |||
| downloadRetryCount | int | 0 | Number of retries, in case of a failed download |
| downloadRetryInterval | string | 5s | Interval between retries, in case of a failed download as a sequence of decimal numbers, each with optional fraction and a unit suffix, such as: 300ms, 1.5h, 10m30s, etc., time units are: ns, us (or µs), ms, s, m, h |
| Download - TLS | |||
| serverCert | string | PEM encoded certificate file for secure downloads | |
| Local connectivity | |||
| broker | string | tcp://localhost:1883 | Address of the MQTT server/broker that the software update will connect for the local communication, the format is: scheme://host:port |
| username | string | Username that is a part of the credentials | |
| password | string | Password that is a part of the credentials | |
| Local connectivity - TLS | |||
| caCert | string | PEM encoded CA certificates file | |
| cert | string | PEM encoded certificate file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| key | string | PEM encoded unencrypted private key file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| Logging | |||
| logFile | string | log/software-update.log | Path to the file where log messages are written |
| logLevel | string | INFO | All log messages at this or higher level will be logged, the log levels in descending order are: ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG and TRACE |
| logFileCount | int | 5 | Log file maximum rotations count |
| logFileMaxAge | int | 28 | Log file rotations maximum age in days, use 0 to not remove old log files |
| logFileSize | int | 2 | Log file size in MB before it gets rotated |
Example
The minimal required configuration that sets the software type to firmware.
{
"moduleType": "firmware",
"storageLocation": "/var/lib/software-update",
"logFile": "/var/log/software-update/software-update.log"
}
Template
The configuration can be further adjusted according to the use case. The following template illustrates all possible properties with their default values.
{
"featureId": "SoftwareUpdatable",
"moduleType": "software",
"artifactType": "archive",
"install": [],
"storageLocation": "./",
"installDirs": [],
"mode": "strict",
"downloadRetryCount": 0,
"downloadRetryInterval": "5s",
"serverCert": "",
"broker": "tcp://localhost:1883",
"username": "",
"password": "",
"caCert": "",
"cert": "",
"key": "",
"logFile": "log/software-update.log",
"logLevel": "INFO",
"logFileCount": 5,
"logFileMaxAge": 28,
"logFileSize": 2
}
4.3.2 - Software Updatable API
Install
Install given list of software modules.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>/req//install
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/installInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/SoftwareUpdatable/inbox/messages/installA path to the SoftwareUpdatableFeature, it’s message channel, andinstallcommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id UUID Used for correlating protocol messages, the same correlation-id as the response message Value JSON presentation of software module that will be installed correlationId Unique identifier that is used to associate and track the series of messages weight The weight is the priority in case of multiple, parallel instructions metadata The metadata is any other information which should be passed to the device forced true/false Forced to remove the software modules softwareModules An array of software modules to be installed metadata The metadata is any other information which should be passed to the device softwareModule An unique identifier for the software module name The name of the software module version The version of the software module artifacts An array of artifacts contained in the software module filename The file name of the artifact size Artifact file size in bytes download A map with protocols and links for downloading the artifacts key HTTP/HTTPS/FTP/SFTP Available transport protocols url URL to download the artifact md5url MD5URL to download the MD5SUM file checksums A map with checksums to verify the proper download MD5 MD5 checksum SHA1 MD5 checksum SHA256 MD5 checksum
Example : Install a hello-world software module.
Topic: command//edge:device/req//install
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/install",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/SoftwareUpdatable/inbox/messages/install",
"value":{
"correlationId":"other_correlation_id",
"softwareModules":[
{
"softwareModule":{
"name":"install-hello",
"version":"1.0.0"
},
"artifacts":[
{
"checksums":{
"SHA256":"db954c633393c1402f145a60fd58d312f5af96ce49422fcfd6ce42a3c4cceeca",
"MD5":"8c5a0fa2c01e218262d672bf643652fd",
"SHA1":"7539b451d818d94bcd97d401a5467b3e1c0b8981"
},
"download":{
"HTTPS":{
"url":"https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/kanto/raw/main/quickstart/install_hello.sh"
}
},
"filename":"install.sh",
"size":544
}
]
}
]
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>/res//install
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/installInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/SoftwareUpdatable/outbox/messages/installA path to the SoftwareUpdatableFeature, it’s message channel, andinstallcommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the sent request message Status Status of the operation install software modules
Example : The response of the install software modules operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device/res//install``
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/install",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/SoftwareUpdatable/outbox/messages/install",
"status": 204
}
Download
Download software modules.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>/req//download
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/downloadInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/SoftwareUpdatable/inbox/messages/downloadA path to the SoftwareUpdatableFeature, it’s message channel, anddownloadcommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id UUID Used for correlating protocol messages, the same correlation-id as the sent back response message Value JSON representation of the software modules that will be downloaded correlationId Unique identifier that is used to associate and track the series of messages weight The weight is the priority in case of multiple, parallel instructions metadata The metadata is any other information which should be passed to the device forced true/false Remove the software modules forcefully softwareModules An array of software modules that will be downloaded metadata The metadata is any other information which should be passed to the device softwareModule A unique identifier for the software module name The name of the software module version The version of the software module artifacts An array of artifacts contained in the software module filename The file name of the artifact size Artifact file size in bytes download A map with protocols and links for downloading the artifacts key HTTP/HTTPS/FTP/SFTP Available transport protocols url URL to download the artifact md5url MD5URL to download the MD5SUM file checksums A map with checksums to verify the proper download MD5 MD5 checksum SHA1 MD5 checksum SHA256 MD5 checksum
Example : Download a hello-world software module.
Topic: command//edge:device/req//download
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/download",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/SoftwareUpdatable/inbox/messages/download",
"value": {
"correlationId":"other_correlation_id",
"softwareModules":[
{
"softwareModule":{
"name":"install-hello",
"version":"1.0.0"
},
"artifacts":[
{
"checksums":{
"SHA256":"db954c633393c1402f145a60fd58d312f5af96ce49422fcfd6ce42a3c4cceeca",
"MD5":"8c5a0fa2c01e218262d672bf643652fd",
"SHA1":"7539b451d818d94bcd97d401a5467b3e1c0b8981"
},
"download":{
"HTTPS":{
"url":"https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/kanto/raw/main/quickstart/install_hello.sh"
}
},
"filename":"install.sh",
"size":544
}
]
}
],
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>/res//download
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/downloadInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/SoftwareUpdatable/outbox/messages/downloadA path to the SoftwareUpdatableFeature, it’s message channel, anddownloadcommandHeaders Additional headers correlation-id container UUID The same correlation id as the request message Status Status of the downloadoperation
Example : Successful download response.
Topic: `command//edge:device/res//download``
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/download",
"headers":{
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/SoftwareUpdatable/outbox/messages/download",
"status":204
}
4.4 - File Upload
4.4.1 - File upload configuration
Properties
To control all aspects of the file upload behavior.
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| featureId | string | AutoUploadable | Feature unique identifier in the scope of the edge digital twin |
| type | string | file | Type of the files that are uploaded by this feature |
| context | string | edge | Context of the files that are uploaded by this feature, unique in the scope of the type |
| files | string | Glob pattern to select the files for upload | |
| mode | string | strict | Restriction on files that can be dynamically selected for an upload, the supported modes are: strict, lax and scoped |
| singleUpload | bool | false | Forbid triggering of new uploads when there is an upload in progress |
| checksum | bool | false | Send MD5 checksum for uploaded files to ensure data integrity |
| stopTimeout | string | 30s | Time to wait for running uploads to finish as a sequence of decimal numbers, each with optional fraction and a unit suffix, such as: 300ms, 1.5h, 10m30s, etc., time units are: ns, us (or µs), ms, s, m, h |
| delete | bool | false | Delete successfully uploaded files |
| Upload - TLS | |||
| serverCert | string | PEM encoded certificate file for secure uploads | |
| Auto upload | |||
| active | bool | false | Activate periodic uploads |
| activeFrom | string | Time from which periodic uploads should be active, in RFC 3339 format, if omitted (and active flag is set) current time will be used as start of the periodic uploads | |
| activeTill | string | Time till which periodic uploads should be active, in RFC 3339 format, if omitted (and active flag is set) periodic uploads will be active indefinitely | |
| period | string | 10h | Upload period as a sequence of decimal numbers, each with optional fraction and a unit suffix, such as: 300ms, 1.5h, 10m30s, etc., time units are: ns, us (or µs), ms, s, m, h |
| Local connectivity | |||
| broker | string | tcp://localhost:1883 | Address of the MQTT server/broker that the file upload will connect for the local communication, the format is: scheme://host:port |
| username | string | Username that is a part of the credentials | |
| password | string | Password that is a part of the credentials | |
| Local connectivity - TLS | |||
| caCert | string | PEM encoded CA certificates file | |
| cert | string | PEM encoded certificate file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| key | string | PEM encoded unencrypted private key file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| Logging | |||
| logFile | string | log/file-upload.log | Path to the file where log messages are written |
| logLevel | string | INFO | All log messages at this or higher level will be logged, the log levels in descending order are: ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG and TRACE |
| logFileCount | int | 5 | Log file maximum rotations count |
| logFileMaxAge | int | 28 | Log file rotations maximum age in days, use 0 to not remove old log files |
| logFileSize | int | 2 | Log file size in MB before it gets rotated |
Example
The minimal required configuration that sets the file type to log.
{
"type": "log",
"files": "/var/tmp/file-upload/*.*",
"logFile": "/var/log/file-upload/file-upload.log"
}
Template
The configuration can be further adjusted according to the use case. The following template illustrates all possible properties with their default values.
{
"featureId": "AutoUploadable",
"type": "file",
"context": "edge",
"files": "",
"mode": "strict",
"singleUpload": false,
"checksum": false,
"stopTimeout": "30s",
"delete": false,
"serverCert": "",
"active": false,
"activeFrom": "",
"activeTill": "",
"period": "10h",
"broker": "tcp://localhost:1883",
"username": "",
"password": "",
"caCert": "",
"cert": "",
"key": "",
"logFile": "log/file-upload.log",
"logLevel": "INFO",
"logFileCount": 5,
"logFileMaxAge": 28,
"logFileSize": 2
}
4.4.2 - File Upload API
Start
Start a file upload operation.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>/req//start
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/startInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/AutoUploadable/inbox/messages/startA path to the AutoUploadableFeature, it’s message channel, andstartcommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id UUID Used for correlating protocol messages, the same correlation-id as the sent back response message Value correlationID other UUID Identifier of the uploaded file options Options are specific for each provider storage.provider aws/azure/generic Storage provider that will be used for uploading the files
Example : Start uploading a file.
Topic: command//edge:device/req//start
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/start",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/AutoUploadable/inbox/messages/start",
"value":{
"correlationID":"upload-id-1704439450#n",
"options":{
"aws.access.key.id":"AWSACCESSKEYID",
"aws.region":"eu-central-1",
"aws.s3.bucket":"blob-upload-test",
"aws.secret.access.key":"AWSSECRETACCESSKEY",
"storage.provider":"aws"
}
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>/res//start
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/startInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/AutoUploadable/outbox/messages/startA path to the AutoUploadableFeature, it’s message channel, andstartcommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the sent request message Status Status of the operation start upload the file
Example : Successful response of a start file upload operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device/res//start``
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/start",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/AutoUploadable/outbox/messages/start",
"status": 204
}
Trigger
Trigger a file upload operation.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>/req//trigger
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/triggerInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/AutoUploadable/inbox/messages/triggerA path to the AutoUploadableFeature, it’s message channel, andtriggercommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id UUID Used for correlating protocol messages, the same correlation-id as the sent back response message Value correlationID other UUID Identifier of the triggered file options Options are specific for each provider
Example : Trigger a file upload operation.
Topic: command//edge:device/req//trigger
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/trigger",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/AutoUploadable/inbox/messages/trigger",
"value":{
"correlationID":"other <UUID>",
"options":{}
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>/res//trigger
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/triggerInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/AutoUploadable/outbox/messages/triggerA path to the AutoUploadableFeature, it’s message channel, andtriggercommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the sent request message Status Status of the triggeroperation
Example : Successful response of a trigger operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device/res//trigger``
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/trigger",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/AutoUploadable/outbox/messages/trigger",
"status":204
}
Cancel
Cancel a file upload operation.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>/req//cancel
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/cancelInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/AutoUploadable/inbox/messages/cancelA path to the AutoUploadableFeature, it’s message channel, andcancelcommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id UUID Used for correlating protocol messages, the same correlation-id as the sent back response message Value correlationID other UUID Identifier of the uploaded file statusCode This status code is set to update status code message This message is set to update status message
Example : Cancel a file upload operation.
Topic: command//edge:device/req//cancel
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/cancel",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/AutoUploadable/inbox/messages/cancel",
"value":{
"correlationID":"upload-id-1704439450#n",
"statusCode": 400,
"message":"description why the upload is canceled "
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>/res//cancel
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/cancelInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/AutoUploadable/outbox/messages/cancelA path to the AutoUploadableFeature, it’s message channel, andcancelcommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the sent request message Status Status of the operation cancelfile upload
Example : The response of the cancel file upload operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device/res//cancel``
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/cancel",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/AutoUploadable/outbox/messages/cancel",
"status":204
}
Activate
Activate an upload of a file.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>/req//activate
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/activateInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/AutoUploadable/inbox/messages/activateA path that references a part of a Thing which is affected by this message Headers Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id UUID Used for correlating protocol messages, the same correlation-id as the sent back response message Value from A Time after which the upload must be activated to A Time grater than frommarks the end of activated
Example : Activate file upload.
Topic: command//edge:device/req//activate
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/activate",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/AutoUploadable/inbox/messages/activate",
"value":{
"from":957139200,
"to":959817599
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>/res//activate
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/activateInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/AutoUploadable/outbox/messages/activateA path to the AutoUploadableFeature, it’s message channel, andactivatecommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the sent request message Status Status of the operation activatefile upload
Example : Successful response of an activate file upload operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device/res//activate``
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/activate",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/AutoUploadable/outbox/messages/activate",
"status":204
}
Deactivate
Deactivate a file upload.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>/req//deactivate
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/deactivateInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/AutoUploadable/inbox/messages/deactivateA path to the AutoUploadableFeature, it’s message channel, anddeactivatecommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id UUID Used for correlating protocol messages, the same correlation-id as the response message Value
Example : Deactivate a file upload.
Topic: command//edge:device/req//deactivate
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/deactivate",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/AutoUploadable/inbox/messages/deactivate",
"value":{}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>0/res//deactivate
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/deactivateInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/AutoUploadable/outbox/messages/deactivateA path to the AutoUploadableFeature, it’s message channel, anddeactivatecommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the sent request message Status Status of the operation deactivatefile upload
Example : Successful response of the deactivate file upload operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device/res//deactivate``
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/deactivate",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/AutoUploadable/outbox/messages/deactivate",
"status":204
}
4.5 - File Backup
4.5.1 - File backup configuration
Properties
To control all aspects of the file backup behavior.
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| featureId | string | BackupAndRestore | Feature unique identifier in the scope of the edge digital twin |
| type | string | file | Type of the files that are backed up by this feature |
| context | string | edge | Context of the files backed up by this feature, unique in the scope of the type |
| dir | string | Directory to be backed up | |
| mode | string | strict | Restriction on directories that can be dynamically selected for a backup, the supported modes are: strict, lax and scoped |
| backupCmd | string | Command to be executed before the backup is done | |
| restoreCmd | string | Command to be executed after the restore | |
| singleUpload | bool | false | Forbid triggering of new backups when there is a backup in progress |
| checksum | bool | false | Send MD5 checksum for backed up files to ensure data integrity |
| stopTimeout | string | 30s | Time to wait for running backups to finish as a sequence of decimal numbers, each with optional fraction and a unit suffix, such as: 300ms, 1.5h, 10m30s, etc., time units are: ns, us (or µs), ms, s, m, h |
| keepUploaded | bool | false | Keep successfully uploaded backups locally |
| storage | string | ./storage | Directory where backups and downloads will be stored |
| Upload/Download - TLS | |||
| serverCert | string | PEM encoded certificate file for secure uploads and downloads | |
| Auto backup | |||
| active | bool | false | Activate periodic backups |
| activeFrom | string | Time from which periodic backups should be active, in RFC 3339 format, if omitted (and active flag is set) current time will be used as start of the periodic backups | |
| activeTill | string | Time till which periodic backups should be active, in RFC 3339 format, if omitted (and active flag is set) periodic backups will be active indefinitely | |
| period | string | 10h | Backup period as a sequence of decimal numbers, each with optional fraction and a unit suffix, such as: 300ms, 1.5h, 10m30s, etc., time units are: ns, us (or µs), ms, s, m, h |
| Local connectivity | |||
| broker | string | tcp://localhost:1883 | Address of the MQTT server/broker that the file backup will connect for the local communication, the format is: scheme://host:port |
| username | string | Username that is a part of the credentials | |
| password | string | Password that is a part of the credentials | |
| Local connectivity - TLS | |||
| caCert | string | PEM encoded CA certificates file | |
| cert | string | PEM encoded certificate file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| key | string | PEM encoded unencrypted private key file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| Logging | |||
| logFile | string | log/file-backup.log | Path to the file where log messages are written |
| logLevel | string | INFO | All log messages at this or a higher level will be logged, the log levels in descending order are: ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG and TRACE |
| logFileCount | int | 5 | Log file maximum rotations count |
| logFileMaxAge | int | 28 | Log file rotations maximum age in days, use 0 to not remove old log files |
| logFileSize | int | 2 | Log file size in MB before it gets rotated |
Example
The minimal required configuration that enables backing up a directory and sets the file type to config.
{
"type": "config",
"dir": "/var/tmp/file-backup",
"mode": "scoped",
"storage": "/var/lib/file-backup",
"logFile": "/var/log/file-backup/file-backup.log"
}
Template
The configuration can be further adjusted according to the use case. The following template illustrates all possible properties with their default values.
{
"featureId": "BackupAndRestore",
"type": "file",
"context": "edge",
"dir": "",
"mode": "strict",
"backupCmd": "",
"restoreCmd": "",
"singleUpload": false,
"checksum": false,
"stopTimeout": "30s",
"keepUploaded": false,
"storage": "./storage",
"serverCert": "",
"active": false,
"activeFrom": "",
"activeTill": "",
"period": "10h",
"broker": "tcp://localhost:1883",
"username": "",
"password": "",
"caCert": "",
"cert": "",
"key": "",
"logFile": "log/file-backup.log",
"logLevel": "INFO",
"logFileCount": 5,
"logFileMaxAge": 28,
"logFileSize": 2
}
4.5.2 - File Backup API
Backup
Create a file backup.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>/req//backup
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/backupInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/BackupAndRestore/inbox/messages/backupA path to the BackupAndRestoreFeature, it’s message channel, andbackupcommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id UUID Used for correlating protocol messages, the same correlation-id as the sent back response message Value correlationID UUID Identifier of the backup file providers The providers of the restore command options backup.dir A local directory, to be backed up https.url The URL for restoring the backed up directory
Example : Back up a directory.
Topic: command//edge:device/req//backup
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/backup",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/BackupAndRestore/inbox/messages/backup",
"value":{
"correlationID":"upload-id-1704439450#n",
"providers":{},
"options":{
"backup.dir":"/var/tmp/backup",
"https.url":""
}
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>/res//backup
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/backupInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/BackupAndRestore/outbox/messages/backupA path to the BackupAndRestoreFeature, it’s message channel, andbackupcommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the request message Status Status of the backupoperation
Example : Successful response of a backup operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device/res//backup``
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/backup",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/BackupAndRestore/outbox/messages/backup",
"status":204
}
Restore
Restore the backed up files or directory from a backend service.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>/req//restore
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/restoreInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/BackupAndRestore/inbox/messages/restoreA path to the BackupAndRestoreFeature, it’s message channel, andrestorecommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id UUID Used for correlating protocol messages, the same correlation-id as the sent back response message Value correlationID other UUID Identifier of the restored file providers Storage provider, one of aws,azure,genericoptions Options are specific for each provider backup.dir A local directory, which to be backed up and then uploaded, using a storage provider of choice and temporary credentials https.url The URL for restoring the backed up directory
Example : Restore a backup from a storage provider.
Topic: command//edge:device/req//restore
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/restore",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/BackupAndRestore/inbox/messages/restore",
"value":{
"correlationID":"upload-id-1704439450#n",
"providers":{},
"options":{
"backup.dir":"/var/tmp/backup",
"https.url":"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/eclipse-kanto/container-management/main/containerm/pkg/testutil/config/"
}
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>/res//restore
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/restoreInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/BackupAndRestore/outbox/messages/restoreA path to the BackupAndRestoreFeature, it’s message channel, andrestorecommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the request message Status Status of the operation restore
Example : Response of a successful restore operation.
Topic: `command//edge:device/res//restore``
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/restore",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/BackupAndRestore/outbox/messages/restore",
"status": 204
}
4.6 - System Metrics
4.6.1 - System metrics configuration
Properties
To control all aspects of the system metrics behavior.
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| frequency | string | Initial system metrics reporting frequency as a sequence of decimal numbers, each with optional fraction and a unit suffix, such as: 300ms, 1.5h, 10m30s, etc., time units are: ns, us (or µs), ms, s, m, h | |
| Local connectivity | |||
| broker | string | tcp://localhost:1883 | Address of the MQTT server/broker that the system metrics will connect for the local communication, the format is: scheme://host:port |
| username | string | Username that is a part of the credentials | |
| password | string | Password that is a part of the credentials | |
| Local connectivity - TLS | |||
| caCert | string | PEM encoded CA certificates file | |
| clientCert | string | PEM encoded certificate file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| clientKey | string | PEM encoded unencrypted private key file to authenticate to the MQTT server/broker | |
| Logging | |||
| logFile | string | log/system-metrics.log | Path to the file where log messages are written |
| logLevel | string | INFO | All log messages at this or higher level will be logged, the log levels in descending order are: ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG and TRACE |
| logFileCount | int | 5 | Log file maximum rotations count |
| logFileMaxAge | int | 28 | Log file rotations maximum age in days, use 0 to not remove old log files |
| logFileSize | int | 2 | Log file size in MB before it gets rotated |
Example
The minimal required configuration that enables the auto reporting of system metrics.
{
"frequency": "60s",
"logFile": "/var/log/system-metrics/system-metrics.log"
}
Template
The configuration can be further adjusted according to the use case. The following template illustrates all possible properties with their default values.
{
"frequency" : "",
"broker": "tcp://localhost:1883",
"username": "",
"password": "",
"caCert": "",
"clientCert": "",
"cleintKey": "",
"logFile": "log/system-metrics.log",
"logLevel": "INFO",
"logFileCount": 5,
"logFileMaxAge": 28,
"logFileSize": 2
}
4.6.2 - System Metrics API
Request
Request to receive metrics data.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>/req//request
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/requestInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Metrics/inbox/messages/requestA path to the MetricsFeature, it’s message channel, andrequestcommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id container UUID Used for correlating protocol messages, the same correlation-id as the sent back response message Value frequency Time interval of how often the metrics data will be published as duration string (e.g. 5s) filter Filter defines the type of metric data to be reported id An array of identifiers whose metric data to be reported, supported are: cpu.utilization,memory.utilization,memory.total,memory.used,io.readBytes,io.writeBytes,net.readBytes,net.writeBytes,pidsoriginator Metrics data originator
Example : Request metrics data with specified filter and frequency.
Topic: command//edge:device/req//request
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/request",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Metrics/inbox/messages/request",
"value":{
"filter":[
{
"id":["io.*","cpu.*","memory.*"],
"originator":"SYSTEM"
}
],
"frequency":"5s"
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>/res//request
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/requestInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Metrics/outbox/messages/requestA path to the MetricsFeature, it’s message channel, andrequestcommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the request message Status Status of the operation request the metrics data
Example : Successful response of a request metrics message.
Topic: `command//edge:device/res//request``
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/request",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/Metrics/outbox/messages/request",
"status": 204
}
Data
Metrics data reported by the device.
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>/res//data
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/dataInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/Metrics/outbox/messages/dataA path to the MetricsFeature, it’s message channel, and metrics dataHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type Value The value of the received data from the device in json format timestamp The timestamp in ms when this measure data is published snapshot All the measurements collected at a concrete time per originator originator The originator for whose metric data to be reported measurements An array of measurements identifier and value for originator id The identifier whose metric data to be reported, supported are: cpu.utilization, cpu.load1, cpu.load5, cpu.load15, memory.utilization, memory.total, memory.available, memory.used, io.readBytes, io.writeBytes value The measured value per metric ID
Example : Metrics data from the device.
Topic: `command//edge:device/res//data``
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/data",
"headers":{
"content-type":"application/json",
},
"path":"/features/Metrics/outbox/messages/data",
"value":{
"snapshot":[
{
"originator":"SYSTEM",
"measurements":[
{
"id":"cpu.utilization",
"value":1.1555555555484411
},
{
"id":"cpu.load1",
"value":0.17
},
{
"id":"cpu.load5",
"value":0.27
},
{
"id":"cpu.load15",
"value":0.24
},
{
"id":"memory.total",
"value":10371616768
},
{
"id":"memory.available",
"value":5281644544
},
{
"id":"memory.used",
"value":4563206144
},
{
"id":"memory.utilization",
"value":43.99705702662538
}
]
}
],
"timestamp":1234567890
}
}
4.7 - Update Manager
4.7.1 - Update Manager API
Apply
Applies a desired state to the device.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>/req//apply
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/applyInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/UpdateManager/inbox/messages/applyA path to the UpdateManagerFeature, it’s message channel, andapplycommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id container UUID Used for correlating protocol messages, the same correlation-id as the sent back response message Value activityId The activity id of the new desired state desiredState The desired state to be applied on a device baselines An array of domain or cross-domain dependencies between components title The title of the dependency description The description of the dependency preconditions The preconditions of the dependency components An array of the components of the dependency domains An array of desired state for a single domain id The id of this domain config An array of key/value string pair key The key string value The value of the key string components An array of desired state component with additional key-value configuration pairs id The id of the component version The version of the component key The key string value The value of the key string
Example : Apply a desired state to the device.
Topic: command//edge:device/req//apply
{
"topic":"edge/device/things/live/messages/apply",
"headers":{
"response-required":true,
"content-type":"application/json",
"correlation-id":"<UUID>"
},
"path":"/features/UpdateManager/inbox/messages/apply",
"value":{
"activityId": "d91ad6fe-9b0c-4549-bf31-17d0a71b61de",
"desiredState": {
"baselines": [
{
"title": "simple-baseline",
"description": "",
"precondition": "",
"components": [
"domain:component1",
"domain:component2"
]
}
],
"domains": [
{
"id": "containers",
"config": [
{
"key": "source",
"value": "value"
}
],
"components": [
{
"id": "containers:influxdb",
"version": "2.7.1",
"config": [
{
"key": "image",
"value": "docker.io/library/influxdb:$influxdb_version"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>/res//apply
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/applyInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/UpdateManager/outbox/messages/applyA path to the UpdateManagerFeature, it’s message channel, andapplycommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the request message Status Status of the operation apply
Example : Successful response of an apply desired state operation.
Topic: command//edge:device/res//apply
{
"topic": "edge/device/things/live/messages/apply",
"headers": {
"content-type": "application/json",
"correlation-id": "<UUID>"
},
"path": "/features/UpdateManager/outbox/messages/apply",
"status": 204
}
Refresh
Reads the current state from the device and updates the status of the UpdateManager feature.
Request
Hono Command: command//<name>:<namespace>/req//refresh
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/refreshInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/UpdateManager/inbox/messages/refreshA path to the UpdateManagerFeature, it’s message channel, andrefreshcommandHeaders Additional headers response-required true/false If response is required content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id container UUID The container UUID Value activityId The activity id of the refreshoperation
Example : Update the status of the UpdateManager feature.
Topic: command//edge:device/req//refresh
{
"topic": "edge/device/things/live/messages/refresh",
"headers": {
"response-required": true,
"content-type":" application/json",
"correlation-id": "<UUID>"
},
"path": "/features/UpdateManager/inbox/messages/refresh",
"value": {
"activityId": "e08b071c-c19e-41de-8da0-e2843113161f"
}
}
Response
Hono Command : command//<name>:<namespace>/res//refresh
Ditto Message:
Name Value Description topic <name>/<namespace>/things/live/messages/refreshInformation about the affected Thing and the type of operation path /features/UpdateManager/outbox/messages/refreshA path to the UpdateManagerFeature, it’s message channel, andrefreshcommandHeaders Additional headers content-type application/jsonThe content type correlation-id <UUID> The same correlation id as the request message Status Status of the refreshoperation
Example : Successful response of a refresh operation.
Topic: command//edge:device/res//refresh
{
"topic": "edge/device/things/live/messages/refresh",
"headers": {
"content-type": "application/json",
"correlation-id": "<UUID>"
},
"path": "/features/UpdateManager/outbox/messages/refresh",
"status": 204
}
4.7.2 - Update manager configuration
Properties
To control all aspects of the update manager.
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| General | |||
| domain | string | device | The domain of the update manager, used as MQTT topic prefix |
| domains | string | containers | A comma-separated list of domains handled by the update manager. This configuration option is available only as a flag, but not inside the JSON config file. In JSON config file, the keys inside the Domain agents structure serve as domain names. |
| phaseTimeout | string | 10m | Timeout as duration string for completing an Update Orchestration phase |
| rebootAfter | string | 30s | Time period as duration string to wait before a reboot process is initiated after successful update operation |
| rebootEnabled | bool | true | Enable the reboot process after successful update operation |
| reportFeedbackInterval | string | 1m | Time interval as duration string for reporting intermediate desired state feedback messages during an active update operation |
| currentStateDelay | string | 30s | Time interval as duration string for reporting current state messages |
| thingsEnabled | bool | true | Enable the Update Manager to behave as a thing’s feature |
| ownerConsentCommands | []string | List of commands for which an owner consent should be granted. Possible values are: ‘DOWNLOAD’, ‘UPDATE’, ‘ACTIVATE’ | |
| ownerConsentTimeout | string | 30m | Timeout as duration string to wait for owner consent" |
| Domain agents | Holds a map structure (agents) with update agent configurations where each map key is treated as domain name | ||
| readTimeout | string | 1m | Timeout as duration string for reading the current state for the domain |
| rebootRequired | bool | false | Require a reboot for the domain after successful update |
| Local connectivity | |||
| broker | string | tcp://localhost:1883 | Address of the MQTT server/broker that the container manager will connect for the local communication, the format is: scheme://host:port |
| keepAlive | string | 20s | Keep alive duration for the MQTT requests as duration string |
| disconnectTimeout | string | 250ms | Disconnect timeout for the MQTT server/broker as duration string |
| username | string | Username that is a part of the credentials | |
| password | string | Password that is a part of the credentials | |
| acknowledgeTimeout | string | 15s | Acknowledge timeout for the MQTT requests as duration string |
| connectTimeout | string | 30s | Connect timeout for the MQTT server/broker as duration string |
| subscribeTimeout | string | 15s | Subscribe timeout for the MQTT requests as duration string |
| unsubscribeTimeout | string | 5s | Unsubscribe timeout for the MQTT requests as duration string |
| Logging | |||
| logFile | string | Path to the file where the update manager’s log messages are written | |
| logLevel | string | INFO | All log messages at this or a higher level will be logged, the log levels in descending order are: ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG and TRACE |
| logFileCount | int | 5 | Log file maximum rotations count |
| logFileMaxAge | int | 28 | Log file rotations maximum age in days, use 0 to not remove old log files |
| logFileSize | int | 2 | Log file size in MB before it gets rotated |
Example
An example for configuring the update manager with two domains - containers and custom-domain, report feedback interval at 30 seconds, and log, written to custom log file update-manager.log with
log level DEBUG.
{
"log": {
"logFile": "update-manager.log",
"logLevel": "DEBUG"
},
"agents": {
"containers": {
"readTimeout": "30s"
},
"custom-domain": {
"rebootRequired": true
}
},
"reportFeedbackInterval": "30s"
}
Template
The configuration can be further adjusted according to the use case. The following template illustrates all possible properties with their default values.
{
"domain": "device",
"agents": {
"containers": {
"rebootRequired": false,
"readTimeout": "1m"
}
},
"log": {
"logFile": "",
"logLevel": "INFO",
"logFileCount": 5,
"logFileMaxAge": 28,
"logFileSize": 2
},
"connection": {
"broker": "tcp://localhost:1883",
"keepAlive": "20s",
"acknowledgeTimeout": "15s",
"username": "",
"password": "",
"connectTimeout": "30a",
"disconnectTimeout": "250ms",
"subscribeTimeout": "15s",
"unsubscribeTimeout": "5s"
},
"phaseTimeout": "10m",
"rebootAfter": "30s",
"rebootEnabled": true,
"reportFeedbackInterval": "1m",
"currentStateDelay": "30s",
"thingsEnabled": true,
"ownerConsentCommands": ["DOWNLOAD"]
}