Container management
Container management enables a lightweight standard runtime which is capable to run containerized applications with all advantages of the technology: isolation, portability and efficiency. The deployment and management are available both locally and remotely via an IoT cloud ecosystem of choice. The following use cases are provided:
- Standardized approach - with OCI (Open Container Initiative) compliant container images and runtime
- Lightweight runtime - with a default integration of
containerdand a possibility for another container technology of choice like podman, LXC and more - Isolation - with a default isolation from other containerized applications and the host system
- Portability - with an option to run one and the same containerized application on different platforms
- Pluggable architecture - with extension points on different levels
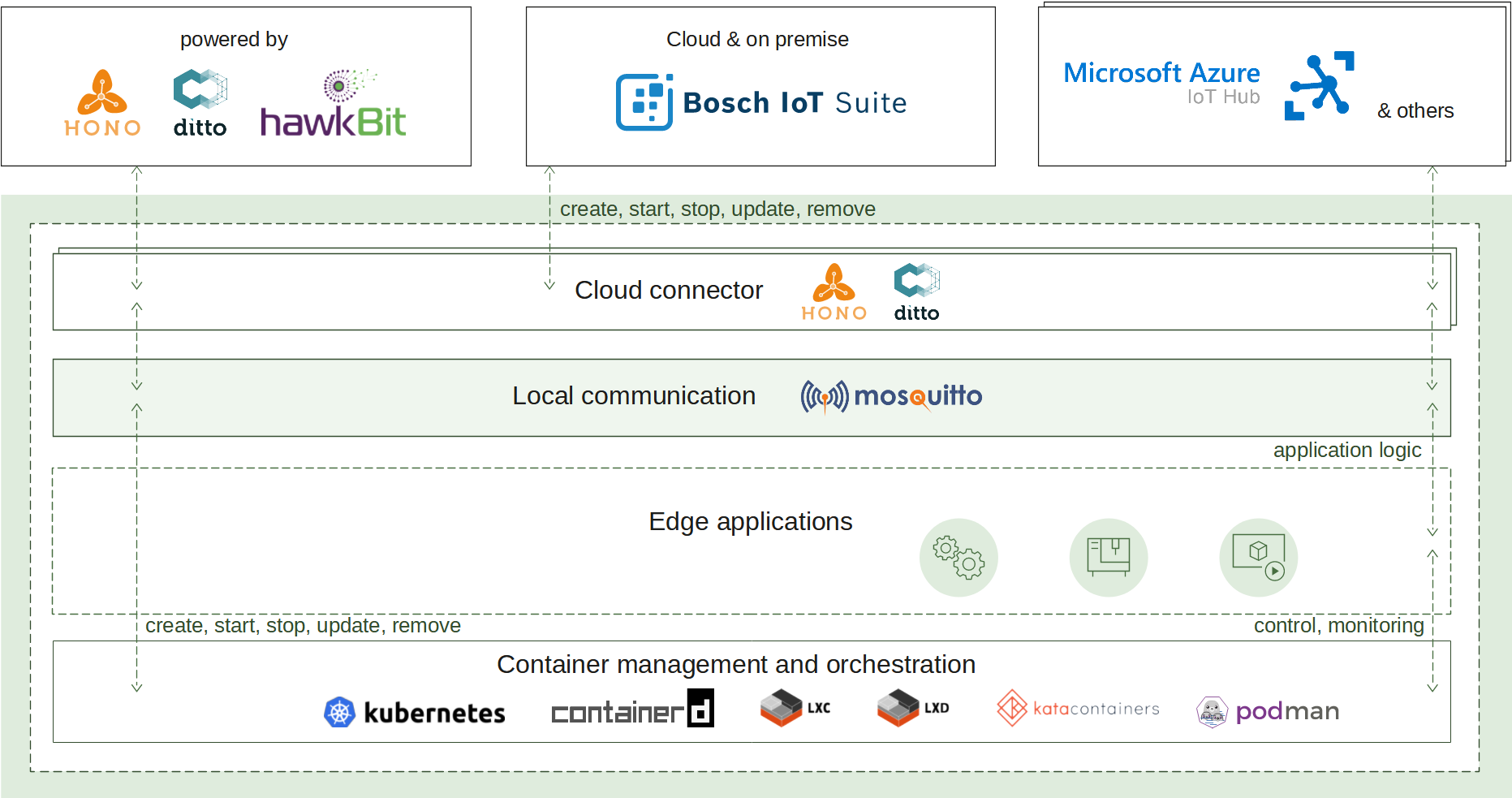
How it works
A container image packs the application executable along with all its needed dependencies into a single artifact that can be built by a tooling of choice. The built image is made available for usage by being pushed to a container image registry where the runtime can refer it to.
To create a new container instance, the container management uses such an image reference and a configuration for it to produce a fully functional container.
The container lifecycle (start, update, stop, remove) and environment (memory constraints, restart policy, etc.) are also handled by the runtime.
The container management continuously ensures the applications availability via state awareness and restart policies, provides monitoring via flexible logging and fine-grained resources management.
All of that is achieved on top of an underlying runtime of choice (containerd by default) that takes care of the low-level isolation mechanisms.