Build Yocto Image for Raspberry Pi
Building a Yocto Image for a Raspberry Pi involves several steps, including setting up the environment, download the necessary layers, configuring the build and compiling the image.
Before you begin
- Install the required packages required for the build on a Ubuntu/Debian system
sudo apt-get update sudo apt install -y gawk wget git-core diffstat unzip texinfo gcc-multilib \ build-essential chrpath socat cpio python3 python3-pip python3-pexpect \ xz-utils debianutils iputils-ping libsdl1.2-dev xterm zstd liblz4-tool \
Clone the Yocto/Poky Repository
Verify the Yocto Version of Kanto availabe in meta-kanto layer, https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/meta-kanto, this example provides information for kirkstone branch.
Create a Source folder
mkdir sources cd sourcesIf it is kirkstone branch then, clone poky for kirkstone version in source directory
git clone https://github.com/yoctoproject/poky.git cd poky git checkout kirkstoneNote : Change branch based on meta-kanto layer.
Add Meta Layers to the source directory
Based on the yocto version, clone the meta layers in the source directory
meta-raspberrypimeta-openembeddedmeta-virtualizationmeta-lts-mixinsClone meta-raspberry pi layer to sources directory
cd .. git clone git://git.yoctoproject.org/meta-raspberrypi cd meta-raspberrypi git checkout kirkstoneClone meta-openembedded layer to sources directory
cd .. git clone https://github.com/openembedded/meta-openembedded.git cd meta-openembedded git checkout kirkstoneClone meta-virtualization layer to sources directory
cd .. git clone https://git.yoctoproject.org/git/meta-virtualization cd meta-virtualization git checkout kirkstoneClone meta-lts-mixins layers to source directory
cd .. git clone https://git.yoctoproject.org/git/meta-lts-mixins cd meta-lts-mixins git checkout kirkstone/goNote : The above layer is required to get the updated go version to be added in the yocto build, since kanto requires go version 1.19 and above.
Add meta-kanto layer to the sources directory
Clone meta-kanto layer to the sources directory
cd .. git clone https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/meta-kanto.git cd meta-kanto git checkout kirkstoneNote : Make sure all the layers cloned are of same yocto version ( kirkstone in this case)
Create Build Directory
After cloning all the required meta layers, move out of source directory to create build directory
cd ../.. source sources/poky/oe-init-build-envRun the below command to view the layers present in
bblayers.conffilebitbake-layers show-layersNote : Resolve any dependendencies if occured while running bitbake command.
Configure bblayer.conf file
By Default in the bblayer.conf file some of the layers will be added
Add all the layers to the bblayers.conf file with below command
bitbake-layers add-layer /home/path/to/meta/layer/directoryThe following layers should be added in the bblayer.conf file
meta-raspberrypi meta-openembedded meta-virtualization meta-lts-mixins meta-openembedded/meta-oe meta-openembedded/meta-python meta-opemembedded/meta-networking meta-openembedded/meta-filesystems meta-kantoExample to add layers to bblayers.conf file
while adding layers bitbake might have dependencies, add the dependent layers first. Example,
To add meta-kanto layer to bblayer.conf file which is kept at
/home/yocto/sources/meta-kantobitbake-layers add-layers /home/yocto/sources/meta-kantoAfter adding all the required layers in bblayer.conf file, verify again by running the below command
bitbake-layers show-layers
Configure local.conf file
Open local.conf file which is placed at the below location in build directory
vi conf/local.confChange the machine variable in local.conf file to raspberry pi machine
MACHINE ??= "raspberrypi4"Note: Check the sources/meta-raspberrypi/conf/machine for the availabe machines for raspberry pi.
Add required variables in local.conf file as shown and provided in the link below,
https://github.com/eclipse-kanto/meta-kanto# Add the required DISTRO_FEATURES DISTRO_FEATURES:append = " virtualization systemd" # Configure the kernel modules required to be included MACHINE_ESSENTIAL_EXTRA_RRECOMMENDS += "kernel-modules" # System initialization manager setup VIRTUAL-RUNTIME_init_manager = "systemd" DISTRO_FEATURES_BACKFILL_CONSIDERED = "sysvinit" VIRTUAL-RUNTIME_initscripts = "systemd-compat-units" # Add the Eclipse Kanto components IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " mosquitto" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " suite-connector" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " aws-connector" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " azure-connector" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " software-updates" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " file-upload" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " file-backup" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " update-manager" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " container-management" IMAGE_INSTALL:append = " local-digital-twins"Run bitbake `target-name’ availabe as shown below,
Common targets are: core-image-minimal core-image-full-cmdline core-image-sato core-image-weston meta-toolchain meta-ide-supportNote : If any build issues comes up, resolve the issue and run the bitbake `target-name’ command again for the build.
Final Build Image Repository Location
After the successful build, the image will be availabe at the below location.
build/tmp/deploy/images/`machine_name`/
Run & Test the image with QEMU (Quick Emulator)
If RaspberryPi device is not availabe, the image can be run and tested on QEMU. Make the below changes to run on QEMU.
In `build/conf/local.conf’ file
Change the machine variable name to relevant qemu arch as shown below by changing the
MACHINEvarilabe from raspberrypi4 to ‘qemux86_64`# You need to select a specific machine to target the build with. There are a selection # of emulated machines available which can boot and run in the QEMU emulator: # #MACHINE ?= "qemuarm" #MACHINE ?= "qemuarm64" #MACHINE ?= "qemux86" #MACHINE ?= "qemux86-64" # This sets the default machine to be qemux86-64 if no other machine is selected: MACHINE ??= "qemuarm64"Run bitbake
target-namecommand by sourcing theoe-init-build-envscriptIn the same build directory run the below command to run qemu
runqemu qemuarm64
The above command will open a window which boots as “YOCTO PROJECT” and it enters to command line window. Enter login as `root’, and check for kanto components with the below commands.
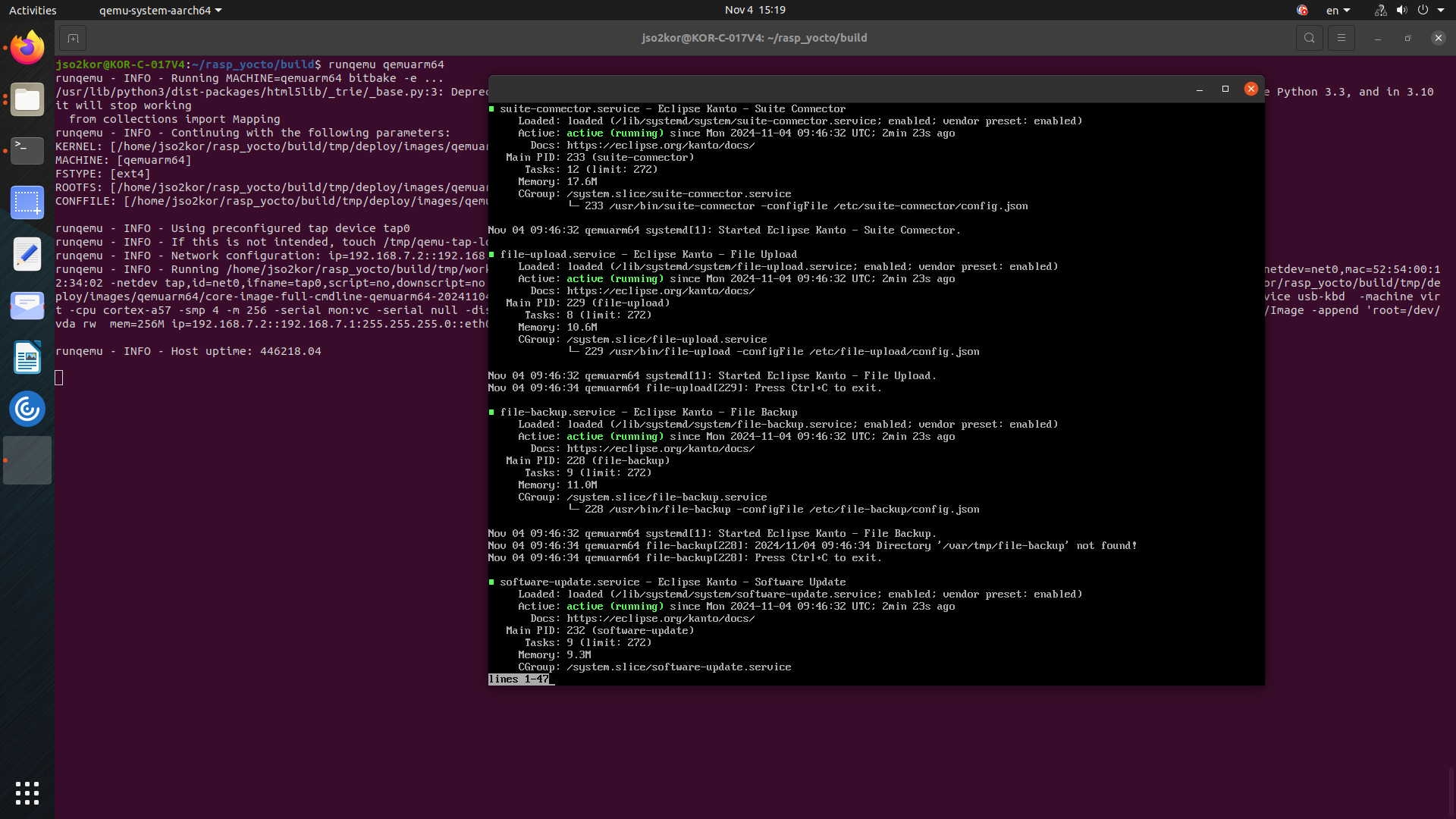
systemctl status \ suite-connector.service \ container-management.service \ software-update.service \ file-upload.service \ file-backup.service \ system-metrics.service \ kanto-update-manager.serviceAll listed services must be in an active running state.
Flash the image on Raspberry Pi
The build image will be availabe at
build/tmp/deploy/images/raspberrypi4/Identify the SD Card Device with the below command to find the device name of your SD card
lsblkFlash the image to sd card
sudo dd if=/path/to/image.wic of=/dev/sdX bs=4M status=progressBoot the Raspberry Pi,
Insert the SD card into your Raspberry Pi and power it on. The Pi should boot from the Yocto image.Login to your device and run the below command to verify the kanto components.
systemctl status \ suite-connector.service \ container-management.service \ software-update.service \ file-upload.service \ file-backup.service \ system-metrics.service \ kanto-update-manager.service