j2ee models

| Java EE project api j2ee models |  |
| Intoduction | |
The Java EE project provides the core models and API for J2EE 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, Java EE 5, 6 specification levels artifacts. The core models are for creating and loading the Java EE artifacts (Enterprise Applications, Application Clients, Web Applications, Web Services, Enterprise Java Bean and Connectors). All the Java EE core models exist in both org.eclipse.jst.j2ee.core org.eclipse.jst.jee plugins of the j2ee sub project. The details of each of core j2ee models usage and api are discussed in the following sections. | |
| Java EE Components | |
In WTP, Java EE projects include a entry for ModuleCoreNature, that indicates metadata
is present for the modulecore model. This model represents the different component types,
and how they are assembled and structured.
FlexibleProject flexProj = ComponentCore.createFlexibleProject(anIProject); IVirtualComponent comp = flexProj.createComponent(compName); | |
| IModelProvider | |
IModelProvider is a simple api for reading and writing registered EMF model's based
on a project type or file URI. WTP provide's default implementation models for each
of the basic Java EE module types. Starting in WTP 3.2, new models were provided to support Java EE 5 and above.
This api will return the model based on either the project's facet level or if file URI is specified.. the file version'
A simple event mechanism is also available for registering against model changes.
Transactions, and reference counting is NOT supported in this api, but could be extended in future releases.
IModelProvider provider = ModelProviderManager.getModelProvider(earProj); Application ear = (Application)provider.getModelObject(); Loading a WS model IModelProvider provider = ModelProviderManager.getModelProvider(warProj, "META-INF/webservices.xml"); WebServices ws = (WebServices)provider.getModelObject(); Loading/Saving EAR Model
final IModelProvider provider = ModelProviderManager.getModelProvider(earProj);
provider.modify(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
Application ear = (Application)provider.getModelObject();
ear.setLibraryDirectory("/foo");
}
}, null);
| |
| ArtifactEdit | |
ArtifactEdit classes are an older internal api mechanism, supporting the
Java EE models (1.2, 1.3 and 1.4). It is recommended to use IModelProvider
api for any new development.
This mechanism was used to create and load emf resources from the emf
resource set in read or write mode. When opened in either mode they have
to be released after the work with the resource is done. The need for
releasing these edit models is needed because accessing the edit models
increments the resource count by 1 on the actual resource in the resource
set. This mechanism of incrementing the resource count is used for
resource synchronization. There are artifact edit classes defined for each j2ee
module type to handle creation,load and editiing scenarios of the their deployment
descriptor resources.
public List getEnterpriseBeans(IVirtualComponent comp) {
EJBArtifactEdit ejbArtifactEdit = null;
try{
ejbArtifactEdit =
EJBArtifactEdit.getEJBArtifactEditForRead(comp);
List enterpriseBeans =
ejbArtifactEdit.getEJBJar().getEnterpriseBeans();
return enterpriseBeans;
}
finally {
if(ejbArtifactEdit != null) {
ejbArtifactEdit.dispose();
}
}
}
| |
Quick EMF model overview: A resource set (@ResourceSet) manages a collection of resources (@link #getResource) A resource contains api to view the (@link #getAllContents) collection of EMF Objects. A resource can be created (@link #createResource) or demand loaded (@link #getResource(URI, boolean)) into the resource set collection. A proxy can be {@link #getEObject} can be resolved by the resource set, and may cause the demand load of a resource. | |
| Common J2EE Model | |
The common J2EE model represents the common schema elements that are
created and used across all the j2ee modules. The
org.eclipse.jst.j2ee.common
java package contains the api for creating and accessing the common
elements
(description, displayName, small-icon,large-icon,ejb-ref,
resource-ref,resource-env-ref,message-desintations-refs,service-refs,message-destinations,security-roles
etc.)
. The following diagram depicts all the elements of the common model that
is being shared across all j2ee module models.
| |
| Enterprise Application Model | |
The org.eclipse.jst.j2ee.application package contains all the api for creating an Application module and the nested modules (Application Client, Web, EJB and Connector) in the Application. | |
The snippet of code below shows how to create an Application:
ApplicationFactory.eINSTANCE.createApplication();
WebModule createWebModule(); JavaClientModule createJavaClientModule(); EjbModule createEjbModule(); ConnectorModule createConnectorModule(); ApplicationPackage getApplicationPackage(); The Application needs to have a minimum of one module as per J2EE specification. The modules can be created as standalone modules or along with an EAR with the module added to the EAR. The standalone module creation api are mentioned in the corresponding module sections below. The following diagram depicts all the elements in the Application that constitutes the Enteprise Application resource (EARFile). The Application needs to have a minimum of one module as per J2EE specification. The modules can created as part of EAR creation or individually as standalone modules. The UML model below depicts the elements of an Application and that contitute the application.xml file. 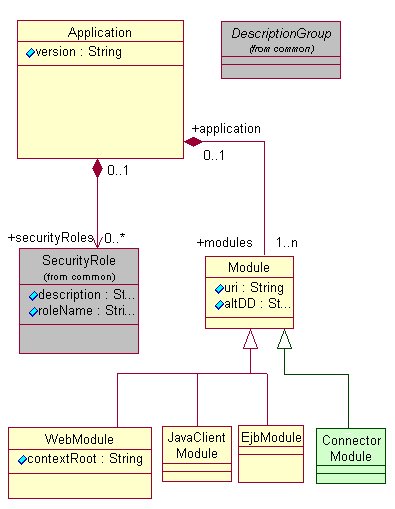
The Application Interface class provides all the necessary api to elements on the Application model. Here are the api avialable on the Application Interface class /*Returns the first module matching the specified uri*/ public Module getFirstModule(String uri); /**Returns the first module where the alt dd matches the specified uri*/ public Module getModuleHavingAltDD(String uri); /*Returns the Securtiy Role in the Application matching the name*/ public SecurityRole getSecurityRoleNamed(String name); | |
| Application Client Model | |
The
org.eclipse.jst.j2ee.client
java package contains all the interfaces and api for creating and
accessing the elements
(env-entry,callback-handler etc.)
an Application Client module. The ApplicationClient interface class has
the all the api to get to the elemmts that constitutes the deployment
decriptor
(application-client.xml)
. The ClientFactory interface is used to create an instances of an
Applciation Client. The following diagram depitcs all the elements of an
Application Client module that constitutes the Application Client jar
(JavaClientFile).
public List getEJBReferences(IVirtualComponent appClientComponent) {
AppClientArtifactEdit appClientArtifactEdit = null;
try {
appClientArtifactEdit =
AppClientArtifactEdit.getAppClientArtifactEditForRead(appClientComponent);
return appClientArtifactEdit.getApplicationClient().getEjbReferences();
}
finally {
if(appClientArtifactEdit != null)
appClientArtifactEdit.dispose();
}
}
| |
| Web Application Model | |
The
org.eclipse.jst.j2ee.webapplication
java package contains all the model api for creating and accessing the
elements
(context-param, servlet, servlet-mapping, session-config,
mime-mapping, welcome-file-list, error-page, taglib, resource-ref,
security-constraint, login-config, security-role, env-entry etc.)
of a Web App. The WebApp and WebResourceCollection are the interfaces
through which all the elements of WebApplication module can be accessed.
The
org.eclipse.jst.j2ee.webapplication.impl
package contains the concrete implemenation of the interface provided in
the
org.eclipse.jst.j2ee.webapplication
package. The following diagram depicts all the elements of a Web Module
module deployment descriptor that constitutes the Web Archive (WARFile)
public List getServlets(IVirtualComponent webComponent) {
WebArtifactEdit webArtifactEdit = null;
try {
webArtifactEdit = WebArtifactEdit.getWebArtifactEditForRead(webComponent);
return webArtifactEdit.getWebApp().getServlets();
}
finally {
if(webArtifactEdit!= null)
webArtifactEdit.dispose();
}
}
| |
| Enterprise Java Bean Model | |
The
org.eclipse.jst.j2ee.ejb
java package contains all the interfaces and api for creating and
accessing the elements
(enterprise-beans, relationships, assembly-descriptor,
ejb-client-jar)
of an Enterprise Java Bean module. The
EJBJar
interface contains all the api for accessing the elements of an
Enterprise Bean module. The
EnterpriseBean
interface provides the api for accessing the elements of an Enterprise
Java Bean. the The following diagram depicts all the elements of a EJB
resource that constitutes EJBJar (EJBJarFile).
public void addNewCMPAttributeToCMP(IVirtualComponent ejbComp, String cmpBeanName) {
EJBArtifactEdit ejbArtifactEdit = null;
try {
ejbArtifactEdit = EJBArtifactEdit.getEJBArtifactEditForWrite(ejbComp);
EJBJar ejbJar = ejbArtifactEdit.getEJBJar();
EnterpriseBean bean = ejbJar.getEnterpriseBeanNamed(cmpBeanName);
if(bean instanceof ContainerManagedEntity) {
ContainerManagedEntity cmpBean = (ContainerManagedEntity)bean;
CMPAttribute attr = EjbFactory.eINSTANCE.createCMPAttribute(); attr.setName("foo");
cmpBean.getCMPAttribute().add(attr);
}
ejbArtifactEdit.saveIfNecessary();
}
finally {
if(ejbArtifactEdit != null)
ejbArtifactEdit.dispose();
}
}
| |
| Connector Model | |
The
org.eclipse.jst.j2ee.jca
java package contains all the interfaces and api for creating and
accessing the elemtns
(vendor-name, spec-version, eis-type, version, license,
resourceadapter,activation-spec)
of an Connector module. The
Connector
interface contains all the api for accessing the elements of an Connector
module. The
ResourceAdapter
interface provides all the api for accessing the elements of the
internals of an Connector modules. The following diagram depicts all the
elements of a Connector resource that constitutes Resource Archive
(RARFile).
public List getConnectorConfigProperties(IVirtualComponent comp) {
ConnectorArtifactEdit connectorArtifactEdit = null;
try {
connectorArtifactEdit = connectorRuntime.getConnectorArtifactEditForRead(comp);
return connectorArtifactEdit.getConnector().getResourceAdapter().getConfigProperties();
}
finally {
if(connectorArtifactEdit != null)
connectorArtifactEdit.dispose();
}
}
| |
| Web Services Model | |
The
org.eclipse.jst.j2ee.webservice.wsclient
java package contains all the interfaces and api for creating and
accessing the elements
(ports,handlers,serviceRefs, componentsScopedRefs etc.)
of a Web Serices Client resource. The
Webservice_clientFactory
interface contains all the api for creating the elements of a Web Service
Client. The
ComponentScopedRefs,Handler,PortComponentRef,ServiceRef
interfaces contain the api for accessing the internal elements of a Web
Services client resource.The
org.eclipse.jst.j2ee.webservice.wsdd
package contains the api to access the elements of Web Services
Deployment Descriptor(WSDD). The
WsddFactory
interface contains the api for creating the elements of a WSDD resource.
The following diagram depicts all the elements of a WSDD and the
WebServicesClient resource.
| |