Understanding EclipseLink,
2.4 |
|
The following sections describe the concepts specific to Object-Relational descriptors.
By default, when you execute an object-level read query for a particular object class, EclipseLink returns all the persistent attributes mapped in the object's descriptor. With this single query, all the object's persistent attributes are defined, and calling their get methods returns the value directly from the object.
When you are interested in only some of the attributes of an object, it may be more efficient to return only a subset of the object's attributes using a fetch group.
Using a fetch group, you can define a subset of an object's attributes and associate the fetch group with either a ReadObjectQuery or ReadAllQuery query. When you execute the query, EclipseLink retrieves only the attributes in the fetch group. EclipseLink automatically executes a query to fetch all the attributes excluded from this subset when and if you call a get method on any one of the excluded attributes.
You can define more than one fetch group for a class. You can optionally designate at most one such fetch group as the default fetch group. If you execute either a ReadObjectQuery or ReadAllQuery query without specifying a fetch group, EclipseLink will use the default fetch group, unless you configure the query otherwise.
Before using fetch groups, Oracle recommends that you perform a careful analysis of system use. In many cases, the extra queries required to load attributes not in the fetch group could well offset the gain from the partial attribute loading.
Fetch groups can be used only with basic mappings configured with FetchType.LAZY (partial object queries).
EclipseLink uses the AttributeGroup that can be used to configure the use of partial entities in fetch, load, copy, and merge operations.
Fetch: Control which attributes and their associated columns are retrieved from the database
Load: Control which relationships in the entities returned from a query are populated
Copy: Control which attributes are copied into a new entity instance
Merge: Merge only those attributes fetched, loaded, or copied into an entity
The following sections describe the possible AttributeGroup types and operations.
The FetchGroup defines which attributes should be fetched (selected from the database) when the entity is retrieved as the result of a query execution. The inclusion of relationship attributes in a FetchGroup only determines if the attribute's required columns should be fetched and populated. In the case of a lazy fetch type the inclusion of the attribute simply means that its proxy will be created to enable lazy loading when accessed. To force a relationship mapping to be populated when using a FetchGroup on a query the attribute must be included in the group and must either be FetchType.EAGER or it must be included in an associated LoadGroup on the query.
FetchGroup also has the notion of named and default FetchGroup which are managed by the FetchGroupManager. A default FetchGroup is defined during metadata processing if one or more basic mappings are configured to be lazy and the entity class implements FetchGroupTracker (typically introduced through weaving). The default FetchGroup is used on all queries for this entity type where no explicit FetchGroup or named FetchGroup is configured.
A Named FetchGroup can be defined for an entity using @FetchGroup annotation or within the eclipselink-orm.xml file.
A FetchGroup when first created is assumed to be empty. The user must add the attributes to the FetchGroup. If a FetchGroup is required with all of the attributes then the FetchGroupManager.createFullFetchGroup() must be used.
A FetchGroup can also be configured to perform a load operation of relationship mappings and nested relationship mappings.
A LoadGroup is used to force a specified set of relationship attributes to be populated in a query result.
The CopyGroup replaces the deprecated ObjectCopyPolicy being used to define how a entity is copied. In addition to specifying the attributes defining what should be copied from the source entity graph into the target copy the CopyGroup also allows definition of:
shouldResetPrimaryKey: Reset the identifier attributes to their default value. This is used when the copy operation is intended to clone the entity in order to make a new entity with similar state to the source. Default is false.
shouldResetVersion: Reset the optimistic version locking attribute to its default value in the copies. Default is false.
depth: defines cascade mode for handling relationships. By default CASCADE_PRIVATE_PARTS is used but it can also be configured to NO_CASCADE and CASCADE_ALL_PARTS.
When a partial entity is merged into a persistence context that has an AttributeGroup associated with it defining which attributes are available only those attributes are merged. The relationship mappings within the entity are still merged according to their cascade merge settings.
Each relational descriptor provides an instance of DescriptorQueryManager that you can use to configure the following:
named queries
custom default queries for basic persistence operations
additional join expressions
An essential part of maintaining object identity is managing the assignment of unique values (that is, a specific sequence) to distinguish one object instance from another.
Sequencing options you configure at the project (or session) level determine the type of sequencing that EclipseLink uses. In a POJO project, you can use session-level sequence configuration to override project-level sequence configuration, on a session-by-session basis, if required.
After configuring the sequence type, for each descriptor's reference class, you must associate one attribute, typically the attribute used as the primary key, with its own sequence.
With object-relational mapping, you can configure a descriptor with any of the following locking policies to control concurrent access to a domain object:
Optimistic—All users have read access to the data. When a user attempts to make a change, the application checks to ensure the data has not changed since the user read the data.
Pessimistic—The first user who accesses the data with the purpose of updating it locks the data until completing the update.
No locking—The application does not prevent users overwriting each other's changes.
Oracle recommends using optimistic locking for most types of applications to ensure that users do not overwrite each other's changes.
This section describes the various types of locking policies that EclipseLink supports, including the following:
With optimistic locking, all users have read access to the data. When a user attempts to make a change, the application checks to ensure the data has not changed since the user read the data.
Optimistic version locking policies enforce optimistic locking by using a version field (also known as a write-lock field) that you provide in the reference class that EclipseLink updates each time an object change is committed.
EclipseLink caches the value of this version field as it reads an object from the data source. When the client attempts to write the object, EclipseLink compares the cached version value with the current version value in the data source in the following way:
If the values are the same, EclipseLink updates the version field in the object and commits the changes to the data source.
If the values are different, the write operation is disallowed because another client must have updated the object since this client initially read it.
EclipseLink provides the following version-based optimistic locking policies:
VersionLockingPolicy
TimestampLockingPolicy
For descriptions of these locking policies, see "Setting Optimistic Locking" in Solutions Guide for EclipseLink.
|
In general, Oracle recommends numeric version locking because of the following:
|
Whenever any update fails because optimistic locking has been violated, EclipseLink throws an OptimisticLockException. This should be handled by the application when performing any database modification. The application must notify the client of the locking contention, refresh the object, and have the client reapply its changes.
You can choose to store the version value in the object as a mapped attribute, or in the cache. In three-tier applications, you typically store the version value in the object to ensure it is passed to the client when updated (see Applying Locking in an Application).
If you store the version value in the cache, you do not need to map it. If you do map the version field, you must configure the mapping as read-only.
To ensure that the parent object's version field is updated whenever a privately owned child object is modified, consider Optimistic Version Locking Policies and Cascading.
If you are using a stored procedure to update or delete an object, your database may not return the row-count required to detect an optimistic lock failure, so your stored procedure is responsible for checking the optimistic lock version and throwing an error if they do not match. Only version locking is directly supported with a StoredProcedureCall. Because timestamp and field locking require two versions of the same field to be passed to the call, an SQL call that uses an ## parameter to access the translation row could be used for other locking policies.
If your database schema is such that both a parent object and its privately owned child object are stored in the same table, then if you update the child object, the parent object's version field will be updated.
However, if the parent and its privately owned child are stored in separate tables, then changing the child will not, by default, update the parent's version field.
To ensure that the parent object's version field is updated in this case, you can either manually update the parent object's version field or, if you are using a VersionLockingPolicy, you can configure EclipseLink to automatically cascade the child object's version field update to the parent.
After you enable optimistic version locking cascading, when a privately owned child object is modified, EclipseLink will traverse the privately owned foreign reference mappings, updating all the parent objects back to the root.
Optimistic version locking cascading is only applied if the child object is registered in a unit of work.
EclipseLink supports optimistic version locking cascading for:
object changes in privately owned one-to-one and one-to-many mappings
relationship changes (adding or removing) in the following collection mappings (privately owned or not):
direct collection
one-to-many
many-to-many
aggregate collection
Consider the example object graph shown in Figure 6-2
Figure 6-2 Optimistic Version Locking Policies and Cascading Example
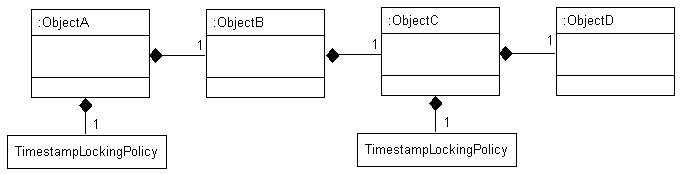
In this example, ObjectA privately owns ObjectB, and ObjectB privately owns ObjectC, and ObjectC privately owns ObjectD.
Suppose you register ObjectB in a unit of work, modify an ObjectB field, and commit the unit of work. In this case, ObjectB checks the cache for ObjectA and, if not present, queries the database for ObjectA. ObjectB then notifies ObjectA of its change. ObjectA forces an update on its version optimistic locking field even though it has no changes to its corresponding table.
Suppose you register ObjectA in a unit of work, access its ObjectB to access its ObjectC to access its ObjectD, modify an ObjectD field, and commit the unit of work. In this case, ObjectD notifies ObjectC of its changes. ObjectC forces an update on its version optimistic locking field even though it has no changes to its corresponding table. ObjectC then notifies ObjectB of the ObjectD change. ObjectB then notifies ObjectA of the ObjectD change. ObjectA forces an update on its version optimistic locking field even though it has no changes to its corresponding table.
With optimistic locking, use the UnitOfWork method commitAndResumeOnFailure to rollback a locked object's value, if you store the optimistic lock versions in the cache.
If you store the locked versions in an object, you must refresh the objects (or their versions) on a failure. Alternatively, you can acquire a new unit of work on the failure and reapply any changes into the new unit of work.
Optimistic field locking policies enforce optimistic locking by using one or more of the fields that currently exist in the table to determine if the object has changed since the client read the object.
The unit of work caches the original state of the object when you first read the object or register it with the unit of work. At commit time, the unit of work compares the original values of the lock fields with their current values on the data source during the update. If any of the lock fields' values have changed, an optimistic lock exception is thrown.
EclipseLink provides the following optimistic field locking policies:
AllFieldsLockingPolicy
ChangedFieldsLockingPolicy
SelectedFieldsLockingPolicy
VersionLockingPolicy
TimestampLockingPolicy
For descriptions of these locking policies, see "Setting Optimistic Locking" in Solutions Guide for EclipseLink.
With pessimistic locking, the first user who accesses the data with the purpose of updating it locks the data until completing the update.
When using a pessimistic locking policy, you can configure the policy to either fail immediately or to wait until the read lock is acquired.
You can use a pessimistic locking policy only in a project with a container-managed persistence type and with descriptors that have EJB information.
You can also use pessimistic locking (but not a pessimistic locking policy) at the query level.
EclipseLink provides an optimization for pessimistic locking when this locking is used with entities with container-managed persistence: if you set your query to pessimistic locking and run the query in its own new transaction (which will end after the execution of the finder), then EclipseLink overrides the locking setting and does not append FOR UPDATE to the SQL. However, the use of this optimization may produce an undesirable result if the pessimistic lock query has been customized by the user with a SQL string that includes FOR UPDATE. In this case, if the conditions for the optimization are present, the query will be reset to nonpessimistic locking, but the SQL will remain the same resulting in the locking setting of the query conflicting with the query's SQL string. To avoid this problem, you can take one of the following two approaches:
Use an expression (see Chapter 11, "Understanding EclipseLink Expressions") for the selection criteria. This will give EclipseLink control over the SQL generation.
Place the finder in a transaction to eliminate conditions for the optimization.
To correctly lock an object in an application, you must obtain the lock before the object is sent to the client for editing.
If you are using optimistic locking, you have the following two choices for locking objects correctly:
Map the optimistic lock field in your object as not read-only and pass the version to the client on the read and back to the server on the update.
Ensure that the original version value is sent to the client when it reads the object for the update. The client must then pass the original version value back with the update information, and this version must be set into the object to be updated after it is registered/read in the new unit of work on the server.
Hold the unit of work for the duration of the interaction with the client.
Either through a stateful session bean, or in an HTTP session, store the unit of work used to read the object for the update for the duration of the client interaction.
You must read the object through this unit of work before passing it to the client for the update. This ensures that the version value stored in the unit of work cache or in the unit of work clone will be the original value.
This same unit of work must be used for the update.
The first option is more commonly used, and is required if developing a stateless application.
If you are using pessimistic locking, you must use the unit of work to start a database transaction before the object is read. You must hold this unit of work and database transaction while the client is editing the object and until the client updates the object. You must use this same unit of work to update the object.