Feature Overview
Eclipse Free BIRD Tools provides seamless GitHub integration for creating pull requests with your processed regulatory data and transformations. This feature enables collaborative development workflows by allowing you to export your work, create forks, and submit changes for review through GitHub's pull request mechanism.
Purpose
The Pull Request Creation feature serves as the bridge between your local data processing and collaborative repository management. It provides:
- Version Control Integration: Seamlessly export processed data to GitHub repositories
- Collaborative Review Process: Submit work for peer review and approval before integration
- Secure Development: Work in isolated forks without affecting the main repository
- Automated Workflow: One-click creation of forks, branches, and pull requests
This feature is essential for teams working on a common and open ontology projects, enabling multiple contributors to collaborate while maintaining the integrity of ontology and review processes.
Getting Started
Prerequisites
Before creating pull requests, ensure:
- Database is initialized and contains processed ontology
- Configuration is saved and validated
- GitHub personal access token with appropriate permissions
- Access to the target GitHub repository
- Workflow processing tasks are completed (recommended)
Access Methods
There are two primary methods to create pull requests:
- Quick Actions - Automated one-click approach (recommended)
- Manual Export - Advanced control over the export process
Step-by-Step Guide
Method 1: Quick Actions - Create Review
The recommended approach for creating pull requests is to use the automated "Create Review" feature after completing your workflow tasks.
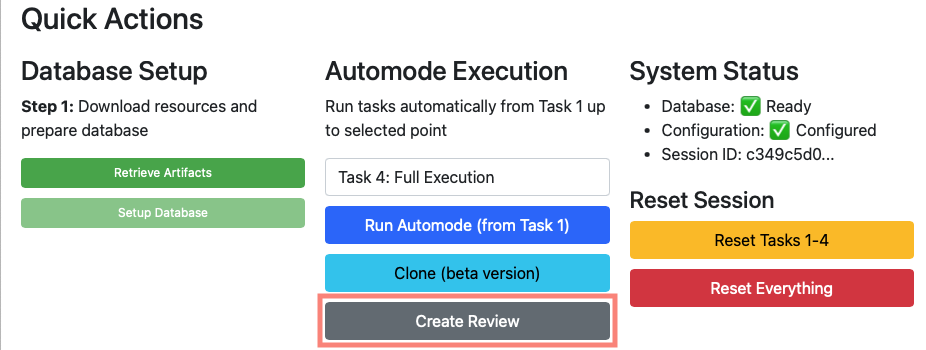
The "Create Review" button appears in Quick Actions when your database setup is complete, configuration is saved, workflow tasks have been executed, and the system is ready for review submission. To use this feature, first complete executing Tasks 1-4 or your desired endpoint. Verify that your database and configuration show ready status. Then click "Create Review" located in the Quick Actions Automode Execution section. The system will automatically handle the fork creation, branch setup, and pull request submission.
When you click "Create Review", the system automatically creates a secure fork of the target repository, generates a new branch for your changes, exports your processed data and transformations, commits the changes and pushes them to your fork, and creates a pull request back to the original repository.
Method 2: Manual Export - Database to CSV Files
For advanced users who need more control over the export and postprocessing process, you can use the manual export functionality.
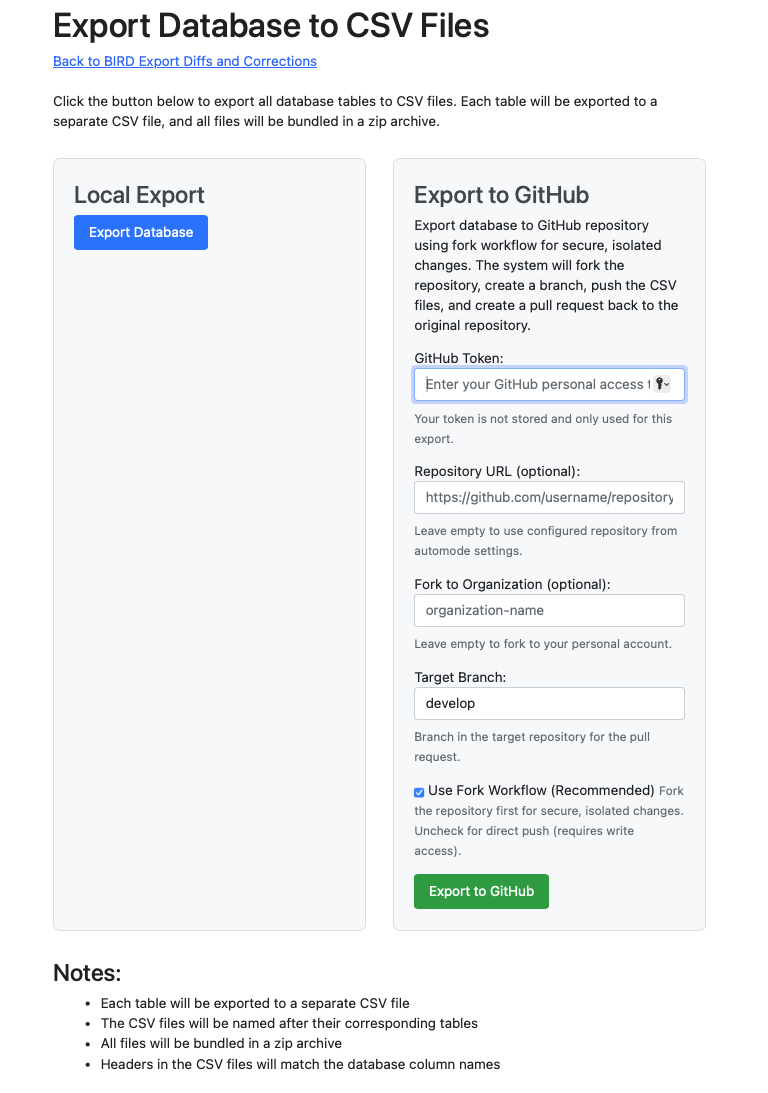
To access the export functionality, navigate to "Export Database to CSV Files" and choose the "Export to GitHub" option from the right panel. Then configure your GitHub settings as needed.
GitHub Configuration
You need to provide a GitHub token for authentication, which is your personal access token with repository permissions. The token is not stored and is only used for this export. Ensure your token has fork, push, and pull request creation rights.
You can optionally specify a custom repository URL if different from your configuration settings. Leave this empty to use the repository from your automode settings. If you're working in an organizational context, you can specify an organization name for the fork. Leave this empty to fork to your personal account. The target branch defaults to "develop" but you can specify an alternative branch if required.
Fork Workflow
The fork workflow is recommended for security. When enabled, it creates an isolated fork where you can work without affecting the original repository. This approach doesn't require direct write access to the main repository and ensures all changes go through a review process before integration. The system automatically handles fork creation, and repository maintainers can review and approve changes through the pull request.
Export Process Steps
To export your data, first enter your GitHub token and configure any optional settings like repository URL or organization fork. Click "Export to GitHub" to start the process. The system will automatically create a fork if needed, generate CSV files from your database tables, create a new branch, commit the files, and open a pull request. You'll receive a success message with a direct link to the created pull request.
The export creates individual CSV files for each database table, with column names included as headers. All files are bundled in a zip archive and uploaded to your fork with a descriptive commit message.
Best Practices
Always use the fork workflow for isolated, secure development. Complete your workflow tasks before creating pull requests. Limit your GitHub token permissions to the minimum required for the operation. For routine submissions, use the "Create Review" feature in Quick Actions. Include descriptive commit messages and pull request descriptions to help reviewers understand your changes.
Troubleshooting
Common Issues and Solutions
Authentication Issues:
- Verify that your token has the correct permissions (repo, fork, pull request)
- Check the token expiration date
- Ensure you're using the token for the correct GitHub account
- Regenerate token if necessary
Repository Access Problems:
- Verify the repository URL is correctly formatted
- Confirm you have read access to the repository
- Check if the repository is private and requires additional permissions
- Ensure the branch name exists and is accessible
Fork Creation Failures:
- Check if you already have a fork of the repository
- Verify your GitHub account has forking permissions
- Confirm the organization allows forking (for org repos)
- Clear any existing failed forks before retrying
Export Failures:
- Verify database connectivity and data integrity
- Ensure stable network connectivity to GitHub
- Try exporting smaller datasets if timeouts occur
- Review export logs for specific error messages
Conclusion
The Pull Request Creation feature streamlines the process of submitting regulatory data for review and integration. Whether using the automated Quick Actions approach or the manual export method, you can efficiently share your processed data while maintaining security and compliance standards.
Next Steps
- Learn about Workflow Dashboard to prepare data for pull requests
- Explore DPM Operations for data processing workflows
- Review Execute Datapoint Guide for execution details
For GitHub integration support or collaboration assistance, connect with us on Eclipse Chat or email efbt-dev@eclipse.org.