Technical Details
The goal of the Agent Definition Language (ADL) is to provide a reliable and efficient way to define and manage the behavior of an agent that is accessible to anyone, regardless of their technical background.
Traditional prompting has grown into a discipline of its own, with many best practices and techniques. This makes it both difficult and time-consuming to define and manage complex Agent behaviors.
Furthermore, with each new model release, modifications to the prompts may be required.
The ADL aims to simplify this process by providing a structured format backed by a set of rules and conventions.
How it works
The core idea of the ADL is to separate the definition of an agent's behavior from the actual prompting that is sent to the Large Language Model (LLM).
For this to work there is a ADL compiler that "complies" the ADL into a system prompt and other artifacts, such as tools, that is then sent to the LLM.
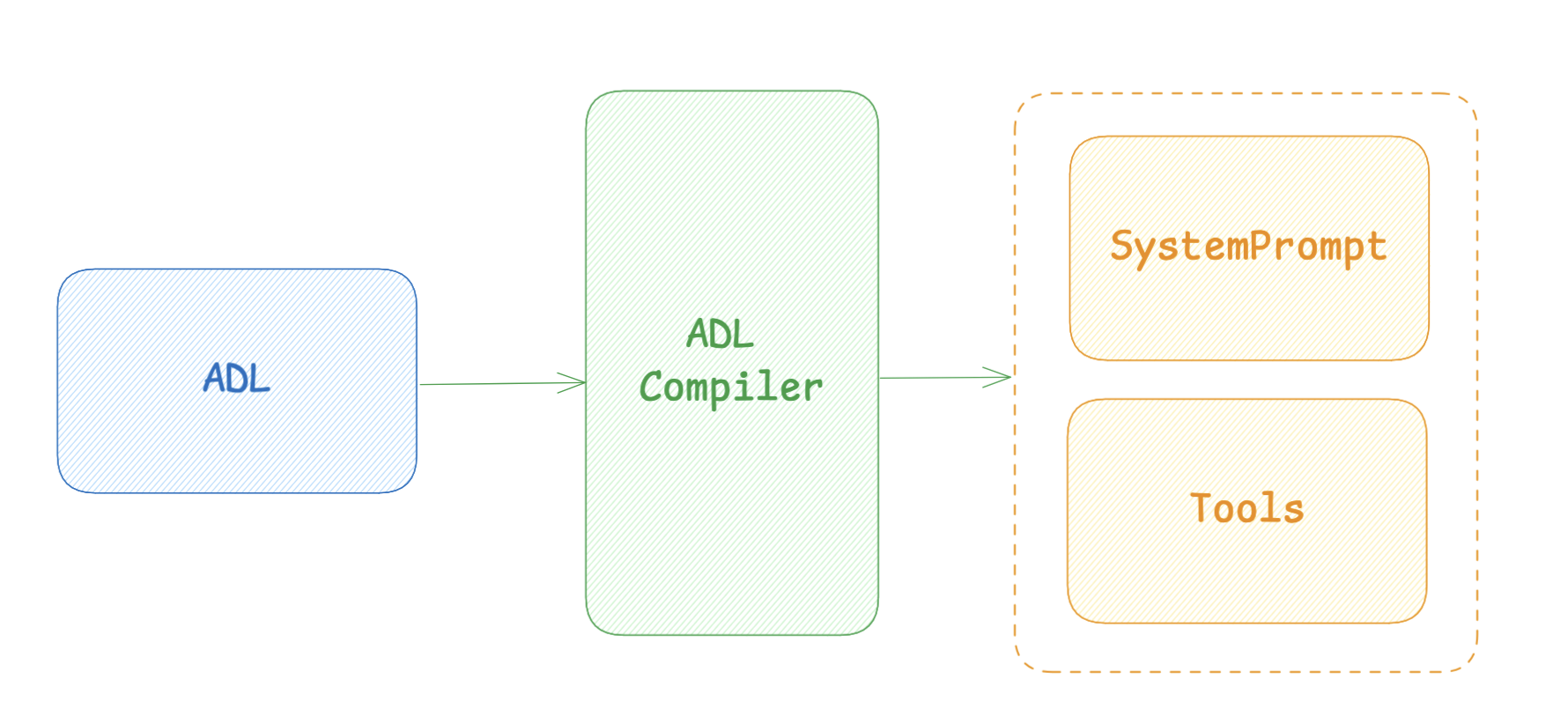
Breakdown of the Format
The ADL structures the behavior of an agent into a set of use cases. Each use case defining how the agent should respond to a specific scenario or query.
The use case format typically consists of the following components:
-
UseCase Name: A concise, descriptive id that uniquely identifies the use case. Should be in lowercase and use underscores to separate words.
-
Description: A detailed explanation of the customer's situation or query.
-
Steps (optional): A sequence of steps for the Agent to perform before providing the final solution. This section is optional and can be used to provide additional context or guidance.
-
Solution: The recommended solution to resolve the issue or fulfill the customer's request.
-
Alternative Solution (optional): An alternative solution that the Agent should try if the primary solution is not effective.
-
Fallback Solution (optional): The fallback solution that the Agent should use if the primary and alternative solutions fail. The fallback solution is to prevent the Agent from getting stuck in a loop where it provides the same solution over and over again. It is triggered after X number of failed attempts, X being a configurable parameter.
-
Examples (optional): A list of example queries or statements that should trigger this use case. This section is optional and can be used to provide additional context or guidance.
Example:
### UseCase: password_reset
#### Description
Customer has forgotten their password and needs to reset it.
#### Steps
- Ask the customer for their registered email address.
- Send a password reset link to the provided email address.
#### Solution
Guide the customer through the password reset process defined on the webpage https://www.example.com/reset-password.
#### Fallback Solution
If the customer cannot access their email, escalate the issue to a higher tier of support.
#### Examples
- I forgot my password.
If the Agent has access to tools, such as send_password_reset_link, these would be called as part of this use case.
Overall Guidelines
-
Use consistent terms and language throughout the use case to ensure clarity and avoid confusion. For example, if you refer to the user as "customer" in one section, use "customer" throughout the document. (Prefer "customer" over "user" as it is more specific and helps maintain a customer-centric focus.)
-
Providing examples when necessary. Examples are a very powerful construct and should only be used if the Agent struggles to understand the use case.
Conditionals
Conditionals is a feature that enables us to omit lines from the use cases based on certain conditions.
Conditionals are defined in brackets, for example, <condition1, condition2>.
Each line containing such a conditional is filtered out before being provided to the LLM unless all conditions
are met. Conditionals can be placed anywhere within the line.
Example:
### UseCase: password_reset
#### Description
Customer has forgotten their password and needs to reset it.
#### Solution
<isBusinessCustomer>Provide the webpage https://www.example.com/business/reset-password.
Provide the webpage https://www.example.com/reset-password.<isPrivateCustomer>
The conditions are defined outside of the use cases. Depending on the implementation, how conditionals are provided can vary.
When using the useCases function in ARC agent the conditionals are provided as a parameter.
useCases("use_cases.md", conditions = setOf("isBusinessCustomer"))
This would produce the following output that would be feed to the Agent:
### UseCase: password_reset
#### Description
Customer has forgotten their password and needs to reset it.
#### Solution
Provide the webpage https://www.example.com/business/reset-password.
Important Conditionals are only supported in the body of Steps, Solution,
Alternative Solution and Fallback Solution.
As mentioned, conditionals are applied to a single line.
If a conditional should span multiple line, the </> tag can be used to denote the end of a conditional.
### UseCase: password_reset
#### Description
Customer has forgotten their password and needs to reset it.
#### Solution
<isBusinessCustomer>
Some solution for business customers.
Some more solutions for business customers.
</>
<isPrivateCustomer>
Some solution for private customers.
Some more solutions for private customers.
</>
Multiple Conditionals
Multiple conditionals can be defined for each line. In this case, all conditionals must be true for the line to be submitted to the LLM.
### UseCase: password_reset
#### Description
Customer has forgotten their password and needs to reset it.
#### Solution
<isBusinessCustomer, isBeta> Some solution for business customers.
In this case, the line is only supplied to the LLM when the conditionals isBusinessCustomer and isBeta is set.
Negative Conditionals
Any conditional can be negated by adding a "!".
### UseCase: password_reset
#### Description
Customer has forgotten their password and needs to reset it.
#### Solution
<!isBusinessCustomer> Provide this line if the conditional is not set.
In this case, the line is only filtered when the isBusinessCustomer is set.
"Or" Conditionals
"Or" conditionals can be defined by using "or" between the conditionals.
### UseCase: password_reset
#### Description
Customer has forgotten their password and needs to reset it.
#### Solution
<isMonday or isTuesday> Provide this line if either isMonday or isTuesday is set.
In this case, the line is submitted to if either isMonday or isTuesday is set.
These statements can have any number of "or" conditionals, for example, <cond1 or cond2 or cond3 or cond4>.
"Else" Conditional
The "else" conditional is true when none of the other conditionals are true.
### UseCase: password_reset
#### Description
Customer has forgotten their password and needs to reset it.
#### Solution
<isMonday> Provide this line if either isMonday is set.
<isTuesday> Provide this line if either isTuesday is set.
<else> Provide this line if neither isMonday nor isTuesday is not set.
Regex Conditionals
Conditionals can also contain regex expressions that are matched against the input. Regex conditionals are "true" when the input from the user matches the regex provided in the conditional.
### UseCase: password_reset
#### Description
Customer has forgotten their password and needs to reset it.
#### Solution
<regex:.*business.*> Provide this line if the conditional is not set.
In this case, the line is only submitted to the LLM when the input contains the phrase "business".
Executable Code Blocks
Use cases can include executable code blocks that run on every request. This allows for dynamic generation of responses based on real-time data or computations.
Basic Syntax
Code blocks are defined using standard markdown code fence syntax with a language identifier:
### UseCase: current_time
#### Description
The customer wants to know the current time.
#### Solution
The current time is:
```kotlin
time()
```
Supported Languages
The system uses the Java ServiceLoader mechanism to load available code runners. Currently supported languages include:
- Kotlin - Built-in support via
arc-kotlin-runnermodule.
Other languages can be added by implementing the CodeBlockRunner interface
and registering it using the ServiceLoader mechanism.
How It Works
- The ADL compiler detects code blocks within use cases
- The appropriate code runner is selected based on the language identifier
- The code is executed in a sandboxed environment with timeout protection
- The result replaces the code block in the compiled output
Comments
Comments can be added to any part of the ADL use cases using "//".
### UseCase: password_reset
#### Description
// this is a comment
Customer has forgotten their password and needs to reset it.
#### Solution
// this is a comment.
Provide the webpage https://www.example.com/reset-password.
Tool calls
Calls to tools / functions can be denoted using the following syntax @my_function().
This is not mandatory, but does provide the following benefits:
- Enables the system to dynamically load any required the tools / functions.
- Enables the system to validate that the required tools / functions are available.
- Enables the system to re-enforce the execution of the tools.
Example
### UseCase: password_reset
#### Description
Customer has forgotten their password and needs to reset it.
#### Solution
Call the function @password_reset_link() to obtain a password reset link.
Then provide the customer with the link and guide them through the password reset process.
To re-enforce the execution of the tool, simply add "!" to the function call, like so: @password_reset_link()!.
Static Responses (WIP)
Sometimes it is desirable to have the LLM respond with static text as supposed to returning a response generated by the LLM.
By wrapping the response in double quotes, the system will re-enforce that the enclosed text is returned when the use case is triggered.
### UseCase: password_reset
#### Description
Customer has forgotten their password and needs to reset it.
#### Solution
"This exact string will be the output."
Use Cases References
Use Cases can reference other use cases using the following syntax #use_case_id.
This is not mandatory, but does provide the following benefits:
- Enables the system to load uses cases that are stored in other location.
- Enables the system to validate that the referenced use cases are available.
Example
### UseCase: password_reset
#### Description
Customer has forgotten their password and needs to reset it.
#### Solution
Call the function @password_reset_link() to obtain a password reset link.
If the customer is a business customer, the use case #business_customer_support should be followed.
Flow Options (WIP)
Flow Options enables Use Case authors to express decision trees within the Use Case markdown.
To achieve this, the Use Case writer can simply add so-called Flow Options to the bottom of any Use Case as follows:
[option 1] command
[option 2] command 2
Option Used to match the user's input to the command that should be executed.
Command This can be any instruction given to the LLM to perform. Examples include:
- Tool calls
- A reply to give to the user
- A use case reference
The options should be placed at the bottom of the solution section of a use case.
There can be any number of options, i.e. from 1 to N.
Example
#### Use Case: buy_car
Customer wants to buy a car Use Case.
#### Description
The customer wants to buy a car.
#### Solution
Ask the customer what type of car they would like to buy.
[bmw] go to the case #buy_bmw
[other] reply that we don't sell that type of car.
#### Case: buy_bmw
Ask the customer what color would they like.
[color selected] go to the final case #buy_bmw_with_color
[other] reply with "ok, we need to know the color "
#### Case: buy_bmw_with_color
Call the tool @buy_car() to finalize the purchase.
And reply to the customer that we are grateful for their businees.
In this flow, we start by asking the customer what type of car they would like to buy.
Based on their response, the agent will either return the solution defined in the #buy_bmw use case or reply that "We dont sell that type of car. "
If the customer wants to buy a BMW, the agent will then ask what color they would like. If the customer provides a color, the agent will proceed to the final case #buy_bmw_with_color where it will call the tool @buy_car() to finalize the purchase and reply to the customer that we are grateful for their business.
By modularizing the flow in this way, the Use Case Compiler can re-enforce that the agent follows the defined flow.
This feature also introduces "Cases". These are Use Cases that are only reachable via a Flow Option. Unlike regular Use Cases, Cases do not have Examples nor a Description section.