Setting up Eclipse IDE
- “Standard” Eclipse distribution 4.5 or newer from http://www.eclipse.org/downloads/
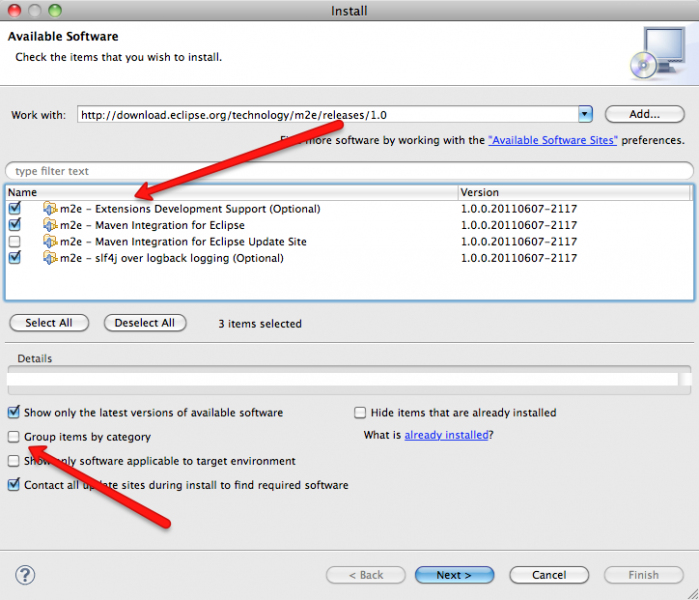
- m2e 1.7 or newer from http://download.eclipse.org/technology/m2e/releases/, including semi-hidden m2e SDK feature (uncheck “Group items by category” to see it)
Command line build
Download and unpack to a local folder Maven 3.0.3 or better available from http://maven.apache.org/download.html
Prerequisites
Some OSGi bundle development and PDE knowledge is assumed.
- Doc: http://help.eclipse.org/luna/index.jsp?topic=/org.eclipse.pde.doc.user/guide/intro/pde_overview.htm
- Getting Started: http://www.eclipse.org/articles/Article-PDE-does-plugins/PDE-intro.html
- Lars Vogel Tutorial:http://www.vogella.de/articles/EclipsePlugIn/article.html
Java code generation overview
Although there are no strict rules, usually maven java code generation plugins like antlr3-maven-plugin or maven-jaxb-plugin take one or more input files from project source tree and generate a number java source files in a subdirectory of target/generated-sources/ directory. These generated sources are usually required to compile and/or run project tests.
To properly support code generation inside Eclipse IDE workspace, the IDE generally needs to perform some configuration (semi) statically during project import and then do actually code generation either on request or automatically as part of workspace build.
m2e extension that provides support for generation will typically need to:
- implement a subclass of org.eclipse.m2e.jdt.AbstractJavaProjectConfigurator to perform necessary project configuration
- implement subclass of MojoExecutionBuildParticipant to delegate actual code generation to underlying maven plugin goal
- provide metadata to register the project configurator with m2e and to map maven plugin execution to the project configurator
m2e/antlr3 code generation support explained
As an example, here is explanation of how different parts of m2e/antlr fit together.
On command line, antlr3-maven-plugin, reads ANTLR grammar files from directory specified by ${sourceDirectory} plugin configuration parameter (defaults to src/main/antlr3) and generates output files in directory specified by ${outputDirectory} plugin configuration parameter (defaults to target/generated-sources/antlr3).
AntlrProjectConfigurator and corresponding metadata
AbstractJavaProjectConfigurator is a convenience abstract implementation of AbstractProjectConfigurator that provides default behaviour common to many java code generation m2e extensions. AbstractJavaProjectConfigurator assumes single additional java source folder needs to be configured for the project and the source folder location is defined by ${outputDirectory} maven plugin configuration parameter. This allows very simple ANTLR project configurator implementation (is explained below)
public class AntlrProjectConfigurator extends AbstractJavaProjectConfigurator {
@Override
public AbstractBuildParticipant getBuildParticipant(IMavenProjectFacade projectFacade,
MojoExecution execution,
IPluginExecutionMetadata executionMetadata) {
return new AntlrBuildParticipant(execution);
}
}
The follow extension in plugin.xml registers ANTLR project configurator with m2e
<extension point="org.eclipse.m2e.core.projectConfigurators">
<configurator
class="org.sonatype.m2e.antlr.internal.AntlrProjectConfigurator"
id="org.sonatype.m2e.antlr.antlrConfigurator"
name="ANTLR Project Configurator">
</configurator>
</extension>
lifecycle-mapping-metadata.xml located at the root of the project (and at the root of OSGi bundle jar at runtime) maps antlr3-maven-plugin antlr goal to ANTLR project configurator. Note that configurator id in the mapping matches configurator id defined in the extension point above.
<lifecycleMappingMetadata> <pluginExecutions> <pluginExecution> <pluginExecutionFilter> <groupId>org.antlr</groupId> <artifactId>antlr3-maven-plugin</artifactId> <versionRange>[3.1.1,)</versionRange> <goals> <goal>antlr</goal> </goals> </pluginExecutionFilter> <action> <configurator> <id>org.sonatype.m2e.antlr.antlrConfigurator</id> </configurator> </action> </pluginExecution> </pluginExecutions> </lifecycleMappingMetadata>
And finally, the following extension in plugin.xml registers m2e extension as lifecycle mapping metadata source with m2e. This is mostly needed as performance optimization, because without this extension m2e would have to search lifecycle-mapping-metadata.xml file in all installed eclipse plugins.
<extension point="org.eclipse.m2e.core.lifecycleMappingMetadataSource"> </extension>
AntlrBuildParticipant
AntlrBuildParticipant generates java source files (any resources generated by ANTLR, to be precise) during eclipse incremental and full builds.
First AntlrBuildParticipant checks if any of the grammar files have changed and short-cuts code generation if there were no changes.
File source = maven.getMojoParameterValue(getSession(), getMojoExecution(), "sourceDirectory", File.class);
Scanner ds = buildContext.newScanner( source ); // delta or full scanner
ds.scan();
String[] includedFiles = ds.getIncludedFiles();
if (includedFiles == null || includedFiles.length <= 0 ) {
return null;
}
Then, AntlrBuildParticipant delegates to MojoExecutionBuildParticipant.build to execute antlr3-maven-plugin antlr goal. This generates resources on filesystem, but does not update eclipse workspace
Set<IProject> result = super.build( kind, monitor );
Finally, AntlrBuildParticipant refreshes generation output folder in
workspace
File generated = maven.getMojoParameterValue(getSession(), getMojoExecution(), "outputDirectory", File.class);
if (generated != null) {
buildContext.refresh( generated );
}
Testing m2e/antlr code generation support
Test project is setup to fail java compilation if workspace project source folders were not properly configured or ANTLR code generation did not succeed for whatever reason. AntlrGenerationTest.java performs very basic tests to make sure that m2e/antlrv3 integration is not obviously broken.
Import the test project and wait for all background processing triggered by the new project to finish. Even though the test does not assert this, the workspace project should be fully configured at this point
ResolverConfiguration configuration = new ResolverConfiguration(); IProject project1 = importProject( "projects/antlr/antlr-v3-p001/pom.xml", configuration ); waitForJobsToComplete();To make sure no state is retained from one test run to the next,
importProject always creates new/fresh copy of the test project
under target/test workspace location; the copy is removed by the test tearDown logic.
Automatic workspace build is disable during m2e extensions tests by default, so the build needs to be run explicitly from the test code.
project1.build( IncrementalProjectBuilder.FULL_BUILD, monitor ); project1.build( IncrementalProjectBuilder.INCREMENTAL_BUILD, monitor ); waitForJobsToComplete();Note that there are two calls to IProject.build. First, full, build will generate the code. Second, incremental, build will give JDT Java builder the chance to compile the generated code. This matches how java code generation is handled by a “real” eclipse workspace, so it is therefore important that AntlrBuildParticipant performs code generation only when source grammar files change, otherwise workspace build will keep restarting itself forever.
At this point the project should be fully configured, the code should be generated and both generated code should be compiled without errors. Lets assert all that
assertNoErrors( project1 ); IJavaProject javaProject1 = JavaCore.create( project1 ); IClasspathEntry[] cp1 = javaProject1.getRawClasspath(); assertEquals( new Path( "/antlr-p001/target/generated-sources/antlr" ), cp1[3].getPath() ); assertTrue( project1.getFile( "target/generated-sources/antlr/test/SampleParser.java" ).isSynchronized( IResource.DEPTH_ZERO ) ); assertTrue( project1.getFile( "target/generated-sources/antlr/test/SampleParser.java" ).isAccessible() );
TODO add code to assert that expected .class files were created
Building the code and generating p2 repository
This section is not meant as a substitute for Tycho tutorials and documentation, but rather as suggested m2e extension source tree layout and build setup. Explanation is based on m2eclipse-egit project.
Project directory structure overview
m2eclipse-egit/ <= project basedir, all project files are under this directory org.sonatype.m2e.egit/ <= main bundle project src/ pom.xml org.sonatype.m2e.egit.feature/ <= eclipse feature project src/ pom.xml org.sonatype.m2e.egit.tests/ <= automated tests (optional, but highly recommended) feature.xml pom.xml pom.xml <= aggregator/parent pom.xml
Parent pom.xml
This pom.xml snippet tells Maven to enable Tycho for all modules of this project.
...
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.eclipse.tycho</groupId>
<artifactId>tycho-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${tycho-version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
...
This snippet configures p2 repositories that will be used to resolve project dependencies. Indigo release repository does not include m2e org.eclipse.m2e.tests.common, so m2e release repository is specified separately.
... <repositories> <repository> <id>eclipse</id> <url>[http://download.eclipse.org/releases/mars](http://download.eclipse.org/releases/mars)</url> <layout>p2</layout> </repository> <repository> <id>m2e</id> <url>[http://download.eclipse.org/technology/m2e/releases/1.6](http://download.eclipse.org/technology/m2e/releases/1.6)</url> <layout>p2</layout> </repository> </repositories> ...
org.sonatype.m2e.egit and org.sonatype.m2e.egit.tests
org.sonatype.m2e.egit and org.sonatype.m2e.egit.tests are conventional PDE Plug-In projects and only requires minimal pom.xml file.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.sonatype.m2e.egit</groupId>
<artifactId>org.sonatype.m2e.egit.parent</artifactId>
<version>0.14.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<artifactId>org.sonatype.m2e.egit</artifactId>
<packaging>eclipse-plugin</packaging>
<name>Maven SCM Handler for EGit Plug-in</name>
</project>
There is, however, tycho-surefire-plugin configuration in the parent pom that affects test execution.
org.sonatype.m2e.egit.feature
org.sonatype.m2e.egit.feature is a PDE Feature project and it serves two purposes. It defines Eclipse Feature that can be installed using p2 installation GUI (it is not possible to install individual bundles). It also generates and optionally deploys to a remote server p2 repository containing the feature and the main bundle.
feature.xml, feature.properties and license.html files in the root of the project define contents of the feature. This is standard eclipse fare and regular PDE documentation fully applies. Beware that a feature must provide correct license information to be accepted to m2e marketplace catalog.
p2 repository generation is configured in pom.xml with additional configuration provided via category.xml file located in the root of the project. Additionally, repository zip file contents is controlled by src/main/assembly/assembly.xml.
Specifically
Aggregate feature’s “included” dependencies under conventional target/site directory.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.eclipse.tycho</groupId>
<artifactId>tycho-packaging-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${tycho-version}</version>
<configuration>
<deployableFeature>true</deployableFeature>
</configuration>
</plugin>
Generate p2 repository metadata for artifacts collected in target/site.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.eclipse.tycho</groupId>
<artifactId>tycho-p2-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${tycho-version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>categorization</id>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>category-p2-metadata</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<metadataRepositoryName>Maven SCM Handler for EGit</metadataRepositoryName>
<artifactRepositoryName>Maven SCM Handler for EGit</artifactRepositoryName>
</configuration>
</plugin>
By convention, p2 repository category information comes from category.xml file.
<site> <feature url="features/org.sonatype.m2e.egit.feature_0.0.0.qualifier.jar" id="org.sonatype.m2e.egit.feature" version="0.0.0.qualifier"> <category name="m2eclipse-egit"/> </feature> <category-def name="m2eclipse-egit" label="Maven SCM Handler for EGit"/> </site>
Create p2 repository zip file.
<plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <descriptors> <descriptor>src/main/assembly/assembly.xml</descriptor> </descriptors> </configuration> <executions> <execution> <id>make-assembly</id> <phase>package</phase> <goals> <goal>single</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin>
… using assembly descriptor src/main/assembly/assembly.xml
<assembly>
<id>site</id>
<formats>
<format>zip</format>
</formats>
<includeBaseDirectory>false</includeBaseDirectory>
<fileSets>
<fileSet>
<directory>${project.build.directory}/site</directory>
<outputDirectory>/</outputDirectory>
</fileSet>
</fileSets>
</assembly>
Publishing p2 repository
TBD
