Versions
- v1
- v2
- v3 (current)
Introduction
The AppManifest defines the properties of your Vehicle App and its functional interfaces (FIs).
FIs may be:
- required service interfaces (e.g. a required gRPC service interface)
- the used vehicle model and accessed data points.
- an arbitrary abstract interface description used by 3rd parties
In addition to required FIs, provided FIs can (and need) to be specified as well.
These defined interfaces are then used by the Velocitas toolchain to:
- generate service stubs for either a client implementation (required IF) or a server implementation (provided IF) (i.e. for gRPC)
- generate a source code equivalent of the defined vehicle model
Overview
The image below depicts the interaction between App Manifest and DevEnv Configuration at -development time- The responsibilities are clearly separated; the App Manifest describes the application and its interfaces whereas DevEnv Configuration (or .velocitas.json) defines the configuration of the development environment and all the packages used by the Velocitas toolchain.
Context
To fully understand the AppManifest, let’s have a look at who interacts with it:
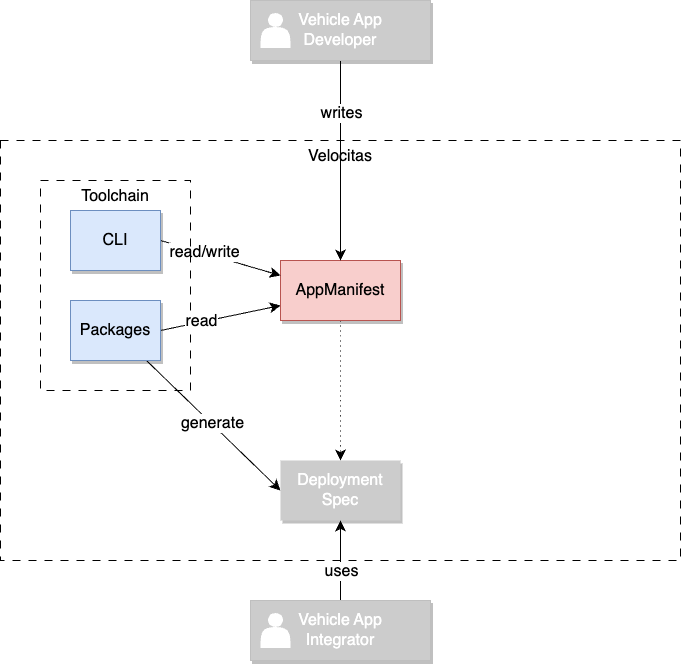
Purpose
- Define the requirements of a Vehicle App in an abstract way to avoid dependencies on concrete Runtime and Middleware configurations.
- Description of your applications functional interfaces(VehicleModel, services, APIs, …)
- Enable loose coupling of functional interface descriptions and the Velocitas toolchain. Some parts of the toolchain are responsible for reading the file and acting upon it, depending on the type of functional interface
- Providing an extendable syntax to enable custom functional interface types which may not provided by the Velocitas toolchain itself, but by a third party
- Providing a single source of truth for generation of deployment specifications (i.e. Kanto spec, etc…)
Example
// AppManifest.json
{
"manifestVersion": "v3",
"name": "SampleApp",
"interfaces": [
{
"type": "vehicle-signal-interface",
"config": {
"src": "https://github.com/COVESA/vehicle_signal_specification/releases/download/v3.0/vss_rel_3.0.json",
"datapoints": {
"required": [
{
"path": "Vehicle.Speed",
"optional": "true",
"access": "read",
}
],
"provided": [
{
"path": "Vehicle.Cabin.Seat.Row1.Pos1.Position",
}
]
}
}
},
{
"type": "grpc-interface",
"config": {
"src": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/eclipse-kuksa/kuksa-incubation/0.4.0/seat_service/proto/sdv/edge/comfort/seats/v1/seats.proto",
"required": {
"methods": [ "Move", "MoveComponent" ]
},
}
},
{
"type": "pubsub",
"config": {
"reads": [ "sampleapp/getSpeed" ],
"writes": [ "sampleapp/currentSpeed", "sampleapp/getSpeed/response" ]
}
}
]
}
The VehicleApp above has an:
-
interface towards our generated Vehicle Signal Interface based on the COVESA Vehicle Signal Specification . In particular, it requires read access to the vehicle signal
Vehicle.Speedsince the signal is marked as optional the application will work, even if the signal is not present in the system. Additionally, the application acts as a provider for the signalVehicle.Cabin.Seat.Row1.Pos1.Positionmeaning that it will take responsibility of reading/writing data directly to vehicle networks for the respective signal. -
interface towards gRPC based on the
seats.protofile. Since thedirectionisrequireda service client for theseatsservice will be generated who interacts with the Velocitas middleware. -
interface towards the
pubsubmiddleware and is reading to the topicsampleapp/getSpeedand writing the topicssampleapp/currentSpeed,sampleapp/getSpeed/response.
The example has no provided interfaces.
Structure
Describes all external properties and interfaces of a Vehicle Application.
Properties
| Property | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
manifestVersion |
string | Yes | The version of the App Manifest. |
name |
string | Yes | The name of the Vehicle Application. |
interfaces |
object [] | No | Array of all provided or required functional interfaces. |
Interfaces
Properties
| Property | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | The type of the functional interface. |
config |
object | No | The configuration of the functional interface type. Content may vary between all types. |
Config
The configuration of the functional interface type. Content may vary between all types.
Refer to the JSON Schema of the current AppManifest here .
Visualization
graph TD
manifest(AppManifest.json)
manifest --> manifestVersion[manifestVersion]
manifest --> name[name]
manifest -.-> interfaces[interfaces]
interfaces -- "0..n" --> interfaces.item(object)
interfaces.item --> interfaces.item.type[type]
interfaces.item -.-> interfaces.item.config[config]
Functional interface types supported by Velocitas
Here is a list of functional interface types directly supported by the Velocitas toolchain and which Velocitas CLI packages are exposing the support:
Support for additional interface types may be added by providing a 3rd party CLI package .
Planned, but not yet available features
Some FIs are dependent on used classes, methods or literals in your Vehicle App’s source code. For example the vehicle-model FI requires you to list required or provided datapoints. At the moment, these attributes need to be filled manually. There are ideas to auto-generate these attributes by analyzing the source code, but nothing is planned for that, yet.
Further information
- Tutorial: Quickstart
- Tutorial: Vehicle Model Creation
- Tutorial: Vehicle App Development
- Concept: Lifecycle Management