TYPE.NUMBER
ΜMIC.200
This module uses the library provided for the µMIC.200.
You need the umic_dio.h, umic_relay.h and umic_led.h headers and also the umic.so library to be present in your system and accessible by the compiler.
The parameters should be the type and its number separated by a dot:
NUMBER depends on TYPE, where TYPE can be (all are in lower case):
-
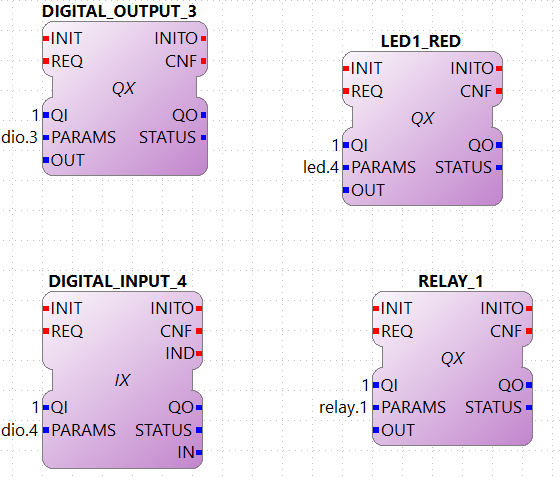
led: controls the LED1-4 of the µMIC.200 (Only QX can be used withled). The possible numbers for NUMBER are from 0 to 7 according to the table below:-
0 → LED1_GREEN
-
1 → LED2_GREEN
-
2 → LED3_GREEN
-
3 → LED4_GREEN
-
4 → LED1_RED
-
5 → LED2_RED
-
6 → LED3_RED
-
7 → LED4_RED
Example:
led.4 → controls the LED1 color red
-
-
dio: controls the 8 digital I/O at pins 5-12. Number can be from 1 to 8. Use IX to make it input, and QX to make it output.Example:
dio.3→ will access Digital I/O 3 at pin 7 of the µMIC.200 -
relay: controls the relays. The possible numbers are 1 and 2. The 1 controls the NO relay and 2 the NC. Only QX can be used withrelay.Example:
relay.1→ will control the NC relay at pins 14- 15
|
Important
|
Using the Releays
To use the relay and led, in some cases you might have to change some header files in your µMIC.200.
You need to find the files
+ //----------------------------------------------------------------------------// #ifdef __cplusplus } #endif // end of C++ compiler wrapper //----------------------------------------------------------------------------// +
If you don’t want to use the relay and led, or you don’t want to change the header files, go to |
Where to go from here?
You can see the supported protocols:
You can see the examples:
If you want to go back to the Where to Start page, we leave you here a fast access
Or Go to top
