Support SSH tunneling for managed connections
With the upcoming release of Eclipse Ditto version 2.0.0 it will be possible to
SSH tunneling for managed connections
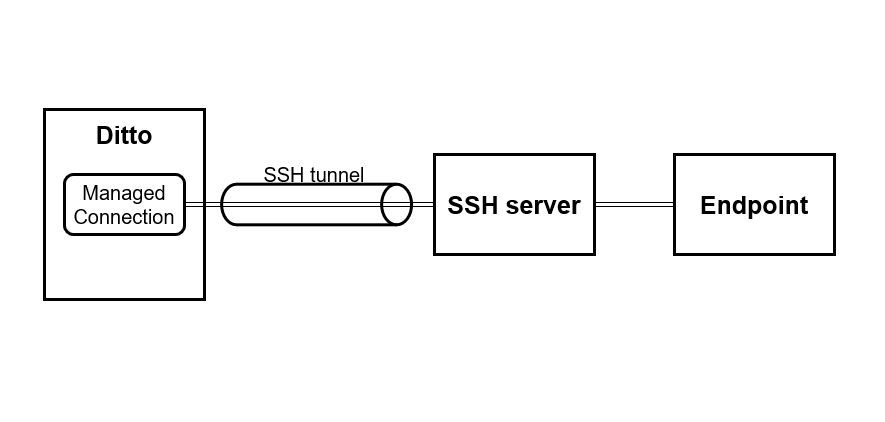
With the upcoming release of Eclipse Ditto version 2.0.0, managed connections support establishing an SSH tunnel, which is then used to connect to the actual target endpoint. This is useful when the target endpoint is not directly accessible. Currently, this feature is available for all connection types supported in Ditto, except for Kafka 2.x.
For further information, see Secure Shell (SSH) Connection Protocol, RFC4254
Setting up connections with SSH tunneling in Ditto
When setting up a tunneled connection, the configuration must specify the sshTunnel section, which contains
the necessary information to establish the SSH port forwarding. For authentication, password and public
key are supported. Also, host validation using public key fingerprints are supported. The tunnel configuration does not
affect the other parts of your connection configuration. If the feature is enabled the connection will establish an SSH
tunnel and afterwards use this tunnel to connect to the desired endpoint. In case you later disable the SSH tunnel
feature, the payload will be processed directly to the desired endpoint.
Basic Authentication
When using basic authenticating the sshTunnel configuration should contain the credentials.type plain, as
well as the username and password fields:
{
"name": "tunneled-connection",
"connectionType": "mqtt",
"uri": "tcp://mqtt.eclipseprojects.io:1883",
"sources": [{ ... }],
"sshTunnel": {
"enabled": true,
"uri": "ssh://ssh-host:2222",
"credentials": {
"type": "plain",
"username": "username",
"password": "password"
},
"validateHost": true,
"knownHosts": ["MD5:e0:3a:34:1c:68:ed:c6:bc:7c:ca:a8:67:c7:45:2b:19"]
}
}
Authentication with public key
On public key authentication the credentials.type is public-key. In addition to the username the publicKey and
privateKey have to be provided. The public key must be provided as PEM-encoded key in X.509 format. The private
key must be provided as PEM-encoded key in unencrypted PKCS8 format as specified by RFC-7468.
{
"name": "tunneled-connection",
"connectionType": "mqtt",
"uri": "tcp://mqtt.eclipseprojects.io:1883",
"sources": [{ ... }],
"sshTunnel": {
"enabled": true,
"uri": "ssh://ssh-host:2222",
"credentials": {
"type": "public-key",
"username": "username",
"publicKey": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9.....\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----",
"privateKey": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\nMIIEvAIBADANBgkqhki....\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----"
},
"validateHost": true,
"knownHosts": ["MD5:e0:3a:34:1c:68:ed:c6:bc:7c:ca:a8:67:c7:45:2b:19"]
}
}
The following command can be used to convert a standard OpenSSL key in PKCS1 format to the PKCS8 format accepted by Ditto:
openssl pkcs8 -topk8 -nocrypt -in client-private.pem.key -out client-private.pem.pk8
Host validation using public key fingerprints
When validateHost is enabled, the host public key fingerprints are validated. They can be provided
in the format the standard command line tool ssh-keygen produces them. The fingerprints are
prefixed with an alias of the hash algorithm that was used to calculate the fingerprint. Ditto supports the following
hash algorithms for public key fingerprints: MD5, SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384 and SHA512. To generate a
valid fingerprint with an MD5 hash algorithm from the public key, following can be used:
ssh-keygen -lf id_rsa.pub -E md5
Feedback?
Please get in touch if you have feedback or questions regarding this new functionality.
–
The Eclipse Ditto team