Actors
Description
The actor is the basic structural building block for building systems with ROOM. An actor can be refined hierarchically and thus can be of arbitrarily large scope. Ports define the interface of an actor. An actor can also have a behavior usually defined by a finite state machine.
Motivation
-
Actors enable the construction of hierarchical structures by composition and layering
-
Actors have their own logical thread of execution
-
Actors can be freely deployed
-
Actors define potentially re-usable blocks
Notation
| Element | Graphical Notation | Textual Notation |
|---|---|---|
| ActorClass |
|
|
| ActorRef |
|
|
Details
Actor Classes, Actor References, Ports and Bindings
An ActorClass defines the type (or blueprint) of an actor. Hierarchies are built by ActorClasses that contain ActorReferences which have another ActorClass as type. The interface of an ActorClass is always defined by Ports. The ActorClass can also contain Attributes, Operations and a finite StateMachine.
External Ports define the external interface of an actor and are defined in the Interface section of the ActorClass.
Internal Ports define the internal interface of an actor and are defined in the Structure section of the ActorClass.
Bindings connect Ports inside an ActorClass.
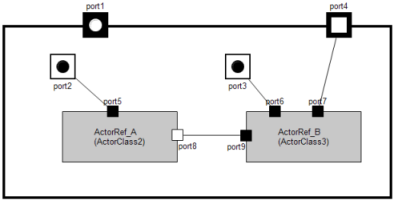
Let us have a look at example:
| Graphical Notation | Textual Notation |
|---|---|
|
|
|
- ActorClass1 contains two ActorReferences (of ActorClass2 and ActorClass3)
- port1 is an external end port. Since it connects external actors with the behavior of the ActorClass, it is defined in the Interface section as well as in the Structure section of the ActorClass.
- port2 and port3 are internal end ports and can only be connected to the ports of contained ActorReferences. Internal end ports connect the behavior of an ActorClass with its contained ActorReferences.
- port4 is a relay port and connects external Actors to contained ActorReferences. This port can not be accessed by the behavior of the ActorClass.
- port5 through port9 are ports of contained actor references. port8 and port9 can communicate without interference with the containing actor class.
- Bindings can connect ports of the actor class and its contained actor references.
Attributes
Attributes are part of the Structure of an actor class. They can be of a PrimitiveType or a DataClass.
Example:
ActorClass ActorClass3 {
Structure {
Attribute attribute1: int32 // attribute of primitive type
Attribute attribute2: DataClass1 // attribute of DataClass type
}
}
Operations
Operations are part of the Behavior of an actor class. Arguments and return values can be of a PrimitiveType or a DataClass. Data classes can be passed by value (implicit) or by reference (ref).
Example:
ActorClass ActorClass4 {
Behavior {
// no arguments, no return value
Operation operation1(): void '''
user code
'''
// argument of primitive type, return value of primitive type
Operation operation2(Param1: int32, Param2: float64): uint16 '''
user code
'''
// arguments and return value by value
Operation operation3(Param1: int32, Param2: DataClass1): DataClass1 '''
user code
'''
// arguments and return value by reference except for primitive types
Operation operation4(Param1: int32, Param2: DataClass1 ref): DataClass1 ref '''
user code
'''
}
}