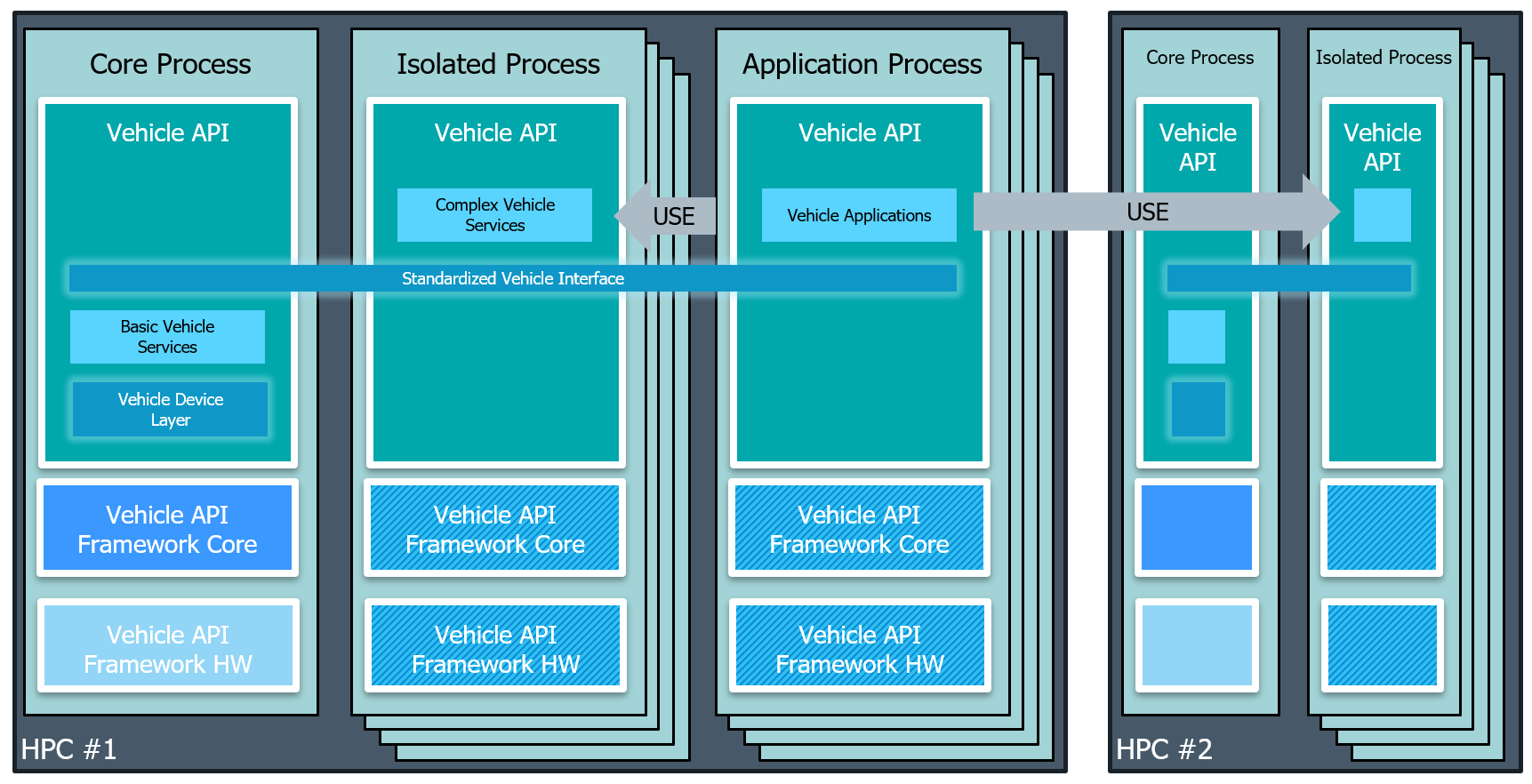
A view under the hood#
Component Definition#
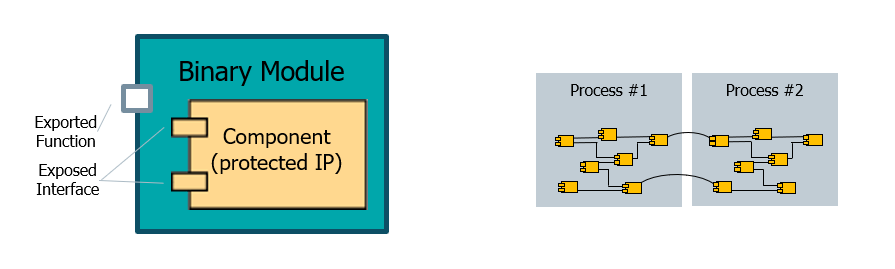
The V-API system uses the following characteristics:#
Components are compiled software modules in binary form
Components are linked dynamically during runtime
Components communicate using interfaces
Components can be used to build a dynamic framework
The functionality of a system is determined by the composition of components
Components are closed source and therefore can be written by 3rd parties
Components are language independent
Components are very close to a C++ class – performance is very high
Components can be used using direct calls within the same process
Components can be called in other processes using Remote Procedure Calls (RPC)
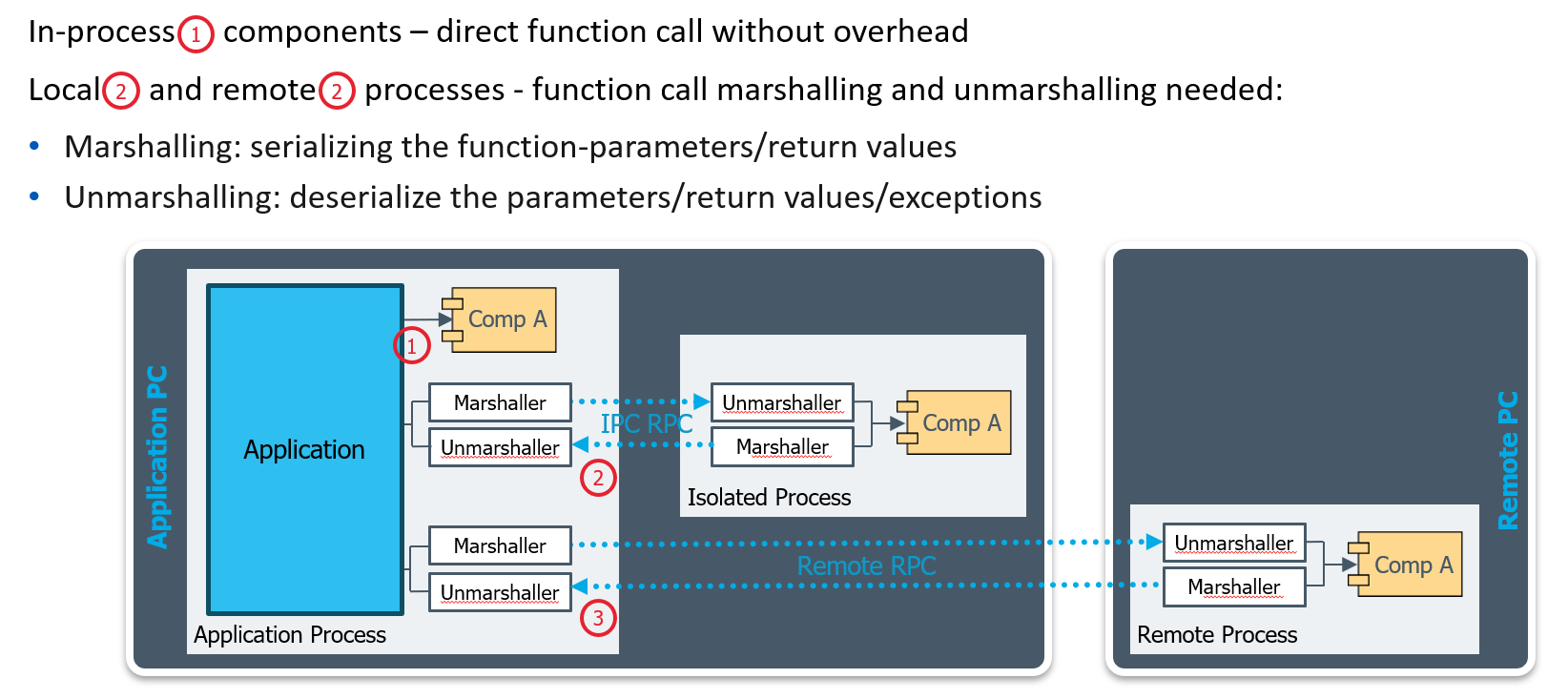
Components implemented easily with C++:#
Interfaces are complex structures with only pure virtual functions
Function pointers are managed through the V-table
Components are classes deriving from interfaces
Binary components supported by OS:#
Most modern OSes support dynamic libraries (DLL or SO)
Library uses dynamic (late) binding (instead of static binding by the linker)
Type safety and error mitigation is responsibility of programmer (tooling)
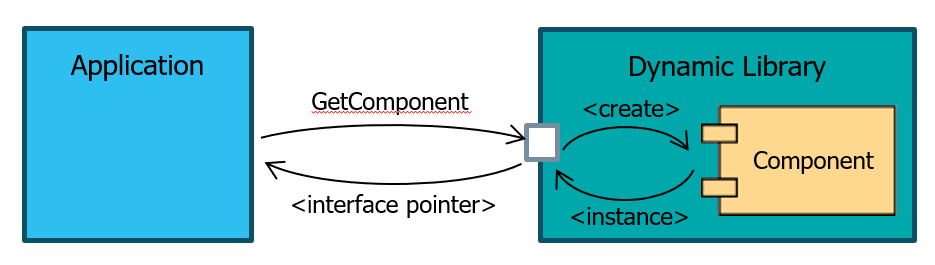
Interface IDL#
Component interface language: OMG IDL (ISO/IEC 19516)#
OMG IDL is part of the CORBA specification
OMG IDL is used in DDS specification
OMG IDL can be used as stand-alone language without CORBA
OMG IDL is around since 1991 and still updated
OMG IDL 4.2 was standardized in 2018 and the latest contribution dates February 2021
OMG IDL license allows the implementation of software based on the (partial) specification
OMG IDL language is very close to the C++ language specification, therefore easy to learn
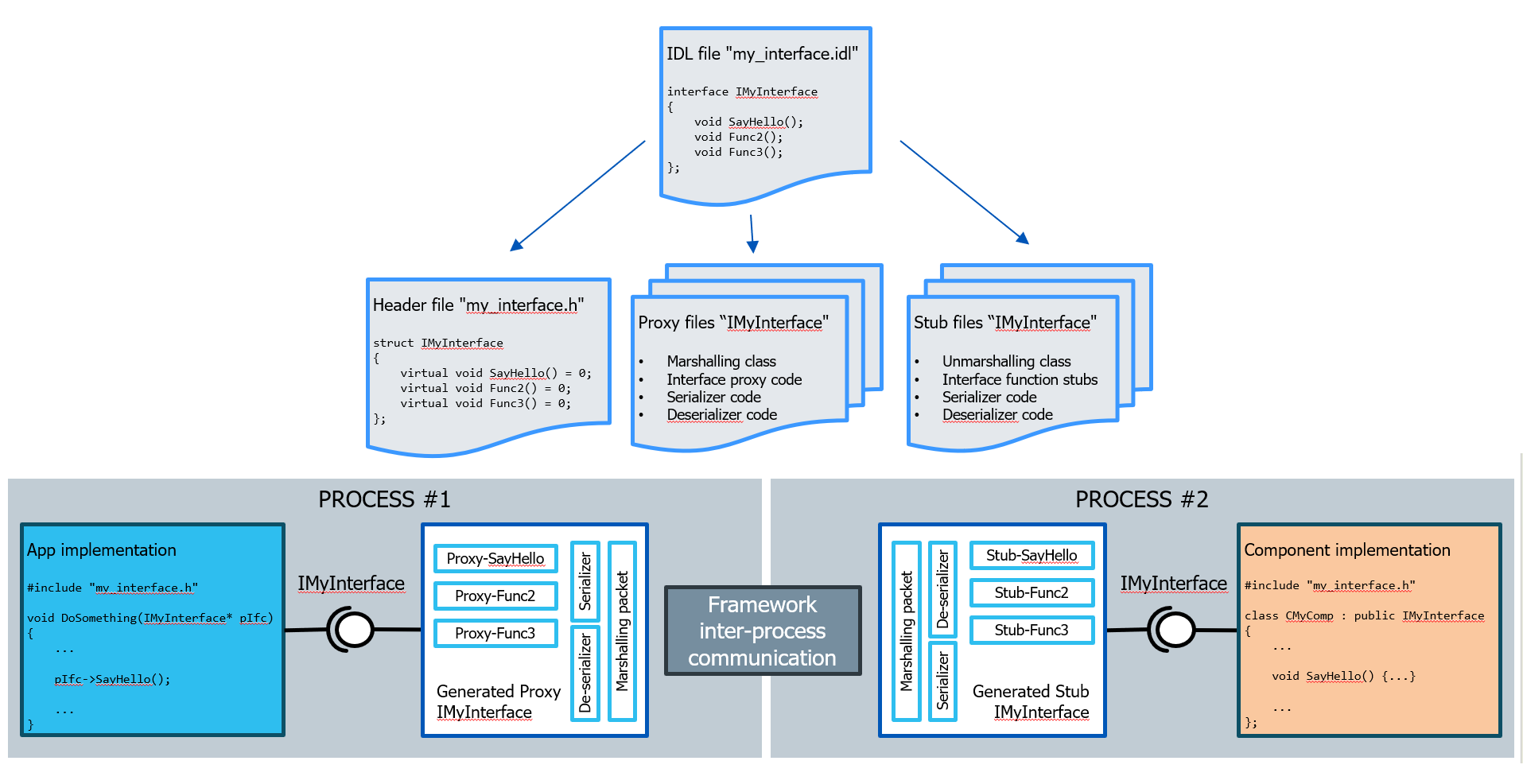
The IDL compiler generates code for:
Header file to be used by caller and callee
Proxy implementation for marshalling and communication
Stub implementations for calling component functions and marshalling
Safety and Security#
There are several safety and security considerations:
Each interface receives a unique ID - allows access to the interface
No interface change of same ID, regardless of platform
Interface change of new ID, no mixing of old and new interfaces
Serialization/deserialization protected with CRC32C
Automatically detection of platform endianness + converting if necessary
Free spec interpretation of data types are fixed within V-API for all platforms (e.g. wchar, wstring, native and any).
Only specified exceptions are marshalled. No exception surprises. Other exceptions are caught and reported.
During the development of the VAPI Framework several safety and security considerations were considered:
Isolate complex services and applications (fault impact reduction)
Profile based feature accessibility
Prepared for the use of security roles
Connection stealing prevented with runtime-based connection identification