Key Building Blocks of Open Vehicle API#
Purpose of the framework: To develop software components that are isolated, modular, and interference-free.
For more features the Open Vehicle API offers go to Key Features.
Here we describe the major building blocks the framework contains.
Free of Interference#
In simple words: It’s a C++ framework for building modular software systems where each Complex Service runs in its own process and communicates through interfaces defined in IDL. This design ensures isolation, scalability, and maintainability.
Key Design Principles
Process Isolation
Each component runs in its own process, ensuring complete separation of memory and execution context.
This prevents unintended side effects and improves fault tolerance.
Interface-Driven Communication
Components interact via well-defined interfaces.
Interfaces are described using IDL (Interface Definition Language), enabling language-agnostic and structured communication.
Loose Coupling
Components are decoupled from each other.
Changes in one component do not affect others, as long as the interface contract remains stable.
Scalability & Maintainability
New components can be added without modifying existing ones.
Easier testing and debugging due to isolated execution.
Technical Highlights
IDL Usage:
Defines the interfaces for communication.
Enables automatic generation of stubs/skeletons for IPC (Inter-Process Communication).
IPC Mechanism:
Could be based on sockets, shared memory, message queues, or a custom protocol.
Ensures reliable and efficient data exchange between processes.
Component Lifecycle Management:
Each component can be started, stopped, and monitored independently.
Optional: Include a supervisor or orchestrator module.
Benefits
Robustness: Failures in one component don’t crash the entire system.
Security: Process boundaries help enforce access control and sandboxing.
Flexibility: Easy to replace or upgrade components.
Testability: Components can be unit-tested in isolation.
Vehicle and Platform Abstraction#
Important
The target of framework is not only to abstract the hardware. The goal of the framework is to run the Basic Service s or Complex Service s on any vehicle by using a vehicle bus standardization. See component stack
Purpose: Decouples application logic from hardware specifics.
Components:
Abstract Interfaces for Vehicle Types.
Platform-Specific Implementations.
Middleware Layer for Communication.
Benefits:
Portability across platforms, supported development platforms: Windows and Linux.
Platform abstraction (file access, process management, …) allows to integrate any middleware by implementing the platform abstraction interfaces through the middleware.
Easier integration with new vehicle models.
For more details see Component Stack.
Mixed-Criticality#
Purpose: Supports multiple applications with different safety to run at the same time.
Components:
Criticality Levels (Safety-Critical ASIL A/B, None-Safety Applications).
Free of interference (Sandboxing).
Benefits:
Safe coexistence of critical and non-critical tasks & applications.
Optimized resource usage.
Open Vehicle API supports Mixed-Criticality. The following picture shows how the Mixed-Criticality is build up. While a possible ASIL Level-A / ASIL Level-B function would run on the Safety Instance and will not be changed at runtime, the QM Function s run on the QM Instance. These QM Function s can be installed/uninstalled and started/stopped at runtime. QM Function instance has no connection to the vehicle network. Both, QM Function s as well as Safety Function s run in isolated processes.
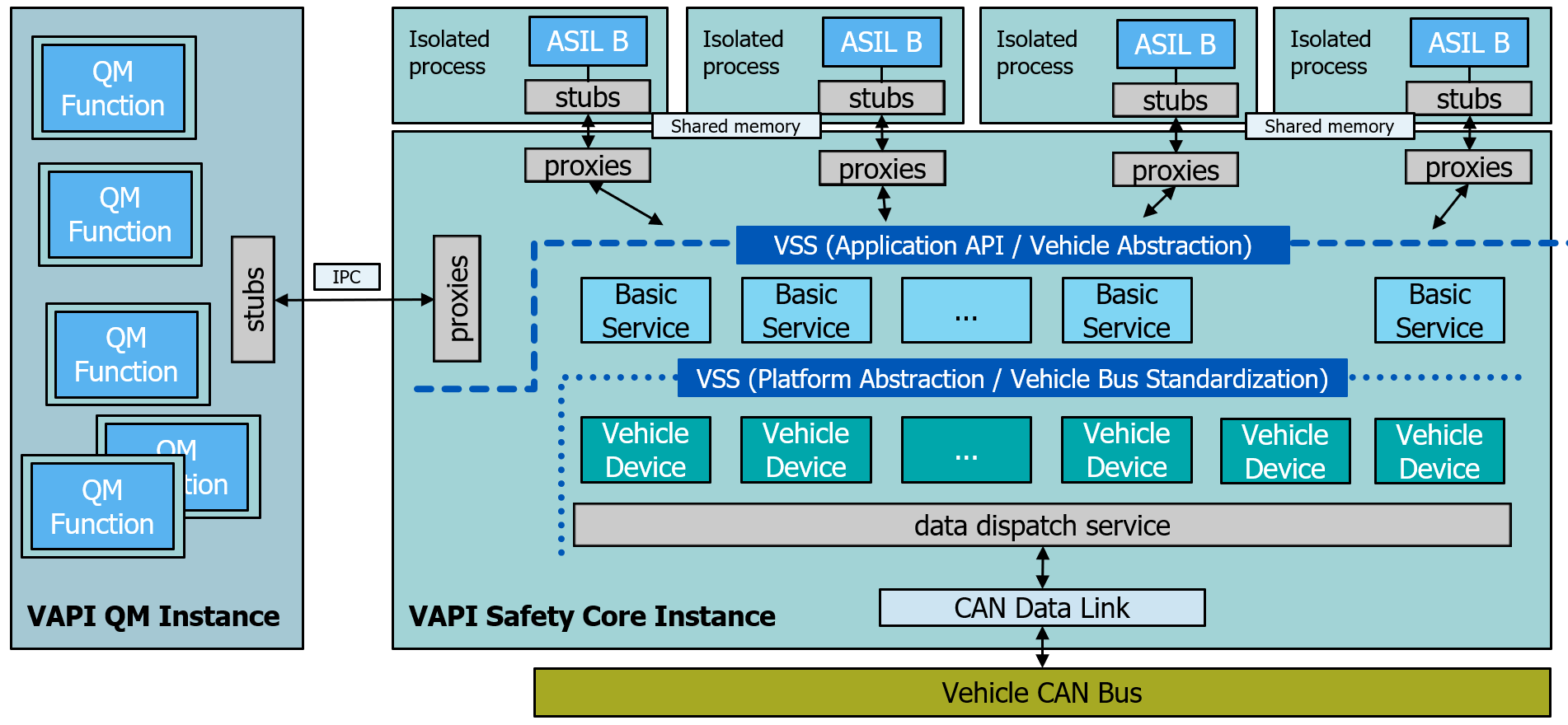
The target is to run multiple applications at the same time and to allow dynamical loading / stopping of QM applications at runtime.
Term |
ASIL Level |
Safety Relevance |
Development Requirements |
Installable & can be started & stopped |
QM Function |
QM |
Low/None |
Standard quality processes |
at runtime |
Safety Function |
A-D |
High |
ISO 26262 safety lifecycle |
at startup of HPC: system is testable |
Event-Driven Architecture#
Purpose: Enables reactive and modular system behavior.
Components:
Event Dispatcher.
Subscriber/Publisher Model.
Benefits:
Loose coupling between components.
Scalability and flexibility.
Besides cyclic execution Open Vehicle API is a event driven framework. It’s possible to support cyclic data connection like a CAN bus or a simulation software like the Open-Source Simulation Software OpenXilEnv. The VAPI Component s then support event driven execution as well as cyclic execution by using the timer service.
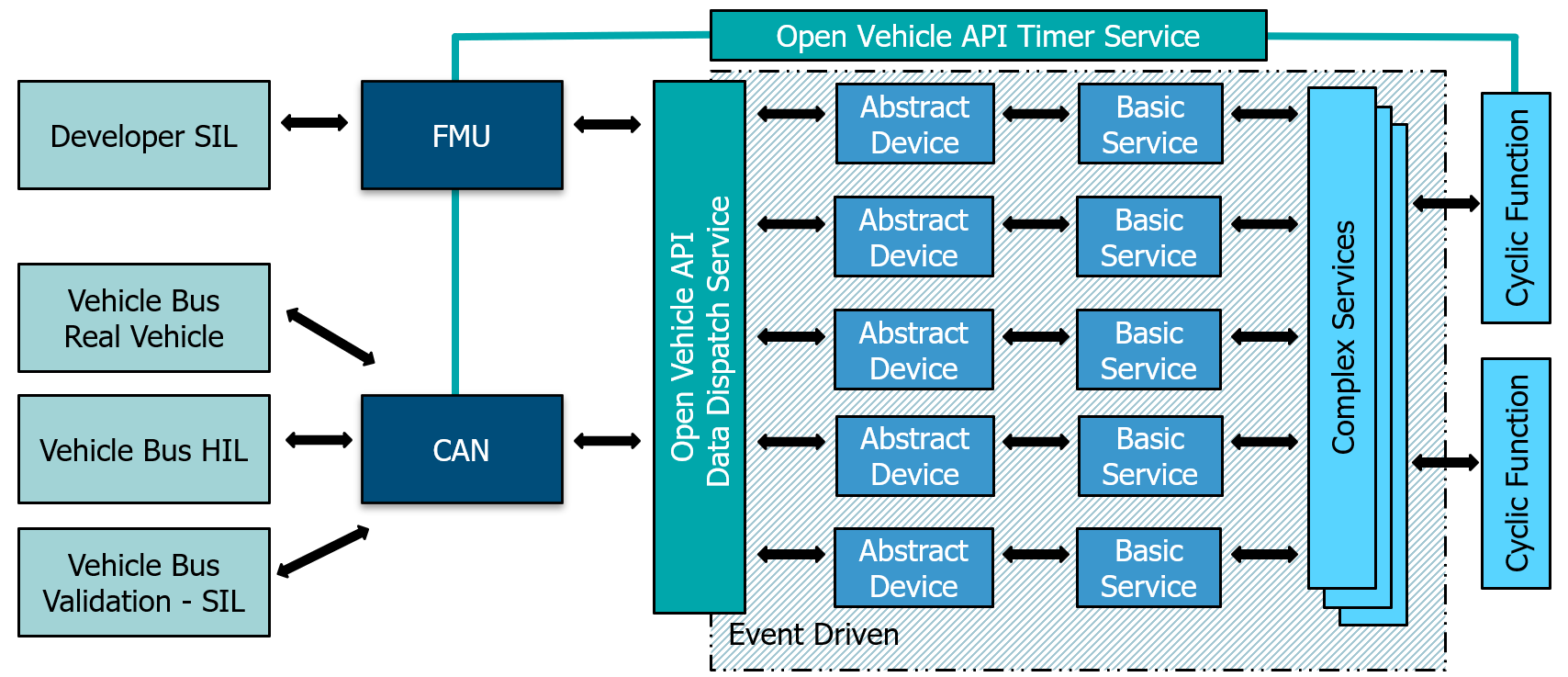
Enhanced Testability & Development Process#
Purpose: Improves development efficiency and reliability.
Components:
Mock Interfaces.
Support of Unit-, Integration- & System Test Frameworks.
Continuous Integration Hooks.
Validation and Release Processes.
Benefits:
Faster development cycles.
Easier debugging and validation.
This framework was developed by Test-Driven Development (TDD) methodology. This approach ensures that the codebase is robust, maintainable, and meets the specified requirements from the outset. Therefore, we have already more than 6000 tests (Development Snapshot: August 1, 2025).
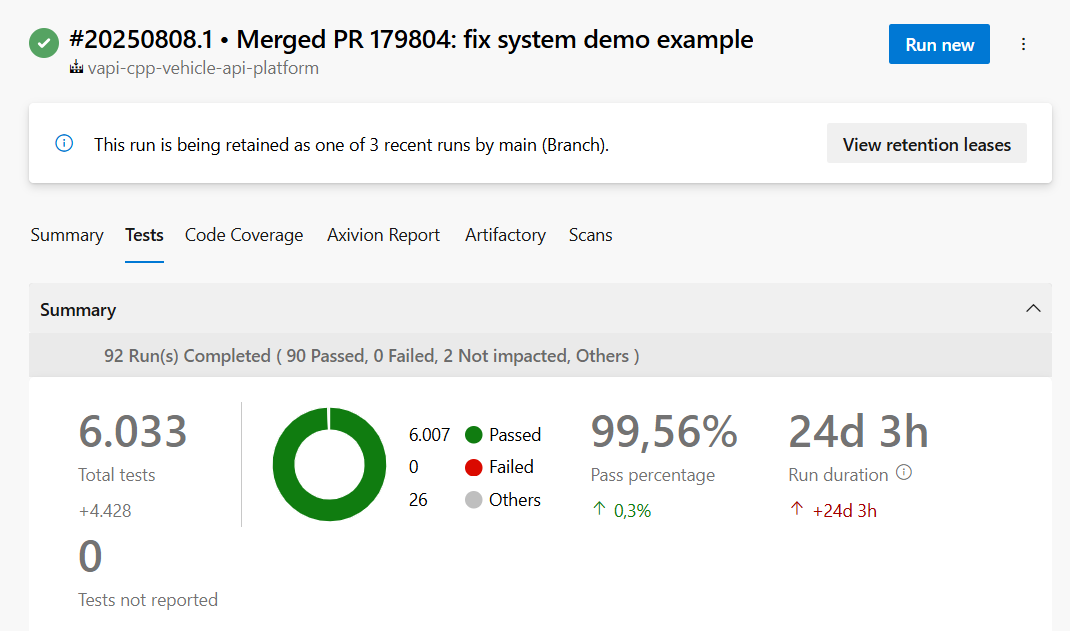
The increasing complexity of modern vehicle software requires robust, scalable, and future-oriented frameworks. Especially in the context of distributed systems and agile development processes- The component-based framework makes it possible that test-driven development can be easily be put into practice. The developer can use his local Operating System to develop his VAPI Component by writing unit and module tests. Testing locally is therefore normally no problem. Additional is it possible from a dbc file to auto generate a FMU with the tool sdv_dbc_util. This FMU can then be used in simulation software like the Open-Source Software OpenXilEnv.
After finishing the development, the automatic validation can be carried out. A build pipeline can trigger system tests by using the CAN Reader/Writer component based on Vector SIL Kit instead of the CAN Reader/Writer component based on CAN Sockets which will be necessary on the real vehicle itself. After successful system test runs the component can be released and be put on the real vehicle.
It’s not worth mentioning that with setting up systems with different VAPI Component s huge test systems are easily be build and will grow by itself.
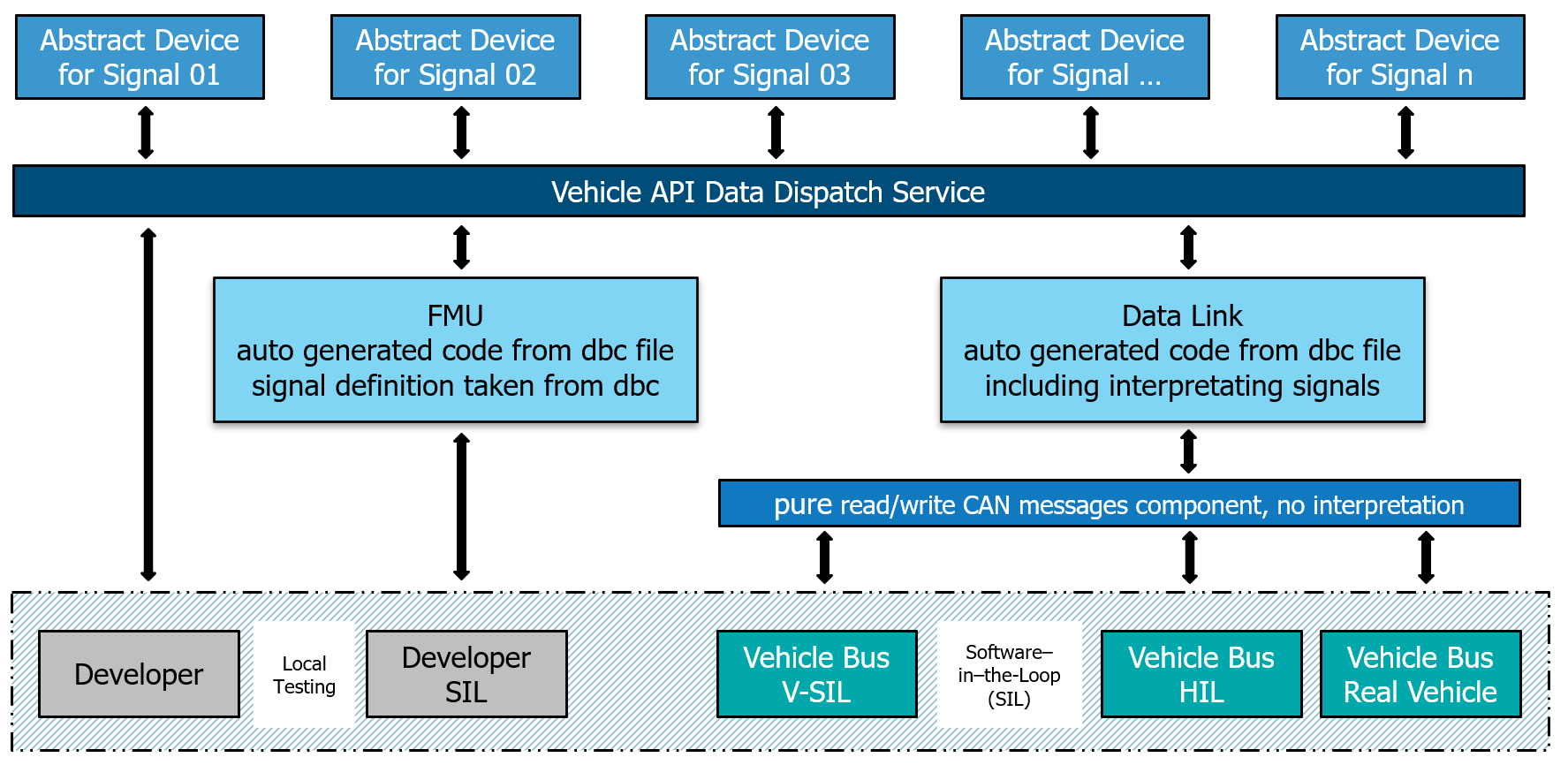
This framework allows to setup a structured test, validation and release process just by implementing/changing one or two components without changing the behavior of the system under test.
Important
To learn more about the difference of ECU and Software development go to ECU compared to Software.
To sum up it is important to speed up the development process. The Open Vehicle API can be a cruical part of it by reducing the impact (smaller components, reusing already tested components) and increasing the detection (test single component in multiple systemss)-
Tip