Aspects of Open Vehicle API#
Important
The increasing complexity of modern vehicle software requires robust, scalable, and future-oriented frameworks. Especially in the context of safety-critical applications, distributed systems, and agile development processes, new approaches must be developed to meet growing demands.
Function development requirements#
Signal-based time triggered
Model-based with code generation
Main language “C” with global variables and methods
Development often done by function developer; no deep programming knowledge available
Programming is a necessary evil, automate as much as possible
Safety almost always an issue
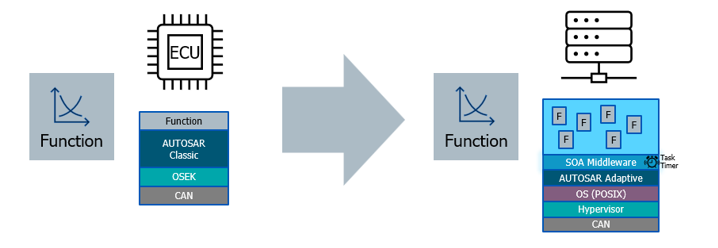
Build one, apply many#
Function development independent of vehicle type and HW infrastructure
Aims for zonal based architecture using one or more (virtual) HPCs running a POSIX OS (Prototype uses Linux)
Development locally and simulation in the cloud on Windows and Linux
Direct testing on development PC (simplified SIL)
Validating functionality for a variety of vehicles in the cloud (validation SIL)
Validating functionality for a variety of HW setups (centralized HIL)
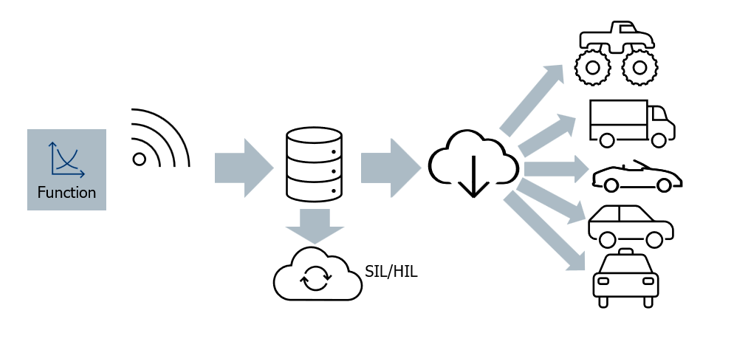
Use standardization and automation#
Allow multiple types of vehicle buses (protype uses CAN).
Automate code generation for the vehicle bus abstraction (protype uses DBC).
Allow multiple standardized application interfaces like Covesa VSS or CAAM (prototype uses VSS).
Automate code generation for the vehicle abstraction, publisher.
Automate code generation for the application, subscriber.
Use a standard interface between software components (IDL based on ISO/IEC -19516*).
Automate code generation for interfacing and marshalling RPC calls.
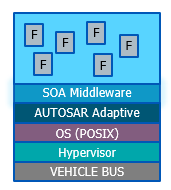
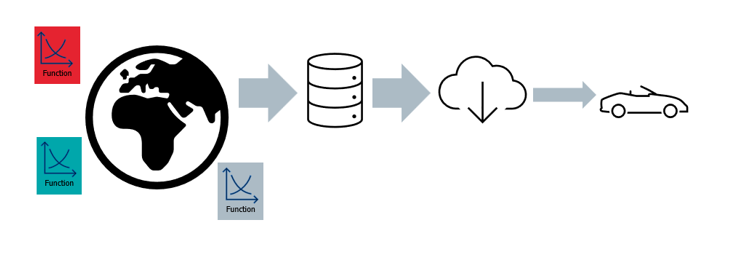
Future aspects#
Multiple vendors supplying functions
Mixed open and closed source development
Fixed setup on a system running within a safety context (ASIL A/B)
Dynamic installation (extendibility) of functions per (temporary) subscription within QM context
Appstore with available functions
Impact reduction of faulty components through process isolation
Installation and update per OTA
Diagnostics per SOVD
Conclusion#
This framework addresses these key topics and requirements to actively support future developments in automotive software engineering. The focus lies on aspects such as mixed-criticality, event-driven architecture, and a structured test, validation, and release process.