Static analysis of neural network computation graphs using Aidge#
In this tutorial, we explore Aidge’s static analysis functionalities by evaluating a DINOv2 model.
We will go through the following steps:
Import the required dependencies and set up the notebook
Import the model
Transform the graph
Run static analysis
1. Import the required dependencies and set up the notebook#
We start by downloading the dependencies.#
aidge_core: Holds the core structure and features of Aidgeaidge_backend_cpu: CPU kernels implementations (Aidge inferences)aidge_onnx: Interoperability with ONNXaidge_model_explorer: Model vizualizer tool
[ ]:
%pip install aidge-core \
aidge-backend-cpu \
aidge-onnx \
aidge-model-explorer
Setting up the notebook#
[ ]:
# Import Aidge modules
import aidge_core
import aidge_backend_cpu
import aidge_onnx
import aidge_model_explorer
# Select low verbose mode
aidge_core.Log.set_console_level(aidge_core.Level.Error)
# Import module to show images in the notebook
from IPython.display import Image
# Import some utility modules
import os
import requests
2. Import the model#
Download the model (if needed)#
You may find the DINOv2 model as well as other supported models in the Aidge Hugging Face webpage.
[ ]:
# Download the DINOv2 model ONNX file, if this has not been done yet
file_url = (
"https://huggingface.co/EclipseAidge/dinov2/resolve/main/dinov2.onnx?download=true"
)
file_path = "dinov2.onnx"
aidge_core.utils.download_file(file_path, file_url)
Import the ONNX model into Aidge#
[ ]:
# We rely on the Aidge ONNX module, which provides an interface between ONNX operators and Aidge's internal representation
dinov2_model = aidge_onnx.load_onnx("dinov2.onnx")
At any point, you can visualize the model with Aidge visualization tool derived from the google model explorer.
[ ]:
aidge_model_explorer.visualize(dinov2_model, "init_model")
You can check which ONNX operator is supported by Aidge.
[ ]:
# Verify Aidge's native operators coverage for this model
aidge_onnx.native_coverage_report(dinov2_model)
3. Transform the graph#
In this section we use some of Aidge’s recipes to simplify the graph representation of the model.
Many complex layers such as LayerNorm have been split when exported to ONNX when the original file was created. We use Aidge capacity to encapsulate the micro-graph of each of these operations into their own operator. Such composite Operator is called a MetaOperator.
Here the recomposed operations are:
Linear
LayerNorm
MultiHeadAttention
GeLU
[ ]:
# Create a clone of the original model to be used for comparison later
clone_dinov2 = dinov2_model.clone()
# Simplify the model using meta-operators via the ``fuse_to_metaops`` recipe
# In this context we use Graph Regex to specify which sequence of operators must be replaced by a given meta operator
aidge_core.fuse_to_metaops(dinov2_model, "MatMul-*>Add", "Linear")
aidge_core.fuse_to_metaops(
dinov2_model,
"ReduceMean-*>Sub#1~>(Pow#1->ReduceMean-*>Add#1->Sqrt)-*>Div#1-*>Mul#1-*>Add#2;"
"Sub#1~*>Div#1;"
"Pow#1<1~Producer;"
"Add#1<*~Producer;"
"Mul#1<*~Producer;"
"Add#2<*~Producer;"
"Sub#1~>$",
"LayerNorm",
)
aidge_core.fuse_to_metaops(
dinov2_model,
"MatMul->Div#1->Softmax-*>MatMul;" "Div#1<1~Producer",
"ScaledDotProductAttention",
)
aidge_core.fuse_to_metaops(
dinov2_model,
"ScaledDotProductAttention#1->Transpose->Reshape#1->Linear;"
"Reshape#1<1~Producer;"
"ScaledDotProductAttention#1<0-(Transpose<-Reshape#2<-Add#1);"
"ScaledDotProductAttention#1<1-(Transpose<-Reshape#3<-Add#2);"
"ScaledDotProductAttention#1<2-(Transpose<-Reshape#4<-Add#3);"
"Reshape#2<1~Producer;"
"Add#1<*-0-Split#1;"
"Add#2<*-1-Split#1;"
"Add#3<*-2-Split#1;"
"Split#1<-MatMul;"
"Split#1<1~Producer",
"MultiHeadAttention",
)
aidge_core.fuse_to_metaops(
dinov2_model,
"Div#1->Erf->Add#1-*>Mul->Mul#2;"
"Div#1<1~Producer;"
"Add#1<*~Producer;"
"Mul#2<*~Producer",
"GeLU",
)
dinov2_model.set_ordered_outputs(
[
dinov2_model.get_ordered_outputs()[0][0].inputs()[0],
dinov2_model.get_ordered_outputs()[0],
]
)
Note: Aidge can be used independently for simplifying models with a suite of pre-made composition formulas using the_ aidge_sim command. You can find more by typing aidge_sim --help
After creating meta-operators, we can verify the updated total number of operators in the graph
[ ]:
_ = aidge_onnx.native_coverage_report(dinov2_model)
The number of operators was reduced from 824 (17 unique) to 277 (12 unique), as depicted in the following image.
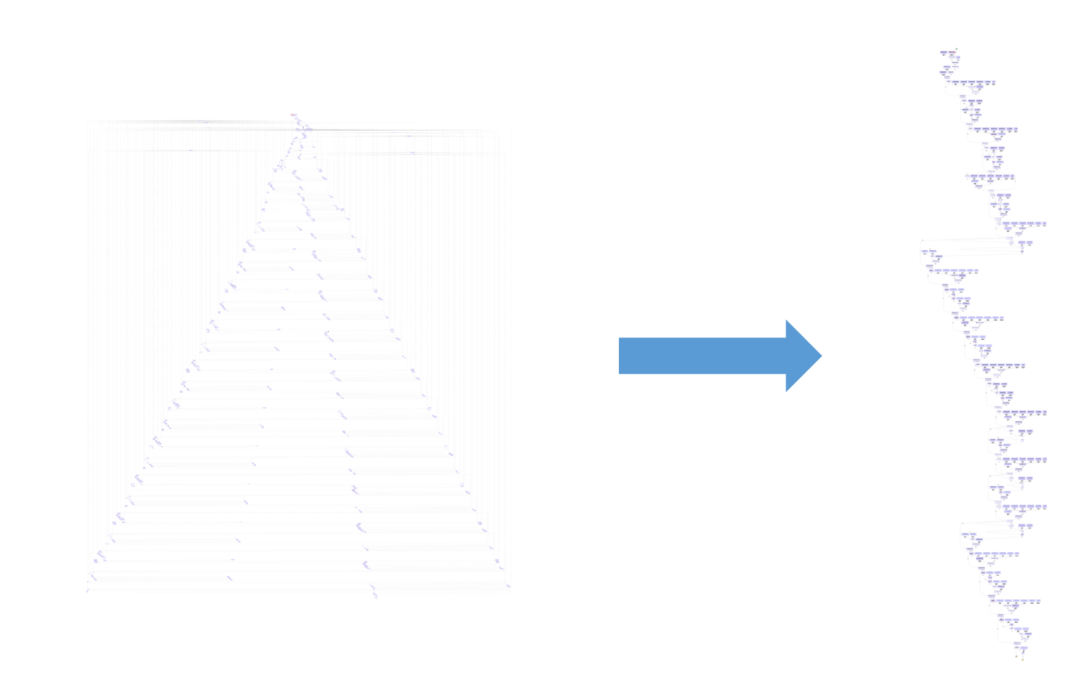
You can explore the model at this stage
[ ]:
aidge_model_explorer.visualize(dinov2_model, "simplified_model")
4. Run static analysis#
This section addresses the core aspects of static metric analysis in neural networks with Aidge.
Model statistics#
Model statistics can be derived by analyzing the computational graph without requiring any associated implementation. It is sufficient to infer the dimensions of internal tensors.
[ ]:
# Internal tensor dimensions must be computed to analyze the network
dinov2_model.forward_dims(dims=[[1, 3, 224, 224]], allow_data_dependency=True)
We instantiate a StaticAnalysis object from the current graph that allows to get for each Node:
# parameters
# operations of a specific type
arithmetic (int/float) — additions, substractions, divisions, multiplications, modulo
logical — logical shift, or, and
comparison — inferior, superior, equal
non-linear — tanh(), erf(), cos()…
MAC — multiply–accumulate
memory size
[ ]:
import aidge_core.static_analysis
dinov2_stats = aidge_core.static_analysis.StaticAnalysis(dinov2_model)
We display a summary of the model nodes the number of each operation type.
[ ]:
dinov2_stats.summary()
# Display certain statistics about the number of operations by node
_ = dinov2_stats.log_nb_ops_by_type("stats_ops.png", log_scale=True)
Inference statistics#
Currently, the model has no implementation and exists only as a data structure. To set an implementation, we will specify a backend and a data type.
[ ]:
import aidge_backend_cpu
dinov2_model.set_backend("cpu")
dinov2_model.set_datatype(aidge_core.dtype.float32)
Finally, to run inference, we need to schedule the execution. To do so we create a Scheduler object, which takes the graph and generates an optimized scheduling using a consummer-producer (C-P) heuristic.
[ ]:
s = aidge_core.SequentialScheduler(dinov2_model)
s.generate_scheduling()
In addition, it is possible to verify the memory usage of the different nodes composing the graph.
[ ]:
_ = aidge_core.generate_optimized_memory_info(
s, "mem_strategy_dino", wrapping=False, display_names=False
)
Image(filename="./mem_strategy_dino/memory_info.png")
We can then compare the modified model with the original one, whose operators have not been fused:
[ ]:
# Compile the model
clone_dinov2.set_backend("cpu")
clone_dinov2.set_datatype(aidge_core.dtype.float32)
clone_dinov2.forward_dims([[1, 3, 224, 224]], True)
# Generate scheduling
s = aidge_core.SequentialScheduler(clone_dinov2)
s.generate_scheduling()
# Visualize memory usage
_ = aidge_core.generate_optimized_memory_info(
s, "mem_strategy_og_dino", wrapping=False, display_names=False
)
Image(filename="./mem_strategy_og_dino/memory_info.png")
In this tutorial the following concepts were studied:
Graph transformations — in particular the
fuse_to_metaopsrecipe;Model static analysis — to measure the graph’s complexity in terms of number of operations;
Static scheduling memory analysis — to visualize the graph’s memory usage over inference time.
