ELK Radial
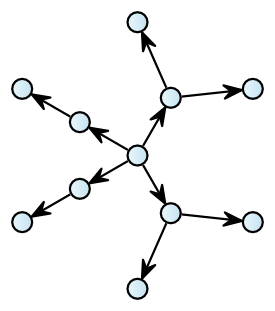
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Identifier: | org.eclipse.elk.radial |
| Meta Data Provider: | options.RadialMetaDataProvider |
Description
A radial layout provider which is based on the algorithm of Peter Eades published in “Drawing free trees.”, published by International Institute for Advanced Study of Social Information Science, Fujitsu Limited in 1991. The radial layouter takes a tree and places the nodes in radial order around the root. The nodes of the same tree level are placed on the same radius.
Category: Radial
Radial layout algorithms usually position the nodes of the graph on concentric circles.
Additional Documentation
The Radial layouter which provides an enviroment for individiual radial layout algorithms is devided in different phases of layout.
Phases
The algorithm we implemented is dividable in 5 consecutive steps, two phases and three alternative intermediate processors. The difference between phases and processors is that phases are essential for the layouter and need an implementation (which is also exchangeable) while processors are optional. The given phases are the node placement phase and the edge routing phase, these suffice to gain a radial layout. The steps of overlap removal, compaction and graph size calculation are the optional steps of the algorithm. In the following all these steps are explained in more detail.

Node placement
The essential phase of the layouter is the node placement, where the nodes are assigned a position. Currently only one node placement algorithm is implemented that is the one of Eades. As mentioned before it would be possible to swap the node placement algorithm by another one. But it also possible to customize the given algorithm of Eades, but beforehand you should know how the algorithm of Eades works.
The Algorithm of Eades
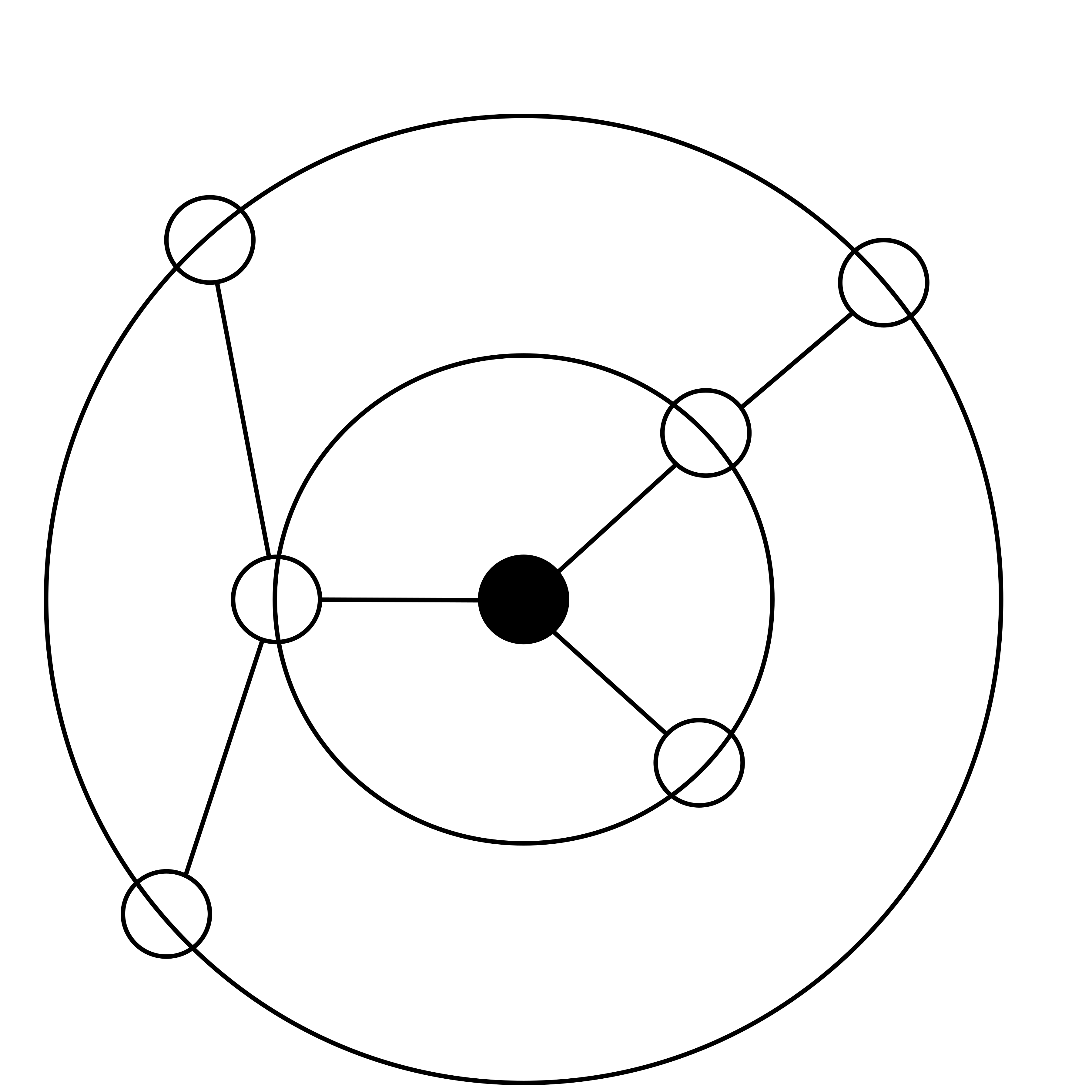
As mentioned Eades provides an algorithm for drawing radial layouts. It was published in “Drawing free trees.”, (published by
International Institute for Advanced Study of Social Information Science, Fujitsu Limited in 1991).
The algorithm he provided can layout trees with nodes of no size. The distance between the single radii is given as a constant input.
But how does Eades’s algorithm work:
The algorithm starts placing the root node and then continues with placing each node of each subtree.
Each subtree is assigned to an annulus wedge, a part of the circle. Each node is then placed in the center of its wedge.
To estimate how big the wedge of each subtree will be, Eades counts the numbers of leaves.
The node which shall be placed gets space according to the number of leaves it has compared to the number of leaves all nodes of the same layer have.
The first wedge starts at the right of the circle, because polar coordinates are used and there is degree zero.
The following examples shall clarify this process:
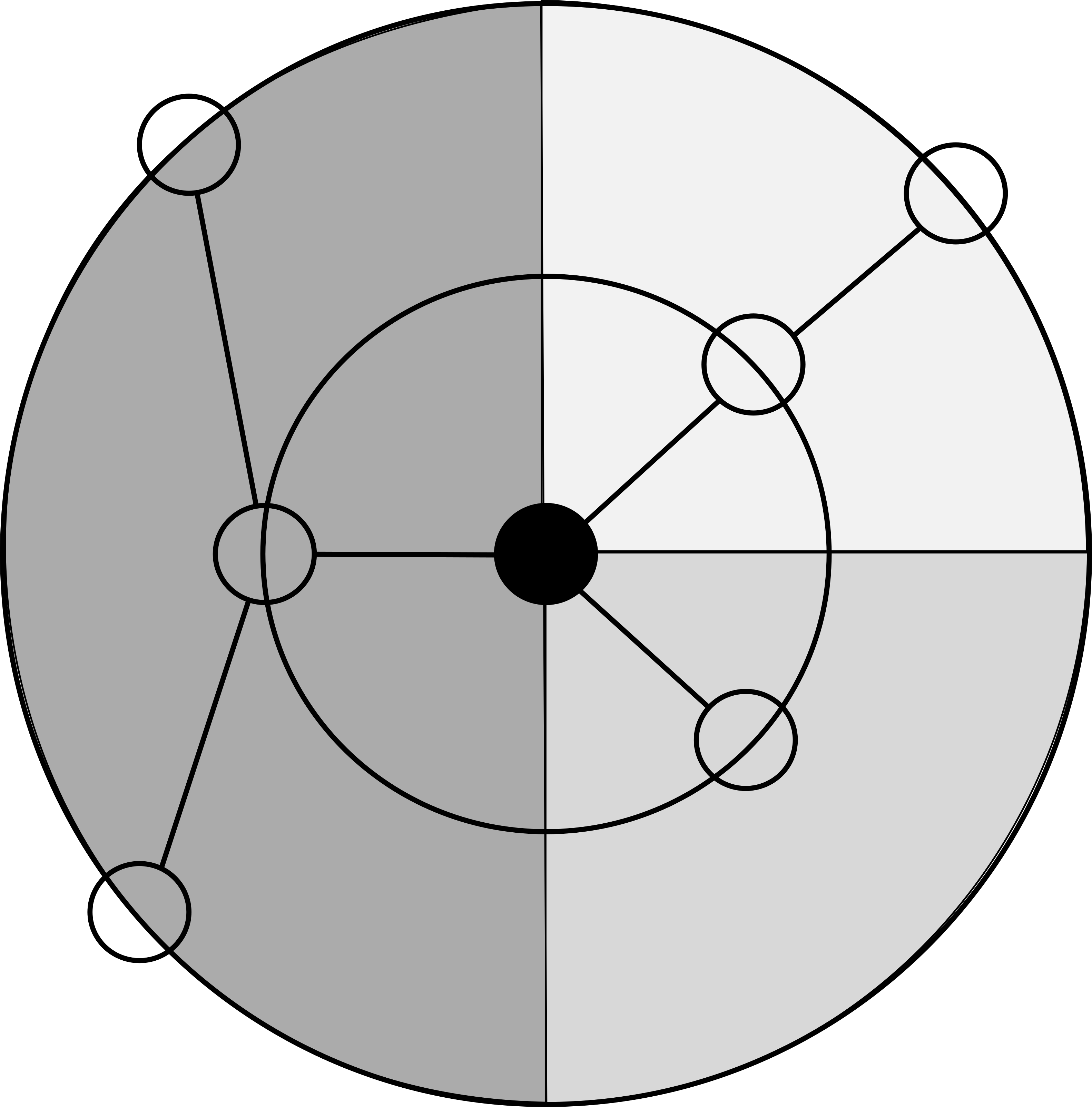
The right lower nodes receives one quarter of the space, because he has (and is) one leaf. The right upper node has one leaf and receives one quarter and the left node has two leaves that is why it receives two quarters.
Customizations
As mentioned the algorithm of Eades do not consider node sizes, therefore we provided an annulus wedge criteria which does. Therefore the available space is not calculated by the number of leaves but by the maximum sum of the length of all node diagonals of a wedge. Another customization is that the first wedge does not start on the right of the circle but on a position which gives a better layout. This means that each node is translated for some degree on the radius. This movement can be used to minimize the edge length or even more valuable, the number of edge crossings.
Overlap Removal
The overlap removal intermediate processor can be started after the node placement. Due to the node sizes it is still not guaranteed that no overlaps occur, because the radius can be chosen too small. The processor starts with the innermost radius and widens it until no more overlaps on the radius occur. This is repeated for each radius.
Compaction
The compaction processor strieves to maintain a more compact layout. There are two different approaches implemented. The first is the radial compaction which alters the radii such as the overlap removal. Each radius is contracted as long as no overlap occurs. The second approach is the wedge compaction strategy which compacts nodes of each wedge as much as possible. For each wedge the radii are contracted as much as possible. This leads to the loss of the radius alignment property, but may provide a much more compact layout.
Graph Size Calculation
To determine the size needed for displaying the graph, it is post-processed. Therefore all nodes are moved into the positive area (beforehand the root node was placed in the origin) and the size of the graph is calculated.
Edge routing
The last phase is the one of edge routing, which provides a layout for the edges of the graph. Edges are drawn from the center of the source to the center of the target and then clipped such that they do no not overlap the nodes.
Advanced options
There are some advanced options which shouldn’t stay uncommented. There are advanced options for the node placement optimization strategy as well as for sorting the nodes. The options are marked as advanced because they require additional information to work properly. The current options require the position option(org.eclipse.elk.position) to be set. The original use is given by assuming there exists a relation between nodes in the parent node and the children. Therefore, the position reflects the position of the nodes in the parent node. These options may be adapted to other purposes.
Supported Options
| Option | Default Value |
|---|---|
| Additional Wedge Space | false |
| Annulus Wedge Criteria | AnnulusWedgeCriteria.NODE_SIZE |
| Center On Root | false |
| Compaction | CompactionStrategy.NONE |
| Compaction Step Size | 1 |
| Node Label Placement | NodeLabelPlacement.fixed() |
| Node Size Constraints | EnumSet.noneOf(SizeConstraint) |
| Node Size Minimum | new KVector(0, 0) |
| Node Size Options | EnumSet.of(SizeOptions.DEFAULT_MINIMUM_SIZE) |
| Node Spacing | 20 |
| Omit Node Micro Layout | false |
| Order ID | 0 |
| Outgoing Edge Angles | false |
| Port Label Placement | PortLabelPlacement.outside() |
| Position | <not defined> |
| Radius | 0.0 |
| Rotate | false |
| Sorter | SortingStrategy.NONE |
| Target Angle | 0 |
| Translation Optimization | RadialTranslationStrategy.NONE |
